Instant rice offers unmatched convenience by significantly reducing cooking time compared to traditional rice, making it ideal for busy lifestyles and quick meals. Traditional rice requires longer cooking times but provides a firmer texture and more authentic flavor, appealing to those who prioritize taste and culinary experience. Choosing between instant and traditional rice depends on balancing convenience with desired texture and flavor preferences.
Table of Comparison
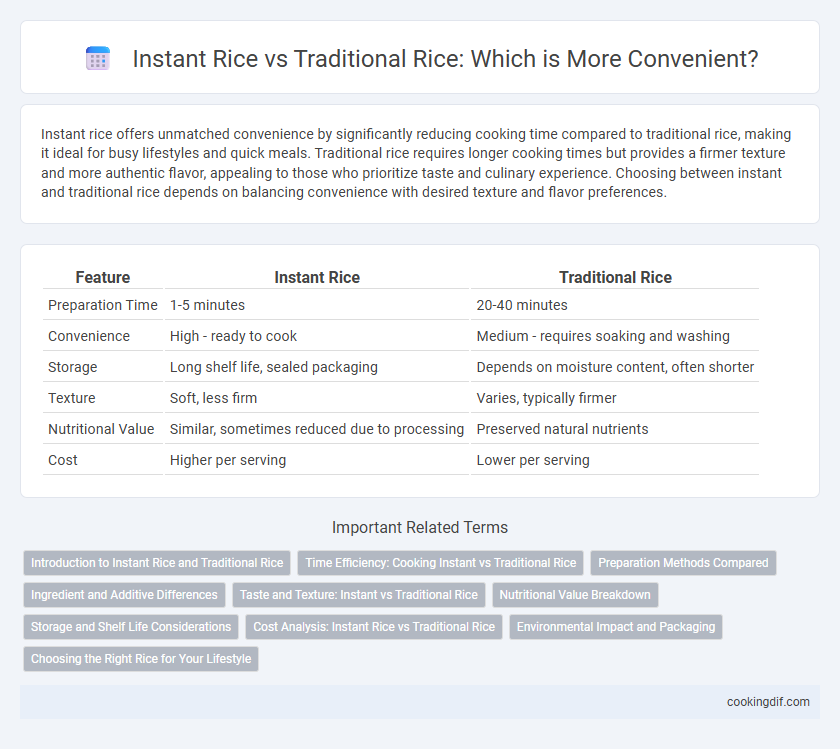
| Feature | Instant Rice | Traditional Rice |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation Time | 1-5 minutes | 20-40 minutes |
| Convenience | High - ready to cook | Medium - requires soaking and washing |
| Storage | Long shelf life, sealed packaging | Depends on moisture content, often shorter |
| Texture | Soft, less firm | Varies, typically firmer |
| Nutritional Value | Similar, sometimes reduced due to processing | Preserved natural nutrients |
| Cost | Higher per serving | Lower per serving |
Introduction to Instant Rice and Traditional Rice
Instant rice is precooked and dehydrated to reduce preparation time to just minutes, making it ideal for quick meals and busy lifestyles. Traditional rice requires thorough washing and longer cooking, usually taking 20-40 minutes, preserving its natural texture and flavor. Consumers prioritize instant rice for convenience and speed, while traditional rice is favored for its authentic taste and versatility in diverse culinary dishes.
Time Efficiency: Cooking Instant vs Traditional Rice
Instant rice offers significant time efficiency by reducing cooking time to just 5-10 minutes, compared to traditional rice, which generally requires 20-40 minutes. This makes instant rice ideal for quick meal preparation, especially in fast-paced environments or busy households. While traditional rice retains more texture and flavor, instant rice's convenience in saving time is unmatched for everyday use.
Preparation Methods Compared
Instant rice requires minimal preparation, typically involving just boiling water for 5 minutes, which suits busy lifestyles and quick meals. Traditional rice needs rinsing and a longer cooking time of 20-40 minutes, allowing for better texture and flavor development. The streamlined preparation of instant rice offers convenience but sacrifices some of the taste and texture found in traditional methods.
Ingredient and Additive Differences
Instant rice contains pre-cooked, dried grains with added stabilizers and preservatives to extend shelf life and reduce cooking time, while traditional rice is typically raw, free from additives, requiring longer cooking but maintaining a natural composition. The ingredient list of instant rice often includes modified starches and sodium-based additives to enhance texture and flavor, contrasting with the pure, additive-free profile of traditional rice. These differences impact convenience by allowing instant rice to be prepared in minutes versus traditional rice needing prolonged boiling or steaming.
Taste and Texture: Instant vs Traditional Rice
Instant rice offers remarkable convenience with quick cooking times, but often lacks the rich, nutty flavor and firm texture characteristic of traditional rice. Traditional rice varieties, such as long-grain Basmati or Jasmine, provide a fuller taste profile and a more satisfying, fluffy texture due to their natural cooking process. While instant rice prioritizes speed, traditional rice remains preferred for culinary dishes demanding authentic flavor and optimal mouthfeel.
Nutritional Value Breakdown
Instant rice offers significant convenience by cooking quickly, often within 5 to 10 minutes, but its nutritional value is generally lower than traditional rice due to processing that reduces fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Traditional rice varieties, including brown and white rice, retain higher levels of essential nutrients such as B vitamins, magnesium, and antioxidants, contributing to better overall health benefits. Choosing traditional rice supports a more nutrient-dense diet, while instant rice prioritizes time-saving convenience with some compromise on nutritional content.
Storage and Shelf Life Considerations
Instant rice offers significant convenience through its extended shelf life and minimal storage requirements, often lasting up to 5 years when kept in a cool, dry place. Traditional rice typically has a shorter shelf life, ranging from 1 to 2 years depending on the variety and storage conditions, requiring airtight containers to maintain freshness. Proper storage of both types in moisture-resistant environments prevents spoilage and preserves nutritional quality over time.
Cost Analysis: Instant Rice vs Traditional Rice
Instant rice typically costs more per serving due to its processing and packaging, making it less economical compared to traditional rice, which can be bought in bulk at a lower price. Traditional rice requires longer cooking times and more energy, slightly increasing overall preparation costs. Consumers prioritizing convenience may accept the higher price of instant rice to save time and reduce cooking effort.
Environmental Impact and Packaging
Instant rice offers greater convenience through faster cooking times and often features compact, lightweight packaging that reduces transportation emissions compared to traditional rice. Traditional rice typically requires longer cooking and uses bulk packaging, which may result in higher energy consumption during cooking and increased packaging waste. Choosing instant rice can lower the environmental footprint by minimizing both cooking energy usage and packaging materials.
Choosing the Right Rice for Your Lifestyle
Instant rice offers unparalleled convenience with its quick cooking time of 5-10 minutes, ideal for busy lifestyles seeking fast meal preparation. Traditional rice varieties, such as basmati or jasmine, require longer cooking times but provide richer flavors and nutritional benefits, suiting those who prioritize taste and health. Selecting the right rice depends on balancing convenience with dietary preferences and meal planning needs.
Instant rice vs Traditional rice for convenience Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com