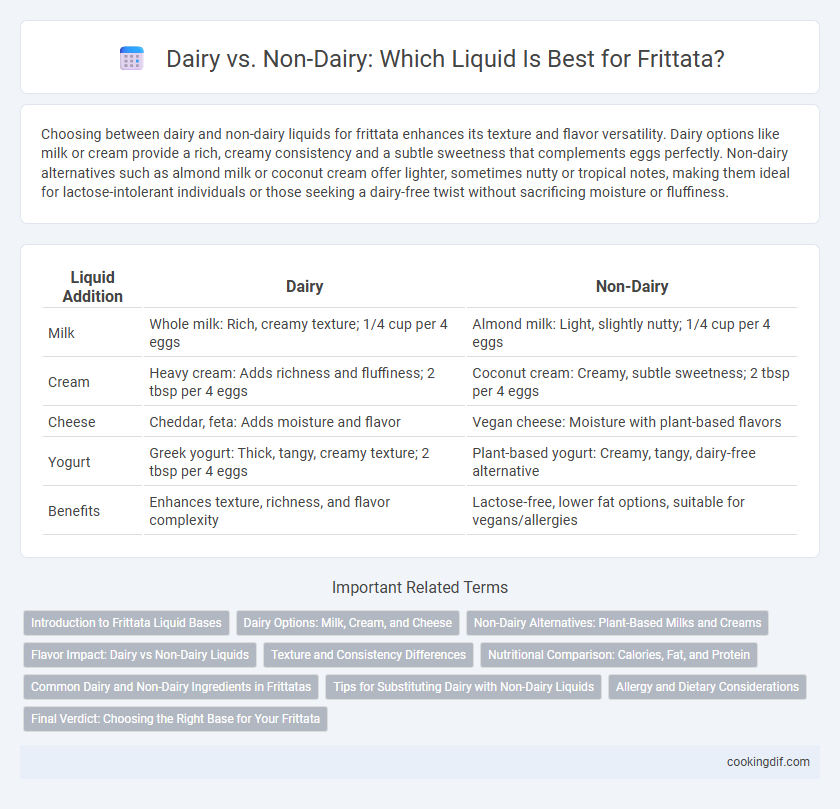
Choosing between dairy and non-dairy liquids for frittata enhances its texture and flavor versatility. Dairy options like milk or cream provide a rich, creamy consistency and a subtle sweetness that complements eggs perfectly. Non-dairy alternatives such as almond milk or coconut cream offer lighter, sometimes nutty or tropical notes, making them ideal for lactose-intolerant individuals or those seeking a dairy-free twist without sacrificing moisture or fluffiness.
Table of Comparison
| Liquid Addition | Dairy | Non-Dairy |
|---|---|---|
| Milk | Whole milk: Rich, creamy texture; 1/4 cup per 4 eggs | Almond milk: Light, slightly nutty; 1/4 cup per 4 eggs |
| Cream | Heavy cream: Adds richness and fluffiness; 2 tbsp per 4 eggs | Coconut cream: Creamy, subtle sweetness; 2 tbsp per 4 eggs |
| Cheese | Cheddar, feta: Adds moisture and flavor | Vegan cheese: Moisture with plant-based flavors |
| Yogurt | Greek yogurt: Thick, tangy, creamy texture; 2 tbsp per 4 eggs | Plant-based yogurt: Creamy, tangy, dairy-free alternative |
| Benefits | Enhances texture, richness, and flavor complexity | Lactose-free, lower fat options, suitable for vegans/allergies |
Introduction to Frittata Liquid Bases
Frittata liquid bases typically include dairy options such as milk, cream, or cheese, which enhance richness and create a creamy texture. Non-dairy alternatives like almond milk, soy milk, or coconut milk provide lighter, plant-based options suitable for lactose intolerance or vegan diets. Choosing the right liquid base impacts the frittata's moisture level, flavor profile, and overall consistency.
Dairy Options: Milk, Cream, and Cheese
Dairy options for frittata liquid additions include milk, cream, and cheese, each enhancing texture and flavor uniquely. Milk adds moisture and a light, creamy consistency, while cream contributes richness and a velvety smooth texture. Cheese, such as cheddar, feta, or parmesan, imparts umami depth and helps bind ingredients, creating a savory and satisfying frittata.
Non-Dairy Alternatives: Plant-Based Milks and Creams
Non-dairy alternatives such as almond milk, coconut milk, oat milk, and cashew cream provide creamy textures and subtle flavors ideal for enhancing frittata without dairy. Plant-based milks are low in saturated fat and offer varying levels of sweetness and thickness, which can influence the frittata's consistency and taste. Using unsweetened, unflavored options helps preserve the dish's savory profile while catering to lactose intolerance and vegan preferences.
Flavor Impact: Dairy vs Non-Dairy Liquids
Dairy liquids like milk and cream enrich a frittata with a creamy texture and subtle sweetness, enhancing the natural flavors of eggs and fillings. Non-dairy alternatives such as almond or oat milk introduce distinct nutty and earthy notes, which can alter the overall taste profile and provide unique flavor variations. Choosing between dairy and non-dairy liquids significantly affects the frittata's mouthfeel and aromatic complexity, catering to dietary preferences and flavor experimentation.
Texture and Consistency Differences
Using dairy liquids such as milk, cream, or half-and-half in frittatas creates a richer, creamier texture and a denser, more custard-like consistency due to higher fat and protein content. Non-dairy alternatives like almond milk, coconut milk, or oat milk typically result in a lighter, less cohesive texture with a slightly more airy and tender bite, influenced by lower fat and protein levels. Adjusting liquid ratios and choosing fortified non-dairy options can help balance moisture and firmness in the final frittata.
Nutritional Comparison: Calories, Fat, and Protein
Using dairy products such as milk or cream in frittata liquid additions typically increases calories and fat content while providing a richer source of protein compared to non-dairy alternatives like almond or oat milk. Non-dairy options tend to be lower in calories and fat, making them suitable for calorie-conscious diets but may contain less protein, which impacts the overall nutritional value of the frittata. Choosing between dairy and non-dairy liquids for frittatas depends on balancing calorie intake, desired fat levels, and protein content to meet specific dietary goals.
Common Dairy and Non-Dairy Ingredients in Frittatas
Common dairy ingredients in frittatas include milk, cream, and cheese, which contribute to a rich and creamy texture. Non-dairy alternatives like almond milk, coconut milk, and nutritional yeast offer lactose-free options that maintain moisture and add unique flavors. Choosing between dairy and non-dairy liquids influences the frittata's consistency, taste, and suitability for dietary preferences such as vegan or lactose-intolerant diets.
Tips for Substituting Dairy with Non-Dairy Liquids
When substituting dairy with non-dairy liquids in frittatas, choose unsweetened almond, oat, or soy milk to maintain flavor balance without added sugars. Use a 1:1 ratio but slightly reduce the volume if using thinner liquids like rice milk to prevent a runny texture. Adding a tablespoon of nutritional yeast or vegan cheese can enhance the savory depth typically found in dairy-based frittatas.
Allergy and Dietary Considerations
Choosing non-dairy alternatives such as almond milk, coconut milk, or oat milk for frittata liquid additions caters to individuals with lactose intolerance or milk allergies while providing a similar creamy texture. Dairy-free options reduce the risk of allergic reactions and support vegan, paleo, or plant-based diets without compromising flavor. Opting for fortified non-dairy milks enhances nutritional value by adding vitamins D and calcium, essential for bone health in restricted diets.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Base for Your Frittata
Choosing the right base for your frittata depends on dietary preferences and desired texture; dairy options like whole milk or cream enrich the dish with a creamy, smooth finish, while non-dairy alternatives such as almond, oat, or coconut milk offer lighter, dairy-free variations suitable for lactose-intolerant individuals. Nutritional considerations also play a role, as dairy adds protein and calcium, whereas plant-based milks vary in fortification and may impart subtle flavor differences. Ultimately, selecting between dairy and non-dairy liquid bases ensures a frittata tailored to taste, texture, and dietary needs.
Dairy vs Non-dairy for frittata liquid additions Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com