Vegetarian gravy offers a plant-based alternative that suits those with dietary restrictions such as allergies, lactose intolerance, or vegan preferences, providing essential nutrients without animal products. Meat-based gravy, rich in protein and iron, supports diets requiring higher nutrient density but may not be suitable for individuals avoiding animal fats or cholesterol. Choosing between vegetarian and meat-based gravy depends on nutritional goals, ethical considerations, and specific health requirements.
Table of Comparison
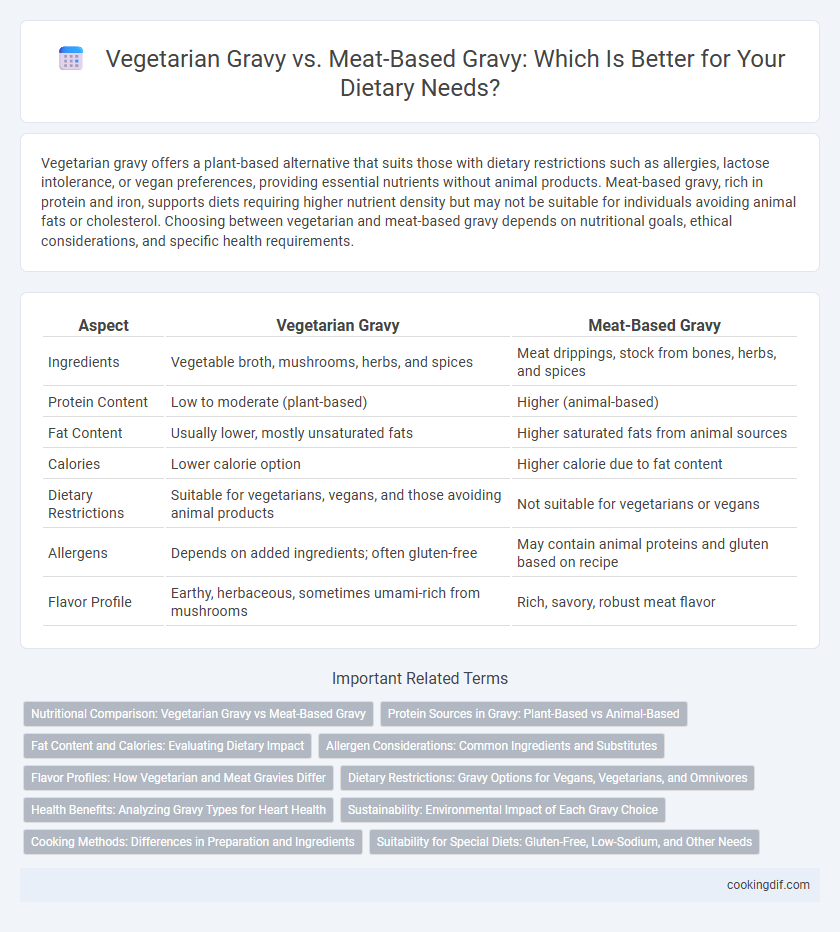
| Aspect | Vegetarian Gravy | Meat-Based Gravy |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | Vegetable broth, mushrooms, herbs, and spices | Meat drippings, stock from bones, herbs, and spices |
| Protein Content | Low to moderate (plant-based) | Higher (animal-based) |
| Fat Content | Usually lower, mostly unsaturated fats | Higher saturated fats from animal sources |
| Calories | Lower calorie option | Higher calorie due to fat content |
| Dietary Restrictions | Suitable for vegetarians, vegans, and those avoiding animal products | Not suitable for vegetarians or vegans |
| Allergens | Depends on added ingredients; often gluten-free | May contain animal proteins and gluten based on recipe |
| Flavor Profile | Earthy, herbaceous, sometimes umami-rich from mushrooms | Rich, savory, robust meat flavor |
Nutritional Comparison: Vegetarian Gravy vs Meat-Based Gravy
Vegetarian gravy typically contains fewer calories and less saturated fat compared to meat-based gravy, making it a healthier option for heart-conscious individuals. Rich in plant-based ingredients, vegetarian gravy often provides higher fiber content and essential vitamins such as vitamin A and antioxidants. Meat-based gravy, while offering more protein and iron, usually has increased sodium levels and cholesterol, which might be less suitable for those managing cardiovascular health or cholesterol.
Protein Sources in Gravy: Plant-Based vs Animal-Based
Vegetarian gravy typically relies on plant-based protein sources such as mushrooms, lentils, or soy, offering a lower fat content and higher fiber compared to meat-based gravy. Meat-based gravy contains animal proteins derived from beef, chicken, or turkey drippings, providing essential amino acids but often higher saturated fats. Choosing between vegetarian and meat-based gravy affects protein intake quality, catering to dietary preferences like veganism or low-cholesterol diets while influencing overall nutritional balance.
Fat Content and Calories: Evaluating Dietary Impact
Vegetarian gravy typically contains lower fat content and fewer calories compared to meat-based gravy, making it a healthier option for those monitoring their dietary intake. Meat-based gravies often include high amounts of saturated fats and cholesterol due to the use of animal fats and drippings, which can contribute to increased calorie consumption. Choosing vegetarian gravy supports a lighter dietary profile while still providing rich flavors suitable for diverse nutritional needs.
Allergen Considerations: Common Ingredients and Substitutes
Vegetarian gravy often uses vegetable broth, soy sauce, and nutritional yeast as common ingredients, avoiding allergens like dairy or gluten by substituting with plant-based milk and gluten-free flour. Meat-based gravy frequently contains allergens such as dairy, gluten, and sometimes shellfish-based broths, requiring alternatives like dairy-free cream or cornstarch for thickening. Careful selection of ingredients and substitutes ensures compatibility with dietary restrictions, including vegan, gluten-intolerant, and allergen-sensitive diets.
Flavor Profiles: How Vegetarian and Meat Gravies Differ
Vegetarian gravy often highlights earthy flavors from mushrooms, herbs, and vegetable broth, delivering a rich and savory taste without animal products. Meat-based gravy typically features robust umami notes from meat drippings and stock, creating a deeper, more intense flavor profile suited to traditional meat dishes. The choice between vegetarian and meat gravies caters to dietary preferences while providing distinct taste experiences influenced by their core ingredients.
Dietary Restrictions: Gravy Options for Vegans, Vegetarians, and Omnivores
Vegetarian gravy, often made from vegetable broth, mushrooms, and herbs, caters to vegans and vegetarians by excluding animal products and ensuring compliance with plant-based dietary needs. Meat-based gravy contains animal fats and meat drippings, providing a richer flavor profile suitable for omnivores but unsuitable for those avoiding animal derivatives. Selecting gravy according to dietary restrictions ensures nutrient intake aligns with vegan, vegetarian, or omnivore preferences while enhancing meal satisfaction.
Health Benefits: Analyzing Gravy Types for Heart Health
Vegetarian gravy, often made from vegetable broth, herbs, and whole-food ingredients, contains less saturated fat and cholesterol compared to meat-based gravy, making it a heart-healthier option for those monitoring cardiovascular risks. Meat-based gravy typically includes animal fats and higher sodium levels, which can contribute to elevated blood pressure and increased risk of heart disease. Choosing vegetarian gravy supports lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduced inflammation, promoting better overall heart health.
Sustainability: Environmental Impact of Each Gravy Choice
Vegetarian gravy typically has a lower environmental impact compared to meat-based gravy, as it requires fewer natural resources like water and land, and generates less greenhouse gas emissions during production. Meat-based gravy relies on animal agriculture, which is associated with higher carbon footprints and greater habitat disruption. Choosing vegetarian gravy supports sustainability by reducing overall ecological strain and promoting resource conservation.
Cooking Methods: Differences in Preparation and Ingredients
Vegetarian gravy typically relies on vegetable broth, mushrooms, and herbs, using flour or cornstarch as thickening agents, while meat-based gravy involves pan drippings, stock from roasted meats, and often butter for richer flavor. Preparation of vegetarian gravy focuses on simmering vegetables and reducing liquids to develop depth without animal fats, contrasting with the meat-based method that emphasizes deglazing pans and incorporating gelatin from meat juices. These distinct cooking techniques directly impact the texture, flavor profile, and suitability for dietary preferences such as veganism or low-cholesterol diets.
Suitability for Special Diets: Gluten-Free, Low-Sodium, and Other Needs
Vegetarian gravy offers a versatile alternative for special dietary needs, often being naturally gluten-free and lower in sodium compared to traditional meat-based gravies, which frequently contain gluten from flour thickeners and higher salt content. Many vegetarian gravies use vegetable broth and gluten-free thickeners like cornstarch, making them suitable for those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, as well as individuals monitoring sodium intake for hypertension management. Meat-based gravies can be adapted for special diets but typically require careful preparation to reduce allergens and salt, whereas vegetarian options inherently align better with a range of dietary restrictions including vegan, low-sodium, and gluten-free requirements.
Vegetarian gravy vs Meat-based gravy for dietary needs Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com