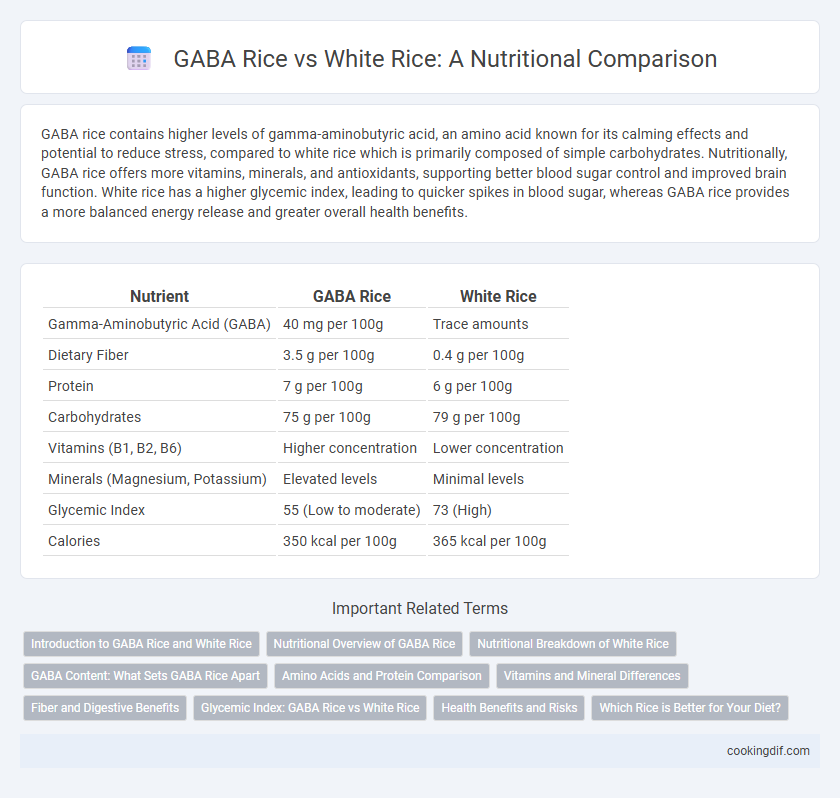
GABA rice contains higher levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid, an amino acid known for its calming effects and potential to reduce stress, compared to white rice which is primarily composed of simple carbohydrates. Nutritionally, GABA rice offers more vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, supporting better blood sugar control and improved brain function. White rice has a higher glycemic index, leading to quicker spikes in blood sugar, whereas GABA rice provides a more balanced energy release and greater overall health benefits.
Table of Comparison
| Nutrient | GABA Rice | White Rice |
|---|---|---|
| Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) | 40 mg per 100g | Trace amounts |
| Dietary Fiber | 3.5 g per 100g | 0.4 g per 100g |
| Protein | 7 g per 100g | 6 g per 100g |
| Carbohydrates | 75 g per 100g | 79 g per 100g |
| Vitamins (B1, B2, B6) | Higher concentration | Lower concentration |
| Minerals (Magnesium, Potassium) | Elevated levels | Minimal levels |
| Glycemic Index | 55 (Low to moderate) | 73 (High) |
| Calories | 350 kcal per 100g | 365 kcal per 100g |
Introduction to GABA Rice and White Rice
GABA rice, also known as germinated brown rice, contains higher levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), essential amino acids, and dietary fiber compared to white rice, which is heavily processed and stripped of most nutrients. The germination process enhances GABA content, contributing to improved antioxidant activity, better blood sugar regulation, and neuroprotective benefits. White rice primarily provides simple carbohydrates with minimal fiber and lower micronutrient levels, making GABA rice a nutritionally superior option for a balanced diet.
Nutritional Overview of GABA Rice
GABA rice, rich in gamma-aminobutyric acid, offers enhanced nutritional benefits compared to white rice, including higher levels of dietary fiber, vitamins B1 and B6, and essential minerals such as magnesium and potassium. Its lower glycemic index supports better blood sugar regulation, making it a healthier option for individuals managing diabetes or metabolic syndrome. The presence of antioxidants and bioactive compounds in GABA rice contributes to improved cardiovascular health and neuroprotection beyond the basic carbohydrate content found in white rice.
Nutritional Breakdown of White Rice
White rice primarily consists of carbohydrates, offering about 130 calories and 28 grams of carbs per 100 grams, with minimal fiber and protein content. In contrast, GABA rice retains more nutrients due to its germinated process, including higher levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals. The germination increases antioxidant activity and enhances B vitamins, making GABA rice a more nutrient-dense option compared to the polished white rice.
GABA Content: What Sets GABA Rice Apart
GABA rice contains significantly higher levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter linked to reduced stress and improved brain function, compared to white rice, which has minimal GABA content due to its polished nature. The germ and bran layers in GABA rice remain intact, preserving essential nutrients and bioactive compounds that are stripped away in white rice processing. This enhanced GABA content positions GABA rice as a nutritionally superior choice, especially for promoting mental wellness and cardiovascular health.
Amino Acids and Protein Comparison
GABA rice contains higher levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid and essential amino acids compared to white rice, contributing to improved protein quality and nutritional value. Its enhanced amino acid profile supports better muscle repair and overall metabolic functions. White rice, while a good energy source, lacks the enriched amino acid content found in GABA rice, making the latter superior for protein intake.
Vitamins and Mineral Differences
GABA rice contains higher levels of essential vitamins such as vitamin B6, niacin, and folate compared to white rice, contributing to better neurological function and energy metabolism. It also provides increased amounts of minerals like magnesium, potassium, and zinc, which support cardiovascular health and immune system function. White rice, in contrast, has lower concentrations of these nutrients due to milling and polishing processes that remove the bran and germ.
Fiber and Digestive Benefits
GABA rice contains higher dietary fiber compared to white rice, enhancing digestive health by promoting regular bowel movements and supporting gut microbiota. The elevated fiber content in GABA rice helps reduce constipation and improve nutrient absorption, unlike white rice which is typically low in fiber due to polishing processes. This makes GABA rice a superior choice for maintaining digestive wellness and overall gastrointestinal function.
Glycemic Index: GABA Rice vs White Rice
GABA rice has a significantly lower glycemic index (GI) than white rice, making it a better option for blood sugar management and sustained energy release. The GI of GABA rice typically ranges between 50 and 60, compared to white rice, which usually has a GI of 70 or higher. This lower GI in GABA rice results from its higher fiber and nutrient content, contributing to slower glucose absorption and improved insulin response.
Health Benefits and Risks
GABA rice contains higher levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid, which supports improved brain function and reduces anxiety compared to white rice. It is also rich in dietary fiber and antioxidants, enhancing digestive health and lowering the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart conditions. White rice, while easier to digest and quicker to cook, lacks these nutrients and poses higher risks of blood sugar spikes and nutrient deficiencies with excessive consumption.
Which Rice is Better for Your Diet?
GABA rice contains higher levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid and essential nutrients such as vitamins B1, B6, and dietary fiber compared to white rice, making it beneficial for blood sugar regulation and improved neurological function. White rice, while more processed and lower in fiber and micronutrients, provides a quicker source of energy and is often easier to digest. For a nutrient-rich diet focused on metabolic health and sustained energy release, GABA rice is generally considered superior to white rice.
GABA rice vs white rice for nutrition Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com