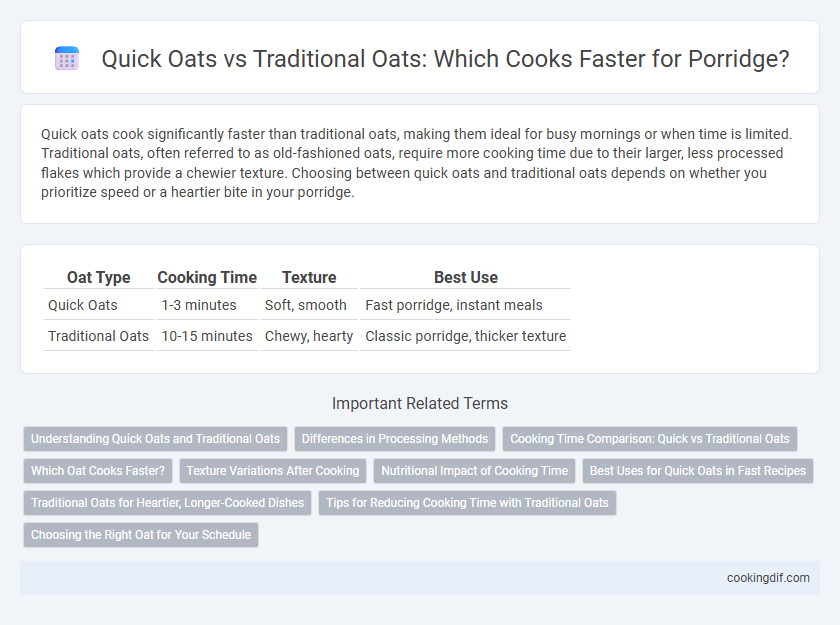
Quick oats cook significantly faster than traditional oats, making them ideal for busy mornings or when time is limited. Traditional oats, often referred to as old-fashioned oats, require more cooking time due to their larger, less processed flakes which provide a chewier texture. Choosing between quick oats and traditional oats depends on whether you prioritize speed or a heartier bite in your porridge.
Table of Comparison
| Oat Type | Cooking Time | Texture | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quick Oats | 1-3 minutes | Soft, smooth | Fast porridge, instant meals |
| Traditional Oats | 10-15 minutes | Chewy, hearty | Classic porridge, thicker texture |
Understanding Quick Oats and Traditional Oats
Quick oats are steamed and rolled thinner than traditional oats, allowing them to cook in about 1 to 2 minutes, making them ideal for fast breakfast options. Traditional oats, also known as old-fashioned oats, retain their thicker flakes and typically require 5 to 10 minutes of cooking to achieve a chewy texture and hearty flavor. Understanding the processing differences helps choose the right oat type based on desired cooking time and texture in porridge preparation.
Differences in Processing Methods
Quick oats undergo a more intensive processing method where they are steamed longer, rolled thinner, and sometimes cut into smaller pieces, resulting in a faster cooking time of about 1 to 2 minutes. Traditional oats, also known as old-fashioned rolled oats, are steamed briefly and rolled thicker, preserving more of their texture and requiring 5 to 10 minutes to cook. This difference in processing methods affects not only cooking time but also the texture and nutritional properties of the porridge.
Cooking Time Comparison: Quick vs Traditional Oats
Quick oats cook significantly faster, typically requiring only 1 to 2 minutes, making them ideal for rapid meal preparation. Traditional oats, or old-fashioned rolled oats, take about 5 to 10 minutes to cook, offering a chewier texture and more robust flavor. This cooking time difference is due to the finer processing of quick oats, which reduces the cooking duration without compromising nutritional value.
Which Oat Cooks Faster?
Quick oats cook significantly faster than traditional oats due to their thinner, more processed texture, typically requiring only about 1 to 2 minutes of cooking time. Traditional oats, also known as old-fashioned oats, take approximately 5 to 10 minutes to cook because they are larger and less processed. Choosing quick oats is ideal for those seeking a rapid breakfast option, while traditional oats offer a chewier texture and longer cooking time.
Texture Variations After Cooking
Quick oats cook in about 1 to 2 minutes, producing a smoother, creamier porridge texture due to their thinner, pre-steamed flakes. Traditional oats require 5 to 10 minutes of cooking, yielding a thicker, chewier consistency with more distinct oat grain structure. The choice between quick and traditional oats ultimately affects the porridge's mouthfeel, with quick oats favored for rapid preparation and traditional oats preferred for a hearty, rustic texture.
Nutritional Impact of Cooking Time
Quick oats cook in about 1 minute, significantly faster than traditional oats, which typically require 5 to 10 minutes. The shorter cooking time of quick oats leads to a slightly lower glycemic index, while longer cooking of traditional oats enhances the bioavailability of nutrients such as beta-glucan and antioxidants. Both types retain essential fiber and protein, but cooking time influences the texture and digestion rate, impacting overall nutritional absorption.
Best Uses for Quick Oats in Fast Recipes
Quick oats cook in about 1 to 2 minutes, making them ideal for fast recipes like instant porridge, smoothies, and baked goods requiring minimal preparation time. Their fine texture absorbs liquid rapidly and creates a creamy consistency, preferred for quick breakfasts or snacks. Traditional oats, with longer cooking times of 10 to 30 minutes, are better suited for hearty, chewy dishes where texture is key.
Traditional Oats for Heartier, Longer-Cooked Dishes
Traditional oats require longer cooking times, typically around 20-30 minutes, making them ideal for hearty, slow-cooked porridges that develop rich textures and robust flavors. Their thicker grain structure holds up well in longer cooking processes, offering a chewy, satisfying bite perfect for warming breakfasts. Unlike quick oats, traditional oats retain more nutrients due to minimal processing, enhancing both flavor and nutritional value in extended cooking recipes.
Tips for Reducing Cooking Time with Traditional Oats
Traditional oats typically require 10 to 15 minutes of cooking, whereas quick oats cook in about 1 to 3 minutes due to their finer texture. To reduce cooking time with traditional oats, soak them overnight or use hot water to soften the grains before heating. Stirring frequently and using a pressure cooker can also significantly speed up the cooking process.
Choosing the Right Oat for Your Schedule
Quick oats cook in about 1 to 2 minutes, making them ideal for busy mornings when time is limited. Traditional oats, or old-fashioned oats, require approximately 5 to 10 minutes to cook, providing a heartier texture and richer flavor. Selecting quick oats allows for fast preparation, while traditional oats offer a more substantial porridge experience when time permits.
Quick oats vs traditional oats for cooking time Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com