Brown sugar adds a rich, molasses-like depth to porridge, enhancing its natural warmth with a subtle caramel flavor. Honey provides a lighter, floral sweetness that can brighten the taste without overpowering the grains. Choosing between brown sugar and honey depends on whether you prefer a robust, earthy sweetness or a delicate, aromatic touch.
Table of Comparison
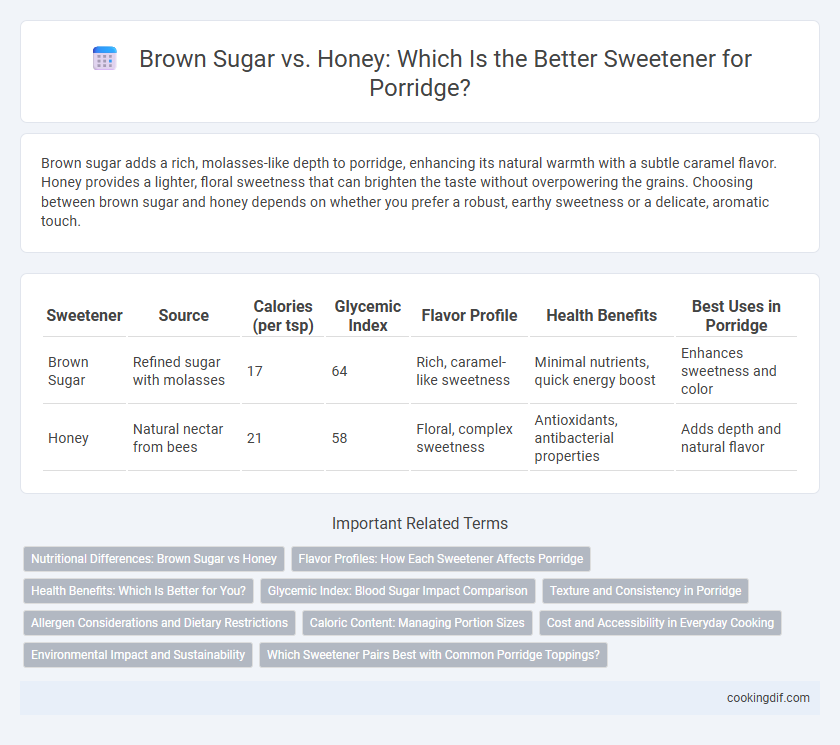
| Sweetener | Source | Calories (per tsp) | Glycemic Index | Flavor Profile | Health Benefits | Best Uses in Porridge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown Sugar | Refined sugar with molasses | 17 | 64 | Rich, caramel-like sweetness | Minimal nutrients, quick energy boost | Enhances sweetness and color |
| Honey | Natural nectar from bees | 21 | 58 | Floral, complex sweetness | Antioxidants, antibacterial properties | Adds depth and natural flavor |
Nutritional Differences: Brown Sugar vs Honey
Brown sugar contains fewer calories and minerals such as calcium, potassium, and iron, but it has a higher glycemic index, causing quicker blood sugar spikes compared to honey. Honey is rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and enzymes that support digestion and immune function while offering a lower glycemic response. Choosing between brown sugar and honey as a porridge sweetener depends on balancing calorie intake with the desire for additional nutrients and a milder impact on blood glucose levels.
Flavor Profiles: How Each Sweetener Affects Porridge
Brown sugar imparts a rich, caramel-like flavor that deepens the porridge's taste and adds a subtle molasses undertone, enhancing its warmth and complexity. Honey offers a floral and fruity sweetness, providing a lighter and more aromatic profile that complements the natural grain flavors without overpowering them. Choosing between brown sugar and honey allows customization of porridge based on desired flavor intensity and aroma, tailoring the sweetness to personal preference.
Health Benefits: Which Is Better for You?
Brown sugar contains trace minerals like calcium, potassium, and iron, offering mild antioxidant properties, while honey provides antibacterial compounds, antioxidants, and enzymes that support digestive health. Honey has a lower glycemic index compared to brown sugar, making it a better option for blood sugar regulation and sustained energy release. However, both should be consumed in moderation due to their high sugar content and caloric values.
Glycemic Index: Blood Sugar Impact Comparison
Brown sugar has a glycemic index (GI) of approximately 64, causing a moderate increase in blood sugar levels. Honey's GI varies between 45 and 64 depending on the floral source, often resulting in a slightly lower or comparable blood sugar impact compared to brown sugar. Choosing honey may offer a more gradual rise in blood glucose, benefiting those managing glycemic response in porridge sweetening.
Texture and Consistency in Porridge
Brown sugar adds a slightly grainy texture and a thicker consistency to porridge due to its molasses content, which enhances caramel notes and viscosity. Honey dissolves more smoothly, giving porridge a silkier texture and a more fluid consistency with a natural floral sweetness. Choosing between brown sugar and honey depends on whether a heartier, richer mouthfeel or a lighter, smoother finish is desired in the porridge.
Allergen Considerations and Dietary Restrictions
Brown sugar and honey differ significantly in allergen considerations and dietary restrictions for porridge. Brown sugar, derived from sugarcane or sugar beet, is generally allergen-free but may not be suitable for strict diabetics due to its high glycemic index, while honey, a natural bee product, can trigger allergic reactions in those sensitive to pollen or bee products and is not vegan-friendly. Choosing between brown sugar and honey depends on individual dietary needs, allergies, and ethical preferences, emphasizing the importance of personalized nutrition in porridge sweetening.
Caloric Content: Managing Portion Sizes
Brown sugar contains approximately 15 calories per teaspoon, while honey provides about 21 calories per teaspoon, making brown sugar a lower-calorie option for sweetening porridge. Managing portion sizes is essential as even small increases in sweetener quantity can significantly impact the overall caloric content of the meal. Choosing the right sweetener and moderating its amount helps maintain a balanced intake for weight management and nutritional goals.
Cost and Accessibility in Everyday Cooking
Brown sugar is a cost-effective sweetener commonly found in most grocery stores and offers consistent availability for everyday cooking. Honey tends to be pricier and may vary in accessibility depending on location and season, sometimes limiting its use as a regular porridge sweetener. Choosing brown sugar ensures affordability and convenience for frequent porridge preparation without compromising sweetness.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Brown sugar production typically involves less processing than refined sugars, resulting in a lower carbon footprint and reduced chemical usage, making it a more environmentally friendly sweetener for porridge. Honey, sourced directly from bees, supports biodiversity and natural ecosystems but can have variable sustainability depending on beekeeping practices and transportation emissions. Choosing locally produced brown sugar or honey can minimize environmental impact by reducing transportation-related carbon emissions and supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
Which Sweetener Pairs Best with Common Porridge Toppings?
Brown sugar enhances porridge with a deep caramel flavor that complements toppings like cinnamon, apples, and nuts, adding a rich sweetness and slight molasses undertone. Honey offers a floral, lighter sweetness ideal for pairing with berries, yogurt, and seeds, elevating the porridge's natural flavors without overpowering them. Choosing between brown sugar and honey depends on whether a robust or delicate taste profile best complements the selected toppings.
Brown sugar vs honey for sweetener Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com