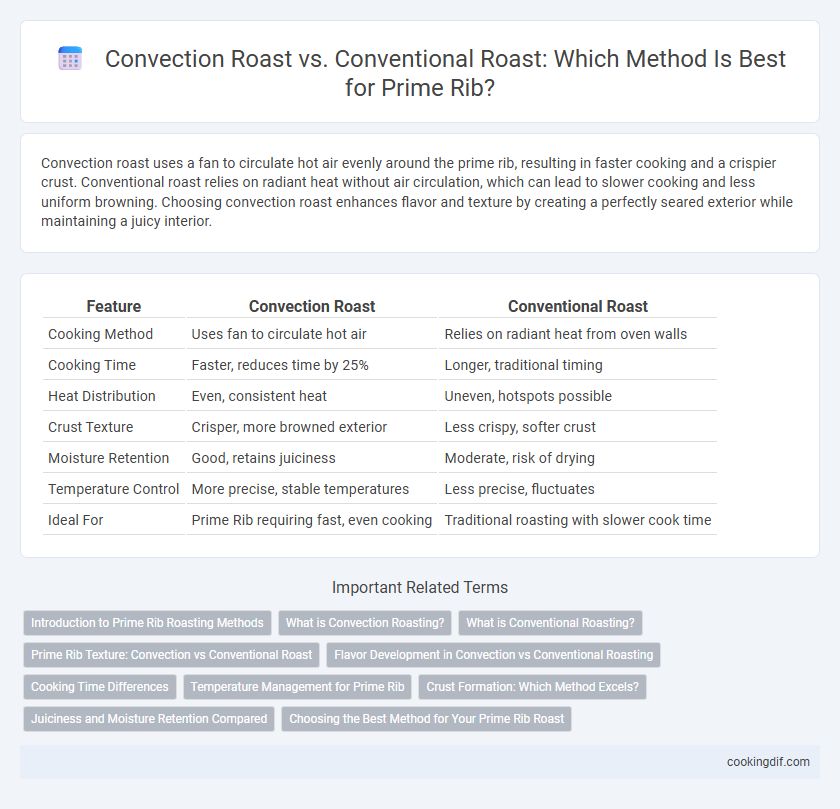
Convection roast uses a fan to circulate hot air evenly around the prime rib, resulting in faster cooking and a crispier crust. Conventional roast relies on radiant heat without air circulation, which can lead to slower cooking and less uniform browning. Choosing convection roast enhances flavor and texture by creating a perfectly seared exterior while maintaining a juicy interior.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Convection Roast | Conventional Roast |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Uses fan to circulate hot air | Relies on radiant heat from oven walls |
| Cooking Time | Faster, reduces time by 25% | Longer, traditional timing |
| Heat Distribution | Even, consistent heat | Uneven, hotspots possible |
| Crust Texture | Crisper, more browned exterior | Less crispy, softer crust |
| Moisture Retention | Good, retains juiciness | Moderate, risk of drying |
| Temperature Control | More precise, stable temperatures | Less precise, fluctuates |
| Ideal For | Prime Rib requiring fast, even cooking | Traditional roasting with slower cook time |
Introduction to Prime Rib Roasting Methods
Prime rib roasting methods include convection roasting and conventional roasting, each offering distinct heat distribution techniques. Convection roasting uses a fan to circulate hot air, promoting even cooking and reducing roast time, which preserves juiciness and enhances crust formation. Conventional roasting relies on radiant heat from the oven walls, providing a slower, more gradual cook ideal for traditional prime rib flavor and texture development.
What is Convection Roasting?
Convection roasting uses a fan and exhaust system to circulate hot air evenly around the prime rib, promoting faster and more uniform cooking compared to conventional roasting. This method helps achieve a crispy, browned crust while retaining juicy, tender meat inside. Convection roasting can reduce cooking time by up to 25%, making it an efficient choice for roasting prime rib.
What is Conventional Roasting?
Conventional roasting uses direct heat from the bottom or top heating element in an oven, cooking prime rib by surrounding it with dry, radiant heat. This method produces a crisp, browned exterior while maintaining a tender, juicy interior by relying on consistent, steady temperatures. Unlike convection roasting, conventional roasting does not circulate hot air, which can lead to longer cooking times and less even heat distribution.
Prime Rib Texture: Convection vs Conventional Roast
Convection roast creates a prime rib with a crispier crust and more even browning due to the hot air circulation, enhancing the Maillard reaction for a deeply textured exterior. Conventional roast produces a tender and juicier interior but may result in less uniform crust development and a softer overall texture. Texture differences impact mouthfeel, with convection offering a pronounced contrast between the crust and the pink, juicy center, while conventional roasting delivers a more consistent, tender bite throughout.
Flavor Development in Convection vs Conventional Roasting
Convection roast enhances flavor development in prime rib by circulating hot air, promoting even browning and a more pronounced crust through consistent Maillard reactions. Conventional roasting relies on radiant heat, which can lead to uneven cooking and less intense caramelization on the meat's surface. This difference results in convection roasting producing a richer, deeper flavor profile with a crispier exterior compared to the traditional conventional roast method.
Cooking Time Differences
Convection roast reduces cooking time for prime rib by circulating hot air evenly, allowing the meat to cook faster and more uniformly compared to conventional roasting. Conventional roast relies on radiant heat from the oven walls, resulting in longer cooking times and potential hot spots that may cause uneven doneness. Using convection roasting can decrease prime rib cooking time by approximately 25-30%, enhancing flavor while maintaining tenderness.
Temperature Management for Prime Rib
Convection roast uses a fan to circulate hot air, enabling more even and efficient temperature management for prime rib, resulting in a consistent internal doneness and a crispy crust. Conventional roast relies on radiant heat without airflow, often causing uneven cooking and requiring closer monitoring to avoid overcooking the edges. Optimal temperature control in convection roasting allows prime rib to maintain juiciness while achieving the desired medium-rare finish with less risk of temperature fluctuations.
Crust Formation: Which Method Excels?
Convection roasting excels in crust formation for prime rib by circulating hot air evenly, promoting faster Maillard reactions and resulting in a consistently crisp, well-browned exterior. Conventional roasting relies on radiant heat, often producing a less uniform crust with potential for uneven browning. For optimal prime rib crust, convection roasting ensures enhanced texture and flavor development through superior heat distribution.
Juiciness and Moisture Retention Compared
Convection roast cooks prime rib faster by circulating hot air evenly, resulting in a well-browned crust while maintaining interior juiciness through consistent heat distribution. Conventional roast relies on radiant heat, which can cause uneven cooking and potential moisture loss, leading to a drier prime rib. Studies show convection roasting enhances moisture retention by reducing cooking time and minimizing exposure to drying temperatures, preserving the prime rib's succulent texture.
Choosing the Best Method for Your Prime Rib Roast
Convection roasting circulates hot air, cooking the prime rib evenly and reducing cooking time while ensuring a crispy exterior and juicy interior. Conventional roasting relies on radiant heat, producing a more traditional crust with slower, gradual cooking that allows flavors to develop deeply. For the best prime rib roast, convection roasting offers efficiency and consistent results, whereas conventional roasting provides a classic texture and flavor profile preferred by purists.
Convection Roast vs Conventional Roast for Prime Rib Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com