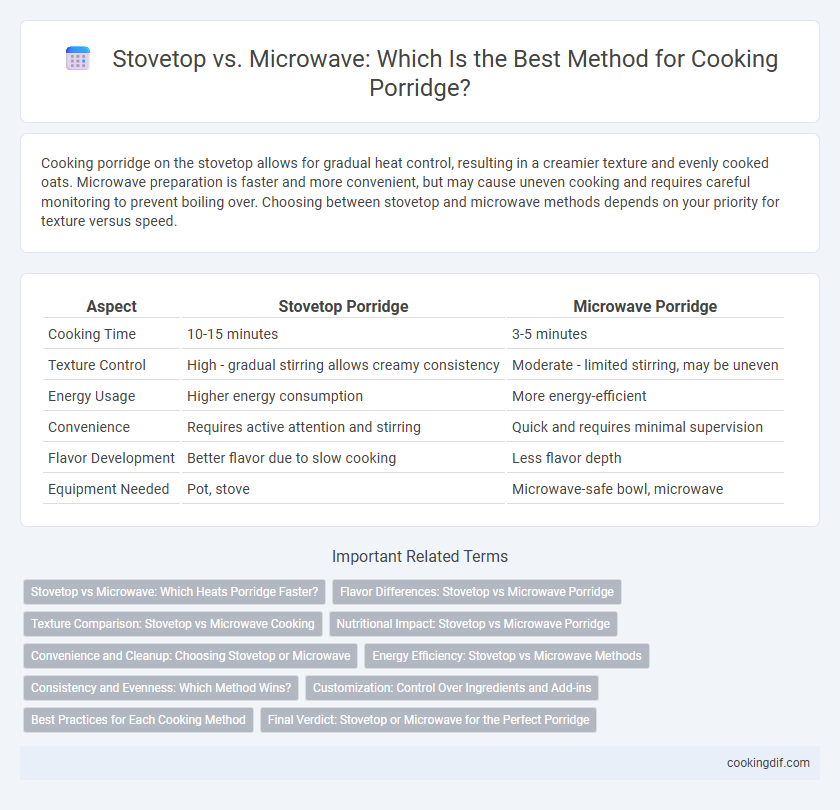
Cooking porridge on the stovetop allows for gradual heat control, resulting in a creamier texture and evenly cooked oats. Microwave preparation is faster and more convenient, but may cause uneven cooking and requires careful monitoring to prevent boiling over. Choosing between stovetop and microwave methods depends on your priority for texture versus speed.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Stovetop Porridge | Microwave Porridge |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Time | 10-15 minutes | 3-5 minutes |
| Texture Control | High - gradual stirring allows creamy consistency | Moderate - limited stirring, may be uneven |
| Energy Usage | Higher energy consumption | More energy-efficient |
| Convenience | Requires active attention and stirring | Quick and requires minimal supervision |
| Flavor Development | Better flavor due to slow cooking | Less flavor depth |
| Equipment Needed | Pot, stove | Microwave-safe bowl, microwave |
Stovetop vs Microwave: Which Heats Porridge Faster?
Microwave ovens heat porridge faster than stovetop methods due to their rapid energy transfer and direct heating of water molecules. Stovetop cooking provides more even heat distribution but requires longer cooking times, typically around 5-10 minutes versus 2-3 minutes in a microwave. For quick preparation, the microwave is more efficient, while stovetop allows for better control over texture and consistency.
Flavor Differences: Stovetop vs Microwave Porridge
Stovetop porridge offers a richer, more complex flavor profile due to the slow, even heating that allows oats to fully absorb liquid and release natural starches. Microwave cooking tends to produce a less creamy texture and can result in uneven cooking, which diminishes the depth of taste compared to stovetop methods. For a fuller flavor and creamier consistency, stovetop porridge remains the preferred choice among enthusiasts.
Texture Comparison: Stovetop vs Microwave Cooking
Stovetop porridge cooking typically results in a creamier and more evenly textured consistency due to gradual heat distribution and constant stirring, which helps prevent clumping and burning. Microwave cooking often produces a slightly uneven texture with occasional lumps because of rapid heating and less control over stirring during the process. For a smooth, thick, and well-incorporated porridge, stovetop methods outperform microwave cooking in texture quality.
Nutritional Impact: Stovetop vs Microwave Porridge
Stovetop cooking preserves more nutrients in porridge by allowing gradual heat application, reducing vitamin degradation compared to microwave methods. Microwaving tends to cause uneven heating, which can lead to nutrient loss, particularly in heat-sensitive vitamins like B-complex and C. Both methods maintain essential macronutrients, but stovetop porridge generally offers superior retention of antioxidants and minerals.
Convenience and Cleanup: Choosing Stovetop or Microwave
Stovetop porridge offers more control over texture and flavor through gradual heating, but requires longer cooking time and more extensive cleanup due to pots and utensils. Microwave porridge is the most convenient option, providing quick preparation and minimal dishes, often limited to a single microwave-safe bowl. Preference depends on balancing the desire for texture customization and flavor depth against the need for speed and easy cleanup.
Energy Efficiency: Stovetop vs Microwave Methods
Stovetop porridge cooking generally consumes more energy due to longer heating times and continuous simmering, whereas microwave cooking uses shorter bursts of energy, resulting in higher energy efficiency. Microwave methods can reduce overall electricity usage by rapidly heating porridge with minimal heat loss, making it a more eco-friendly choice for quick meals. However, stovetop cooking provides more consistent temperature control but at the cost of greater energy expenditure.
Consistency and Evenness: Which Method Wins?
Stovetop cooking offers superior consistency and evenness for porridge as it allows precise temperature control and gradual heat distribution, preventing lumps and scorching. Microwave methods often result in uneven heating, causing hot spots and inconsistent texture due to rapid, uneven energy application. Therefore, stovetop is preferred for achieving smooth, evenly cooked porridge with optimal creaminess.
Customization: Control Over Ingredients and Add-ins
Stovetop porridge cooking offers precise control over ingredient ratios, texture adjustments, and timing, enabling customization of thickness and consistency. Microwave methods prioritize speed but limit gradual ingredient incorporation and fine-tuning of flavors. For recipes requiring specific add-in textures, like nuts or fruit, stovetop cooking better maintains integrity and ensures even distribution.
Best Practices for Each Cooking Method
Stovetop porridge cooking requires constant stirring and moderate heat to prevent burning and achieve a creamy texture. Microwave porridge preparation benefits from using a microwave-safe bowl with frequent stirring intervals to ensure even cooking and avoid overflow. For best results, adding liquid gradually and monitoring cooking times per method enhances porridge consistency and flavor.
Final Verdict: Stovetop or Microwave for the Perfect Porridge
Stovetop cooking allows for precise control over heat and texture, resulting in creamier, evenly cooked porridge with customizable thickness. Microwave methods offer quick and convenient preparation but may yield uneven cooking and require frequent stirring to avoid lumps. For the perfect porridge, stovetop remains the preferred method due to superior texture and flavor development, despite longer cooking time.
Stovetop vs microwave for porridge cooking method Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com