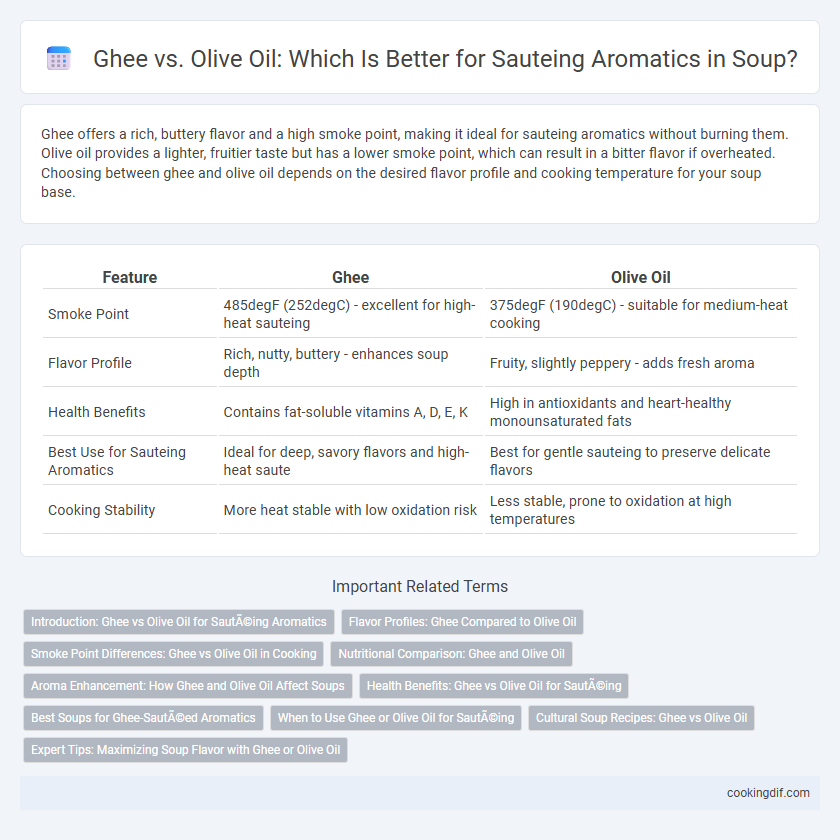
Ghee offers a rich, buttery flavor and a high smoke point, making it ideal for sauteing aromatics without burning them. Olive oil provides a lighter, fruitier taste but has a lower smoke point, which can result in a bitter flavor if overheated. Choosing between ghee and olive oil depends on the desired flavor profile and cooking temperature for your soup base.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ghee | Olive Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Smoke Point | 485degF (252degC) - excellent for high-heat sauteing | 375degF (190degC) - suitable for medium-heat cooking |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, nutty, buttery - enhances soup depth | Fruity, slightly peppery - adds fresh aroma |
| Health Benefits | Contains fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, K | High in antioxidants and heart-healthy monounsaturated fats |
| Best Use for Sauteing Aromatics | Ideal for deep, savory flavors and high-heat saute | Best for gentle sauteing to preserve delicate flavors |
| Cooking Stability | More heat stable with low oxidation risk | Less stable, prone to oxidation at high temperatures |
Introduction: Ghee vs Olive Oil for Sautéing Aromatics
Ghee offers a higher smoke point around 485degF, making it ideal for sauteing aromatics like garlic, onions, and ginger without burning. Olive oil, especially extra virgin, has a lower smoke point near 375degF and imparts a distinct fruity flavor that enhances Mediterranean-style soups. Choosing ghee or olive oil influences the soup's depth of flavor and cooking technique based on heat tolerance and desired taste profile.
Flavor Profiles: Ghee Compared to Olive Oil
Ghee offers a rich, nutty flavor with a slightly caramelized aroma that enhances the depth of sauteed aromatics, making it ideal for soups requiring a warm, buttery undertone. Olive oil, especially extra virgin, provides a fruity, peppery taste that adds a fresh, vibrant character to the base flavors without overpowering delicate ingredients. The choice between ghee and olive oil depends on the desired flavor intensity and complementarity to other soup components.
Smoke Point Differences: Ghee vs Olive Oil in Cooking
Ghee boasts a high smoke point around 485degF (252degC), making it ideal for sauteing aromatics without burning or creating harmful compounds. Olive oil, particularly extra virgin, has a lower smoke point of approximately 375degF (190degC), which can limit its use in high-heat applications and may impart a bitter taste when overheated. Choosing ghee over olive oil for sauteing preserves both flavor and nutritional integrity due to its superior heat tolerance.
Nutritional Comparison: Ghee and Olive Oil
Ghee provides a rich source of fat-soluble vitamins A, E, and K2, along with beneficial short-chain fatty acids that support digestion and inflammation reduction, making it ideal for high-heat sauteing of aromatics without oxidation. Olive oil, especially extra virgin, offers potent antioxidants and monounsaturated fats that promote heart health but has a lower smoke point, which may degrade its nutritional benefits when used at high temperatures. Selecting ghee or olive oil for sauteing aromatics impacts both flavor profiles and nutritional outcomes, with ghee providing heat stability and fat-soluble vitamins, while olive oil contributes antioxidant properties and healthy fats best preserved at moderate heat.
Aroma Enhancement: How Ghee and Olive Oil Affect Soups
Ghee imparts a rich, nutty aroma that enhances the depth and warmth of soups, intensifying flavors of sauteed aromatics. Olive oil provides a fruity, herbaceous fragrance that adds brightness and subtle complexity, complementing lighter soups. The choice between ghee and olive oil influences the aromatic profile, with ghee offering roasted notes and olive oil delivering fresh, green nuances.
Health Benefits: Ghee vs Olive Oil for Sautéing
Ghee contains healthy fats like conjugated linoleic acid and fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K that support immune function and improve digestion, with a high smoke point suitable for sauteing aromatics. Olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, including vitamin E and polyphenols, which reduce inflammation and support heart health. For sauteing aromatics in soup preparation, ghee offers a more stable fat profile while olive oil provides antioxidant benefits, making the choice dependent on flavor preference and specific health goals.
Best Soups for Ghee-Sautéed Aromatics
Ghee's high smoke point of around 485degF makes it ideal for sauteing aromatics in soups like Indian lentil dal, Thai coconut curry, and butternut squash bisque, enhancing flavor with its rich, nutty taste. Olive oil, with a lower smoke point near 375degF, suits Mediterranean soups such as minestrone or tomato basil, where its fruity notes complement lighter spices. Using ghee fosters deeper, more complex savory profiles in hearty soups, while olive oil offers a fresher, herbaceous finish.
When to Use Ghee or Olive Oil for Sautéing
Ghee is ideal for sauteing aromatics when a high smoke point and rich, nutty flavor are desired, enhancing soups with deep, complex undertones. Olive oil suits light, fresh soups where its fruity, slightly peppery notes complement delicate ingredients without overpowering them. Choosing between ghee and olive oil depends on the soup's flavor profile and cooking temperature requirements for optimal aromatic sauteing.
Cultural Soup Recipes: Ghee vs Olive Oil
Ghee is prominent in Indian and Middle Eastern soups, infusing rich, nutty flavors that complement spices like cumin and coriander during sauteing. Olive oil is a staple in Mediterranean soups, offering a fruity and slightly peppery taste that enhances garlic, onions, and herbs like rosemary or thyme. Choosing ghee or olive oil for sauteing aromatics directly influences the cultural authenticity and depth of flavor in traditional soup recipes.
Expert Tips: Maximizing Soup Flavor with Ghee or Olive Oil
Ghee enhances soup flavor by providing a rich, nutty aroma and a higher smoke point, ideal for sauteing aromatics without burning. Olive oil imparts a fruity, slightly peppery taste and contains heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, though it has a lower smoke point, requiring careful temperature control. Experts recommend using ghee for robust, deeply caramelized flavors and olive oil for lighter, Mediterranean-inspired soups.
Ghee vs Olive oil for sautéing aromatics Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com