Pressure cookers significantly reduce soup preparation time by cooking ingredients quickly under high pressure, preserving nutrients and intensifying flavors. Slow cookers allow for gradual simmering, which enhances depth of flavor and tenderizes tough ingredients without constant monitoring. Choosing between the two depends on the desired cooking speed and flavor development for the soup.
Table of Comparison
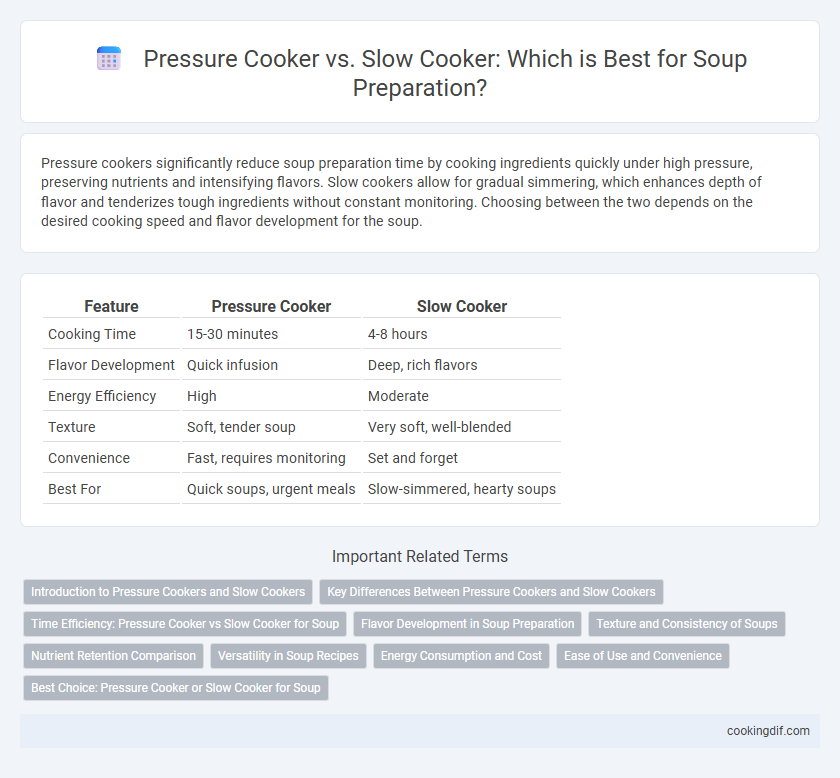
| Feature | Pressure Cooker | Slow Cooker |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Time | 15-30 minutes | 4-8 hours |
| Flavor Development | Quick infusion | Deep, rich flavors |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Texture | Soft, tender soup | Very soft, well-blended |
| Convenience | Fast, requires monitoring | Set and forget |
| Best For | Quick soups, urgent meals | Slow-simmered, hearty soups |
Introduction to Pressure Cookers and Slow Cookers
Pressure cookers use high steam pressure to cook soups quickly, preserving nutrients and extracting deep flavors in a fraction of the traditional cooking time. Slow cookers maintain low, consistent heat over several hours, ideal for developing rich, complex soup textures and allowing ingredients to meld gradually. Both appliances offer distinct culinary advantages for soup preparation based on time efficiency and flavor infusion preferences.
Key Differences Between Pressure Cookers and Slow Cookers
Pressure cookers use high pressure and heat to cook soups quickly, retaining more nutrients and intensifying flavors in a shorter time. Slow cookers rely on low, consistent heat over several hours, allowing flavors to meld gradually and tenderizing ingredients without constant supervision. Key differences include cooking time, temperature control, and energy usage, with pressure cookers being faster and slow cookers better for hands-off, long simmering recipes.
Time Efficiency: Pressure Cooker vs Slow Cooker for Soup
Pressure cookers significantly reduce soup preparation time by using high pressure and temperature to cook ingredients quickly, often completing soups in under an hour. Slow cookers require several hours, typically 4 to 8, to achieve tender, well-blended flavors through gradual heating. For time-efficient soup preparation, pressure cookers offer a practical advantage without compromising taste or nutrient retention.
Flavor Development in Soup Preparation
Pressure cookers intensify flavor development in soup by rapidly extracting and concentrating ingredients' essences due to high-pressure steam cooking. Slow cookers enhance soup flavor through prolonged simmering, allowing spices and aromatics to meld gently, resulting in deep, rich profiles. Choosing between methods depends on desired depth of flavor and time availability, with pressure cookers offering speed and slow cookers providing complexity.
Texture and Consistency of Soups
Pressure cookers produce soups with a rich, well-blended texture by quickly breaking down ingredients under high heat and steam pressure, resulting in a smooth and hearty consistency. Slow cookers allow for prolonged simmering, which enhances the depth of flavor and tenderizes ingredients gradually, creating soups with a more varied texture and slightly thicker consistency. Choosing between the two depends on the desired balance of speed and textural complexity in the final soup.
Nutrient Retention Comparison
Pressure cookers preserve nutrients in soup by using high heat and shorter cooking times, reducing vitamin and mineral loss compared to slow cookers. Slow cookers rely on lower temperatures over extended periods, which can degrade heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex but may enhance flavor development. Studies show pressure cooking retains up to 30% more antioxidants and water-soluble vitamins than slow cooking methods in vegetable-based soups.
Versatility in Soup Recipes
Pressure cookers offer rapid cooking for soups, preserving flavors and nutrients efficiently, making them ideal for recipes that require tenderizing tougher ingredients quickly. Slow cookers provide consistent, low heat that allows complex flavors to develop over hours, perfect for hearty, slow-simmered soups like stews and chowders. Choosing between them depends on the desired soup texture and cooking time, with pressure cookers excelling in speed and slow cookers in flavor depth and texture variety.
Energy Consumption and Cost
Pressure cookers consume significantly less energy than slow cookers by reducing cooking time from hours to minutes, resulting in lower electricity costs. Slow cookers use a consistent low heat over extended periods, leading to higher overall energy consumption and increased utility bills. Choosing a pressure cooker for soup preparation can provide substantial savings on energy consumption and reduce long-term cooking expenses.
Ease of Use and Convenience
Pressure cookers significantly reduce soup cooking time by using high steam pressure, making them ideal for quick meal preparation without constant monitoring. Slow cookers offer a hands-off approach, allowing soups to simmer gently over several hours, which enhances flavor development with minimal effort. Both appliances provide user-friendly controls and safety features, but pressure cookers require careful handling during pressure release, while slow cookers excel in convenience for unattended cooking.
Best Choice: Pressure Cooker or Slow Cooker for Soup
Pressure cookers significantly reduce cooking time while preserving the nutrients and flavors in soups, making them ideal for quick, hearty meals. Slow cookers enhance depth of flavor by allowing soups to simmer gently over several hours, perfect for developing complex taste profiles. Choosing between a pressure cooker and slow cooker depends on desired cooking speed and flavor intensity, with pressure cookers favored for efficiency and slow cookers for rich, slow-cooked flavors.
Pressure Cooker vs Slow Cooker for soup preparation Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com