Brown sugar adds a rich, molasses-like depth and a slightly caramelized flavor to porridge, enhancing its warmth and earthiness. Maple syrup offers a lighter, floral sweetness with subtle woody notes that complement porridge without overpowering its natural taste. Choosing between brown sugar and maple syrup depends on your preferred balance of robust versus delicate sweetness in porridge.
Table of Comparison
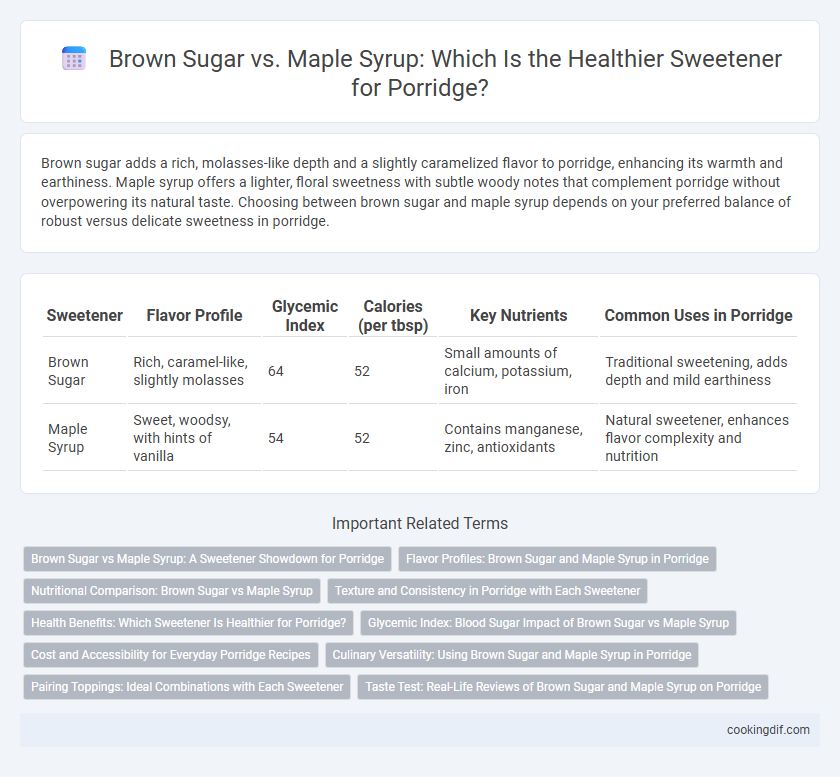
| Sweetener | Flavor Profile | Glycemic Index | Calories (per tbsp) | Key Nutrients | Common Uses in Porridge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown Sugar | Rich, caramel-like, slightly molasses | 64 | 52 | Small amounts of calcium, potassium, iron | Traditional sweetening, adds depth and mild earthiness |
| Maple Syrup | Sweet, woodsy, with hints of vanilla | 54 | 52 | Contains manganese, zinc, antioxidants | Natural sweetener, enhances flavor complexity and nutrition |
Brown Sugar vs Maple Syrup: A Sweetener Showdown for Porridge
Brown sugar and maple syrup each offer distinct flavors and nutritional benefits as porridge sweeteners. Brown sugar provides a rich molasses taste with slightly higher calories and minerals like calcium and potassium, while maple syrup delivers a natural sweetness packed with antioxidants and manganese. Choosing between them depends on whether you prioritize a caramel-like depth or a lighter, more complex sweetness to enhance your porridge experience.
Flavor Profiles: Brown Sugar and Maple Syrup in Porridge
Brown sugar imparts a rich, caramel-like sweetness with molasses undertones that enhance the creamy texture of porridge, creating a warm and robust flavor profile. Maple syrup offers a distinct, earthy sweetness with hints of vanilla and caramel, adding complexity and a natural, aromatic depth to each spoonful. Both sweeteners elevate porridge differently: brown sugar intensifies sweetness with a heavier, more indulgent taste, while maple syrup provides a lighter, nuanced sweetness with subtle woody and fruity notes.
Nutritional Comparison: Brown Sugar vs Maple Syrup
Brown sugar contains about 17 calories per teaspoon and provides small amounts of minerals such as calcium, potassium, and iron, while maple syrup offers approximately 52 calories per tablespoon along with antioxidants and higher levels of manganese and zinc. Maple syrup has a lower glycemic index compared to brown sugar, making it a preferable option for blood sugar control. Choosing maple syrup over brown sugar can enhance porridge's nutritional profile by delivering essential micronutrients and antioxidants.
Texture and Consistency in Porridge with Each Sweetener
Brown sugar melts slowly into porridge, creating a slightly grainy texture that thickens the consistency and adds a rich, caramel-like depth. Maple syrup blends smoothly, imparting a glossy, fluid consistency that enhances the porridge's creaminess without altering its thickness significantly. The choice between brown sugar and maple syrup influences both mouthfeel and porridge texture, catering to preferences for either a denser or a more velvety breakfast experience.
Health Benefits: Which Sweetener Is Healthier for Porridge?
Brown sugar contains molasses, providing trace minerals like calcium, potassium, and iron, while maple syrup offers antioxidants and a lower glycemic index, making it gentler on blood sugar levels. Maple syrup also contains manganese and zinc, which support immune function and metabolism, whereas brown sugar is more processed and higher in sucrose. Choosing maple syrup as a porridge sweetener promotes better nutrient intake and sustained energy release, making it a healthier option overall.
Glycemic Index: Blood Sugar Impact of Brown Sugar vs Maple Syrup
Brown sugar has a higher glycemic index (GI) of around 64, causing quicker spikes in blood sugar levels when used as a sweetener for porridge. Maple syrup features a lower GI of approximately 54, leading to a more gradual increase in blood glucose and better blood sugar management. Choosing maple syrup over brown sugar can help maintain steadier energy levels and reduce insulin spikes after consuming porridge.
Cost and Accessibility for Everyday Porridge Recipes
Brown sugar is generally more affordable and widely available in supermarkets, making it a practical choice for everyday porridge recipes. Maple syrup tends to be more expensive due to its labor-intensive production process and is often found in specialty or organic food stores. For budget-conscious consumers seeking easy access, brown sugar offers a cost-effective and convenient sweetening option.
Culinary Versatility: Using Brown Sugar and Maple Syrup in Porridge
Brown sugar offers a rich, molasses-infused sweetness that enhances the creamy texture of porridge, making it ideal for traditional recipes and baking applications. Maple syrup provides a natural, distinct flavor with a subtle caramel note, adding a unique depth when drizzled over porridge or mixed with nuts and fruits. Both sweeteners bring culinary versatility, allowing customization of porridge from classic comfort food to gourmet breakfast options.
Pairing Toppings: Ideal Combinations with Each Sweetener
Brown sugar pairs exceptionally well with cinnamon, nutmeg, and chopped pecans, enhancing the warm, caramel notes in porridge. Maple syrup complements fresh berries, toasted walnuts, and a sprinkle of sea salt, creating a balanced blend of sweetness and texture. Choosing the right sweetener influences the choice of toppings to elevate the overall flavor profile of porridge.
Taste Test: Real-Life Reviews of Brown Sugar and Maple Syrup on Porridge
Brown sugar imparts a rich, caramel-like sweetness with a slightly molasses undertone, enhancing the creaminess of porridge without overpowering its natural flavors. Maple syrup offers a distinct, woody sweetness with complex notes of vanilla and cinnamon, which complements porridge through a more vibrant and aromatic profile. Real-life reviews reveal a preference split; some favor brown sugar for nostalgic comfort while others prefer maple syrup for its nuanced taste and natural sourcing.
Brown sugar vs Maple syrup for porridge sweetener Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com