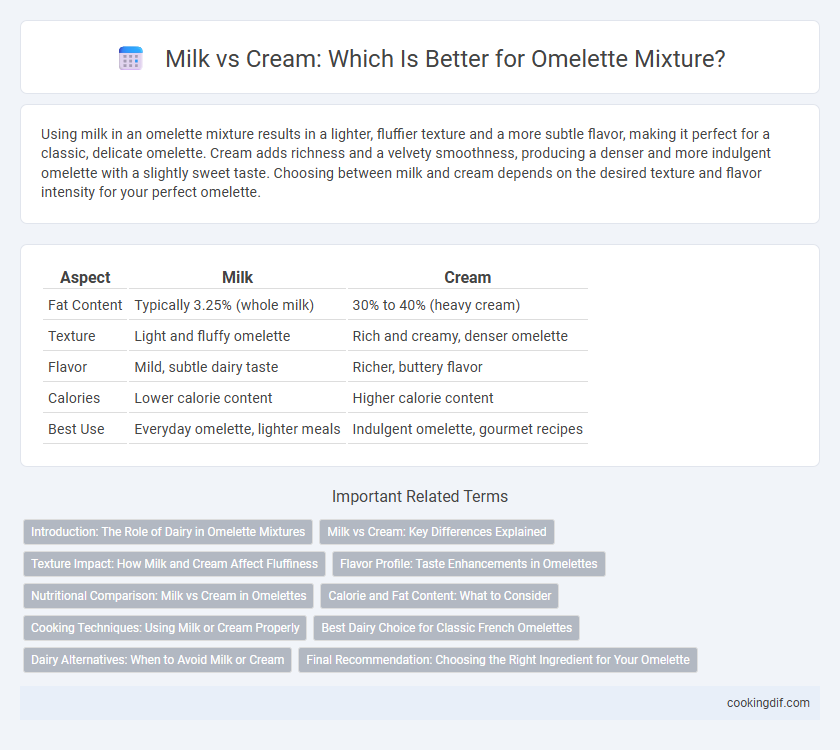
Using milk in an omelette mixture results in a lighter, fluffier texture and a more subtle flavor, making it perfect for a classic, delicate omelette. Cream adds richness and a velvety smoothness, producing a denser and more indulgent omelette with a slightly sweet taste. Choosing between milk and cream depends on the desired texture and flavor intensity for your perfect omelette.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Milk | Cream |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | Typically 3.25% (whole milk) | 30% to 40% (heavy cream) |
| Texture | Light and fluffy omelette | Rich and creamy, denser omelette |
| Flavor | Mild, subtle dairy taste | Richer, buttery flavor |
| Calories | Lower calorie content | Higher calorie content |
| Best Use | Everyday omelette, lighter meals | Indulgent omelette, gourmet recipes |
Introduction: The Role of Dairy in Omelette Mixtures
In omelette mixtures, dairy such as milk or cream plays a crucial role in achieving a tender and fluffy texture. Milk adds moisture and lightness, enhancing the egg's natural flavor without overwhelming it, while cream provides a richer, silkier consistency due to its higher fat content. The choice between milk and cream directly influences the omelette's density, flavor intensity, and overall mouthfeel.
Milk vs Cream: Key Differences Explained
Milk and cream differ significantly in fat content, with cream containing around 30-36% fat compared to milk's 3-4%, impacting omelette texture and richness. Using cream in an omelette results in a thicker, fluffier, and creamier consistency, while milk creates a lighter, less dense texture. The choice between milk and cream affects cooking time and mouthfeel, with cream yielding a richer flavor ideal for decadent omelettes.
Texture Impact: How Milk and Cream Affect Fluffiness
Milk in omelette mixtures enhances lightness and moisture, producing a tender texture without heaviness. Cream adds richness and density, resulting in a thicker, creamier omelette with a more luxurious mouthfeel. Choosing between milk and cream directly influences the omelette's fluffiness, with milk promoting airier, delicate curds and cream creating a denser, silkier consistency.
Flavor Profile: Taste Enhancements in Omelettes
Using cream in omelette mixtures enhances the flavor profile by adding a rich, velvety texture and a subtle sweetness that intensifies the egg's natural taste. Milk contributes a lighter, more delicate flavor, allowing other ingredients like herbs and cheese to stand out more distinctly. Cream's higher fat content creates a luxurious mouthfeel, making the omelette taste more indulgent and satisfying.
Nutritional Comparison: Milk vs Cream in Omelettes
Milk contains fewer calories and less fat than cream, making it a lighter option for omelette mixtures that supports lower calorie intake and heart health. Cream is richer in saturated fats and calories, providing a creamier texture and more luxurious mouthfeel but may contribute to higher cholesterol levels if consumed excessively. Choosing milk over cream in omelettes can enhance protein content with fewer added fats while cream adds richness and vitamins A and D in higher doses.
Calorie and Fat Content: What to Consider
Milk contains fewer calories and less fat compared to cream, making it a lighter option for omelette mixtures while still adding moisture and a slight richness. Cream provides a higher fat content, resulting in a richer, creamier texture but with significantly more calories, which may affect dietary goals. Choosing between milk and cream depends on balancing desired flavor intensity with calorie and fat intake preferences for optimal omelette nutrition.
Cooking Techniques: Using Milk or Cream Properly
Using milk in an omelette mixture results in a lighter texture and quicker cooking time, ideal for fluffy, tender eggs. Cream adds richness and a velvety mouthfeel due to its higher fat content, requiring lower heat and longer cooking to prevent curdling. Proper technique involves gently folding milk or cream into beaten eggs and cooking over medium-low heat to achieve a creamy consistency without overcooking.
Best Dairy Choice for Classic French Omelettes
Cream is often favored over milk in classic French omelettes due to its higher fat content, which results in a richer, silkier texture and enhanced flavor. Whole milk can be used for a lighter texture but may produce a less tender omelette compared to cream. The choice between cream and milk ultimately affects the omelette's consistency, with cream offering a more luxurious finish preferred in traditional French cuisine.
Dairy Alternatives: When to Avoid Milk or Cream
Milk and cream add richness and tenderness to omelettes but can cause issues for those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. Plant-based alternatives like almond, soy, or oat milk offer lactose-free options but may alter texture and flavor, often making the omelette less creamy. Avoid milk or cream when dietary restrictions or personal preferences demand dairy-free solutions to ensure a delicious and accessible dish.
Final Recommendation: Choosing the Right Ingredient for Your Omelette
Using cream in an omelette mixture results in a richer, fluffier texture due to its higher fat content, while milk produces a lighter, more delicate consistency. For a luxurious, custard-like omelette, cream is ideal, especially when seeking extra creaminess and tenderness. If you prefer a healthier option with fewer calories but still want some fluffiness, milk is the recommended choice.
Milk vs Cream for omelette mixture Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com