Dairy-free frittatas cater to those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies, using plant-based alternatives like almond or coconut milk to maintain a creamy texture. Traditional frittatas rely on dairy ingredients such as cheese and milk, which provide rich flavor and smoothness but may trigger sensitivities. Choosing between dairy-free and traditional frittatas ensures personalized nutrition while accommodating diverse dietary needs.
Table of Comparison
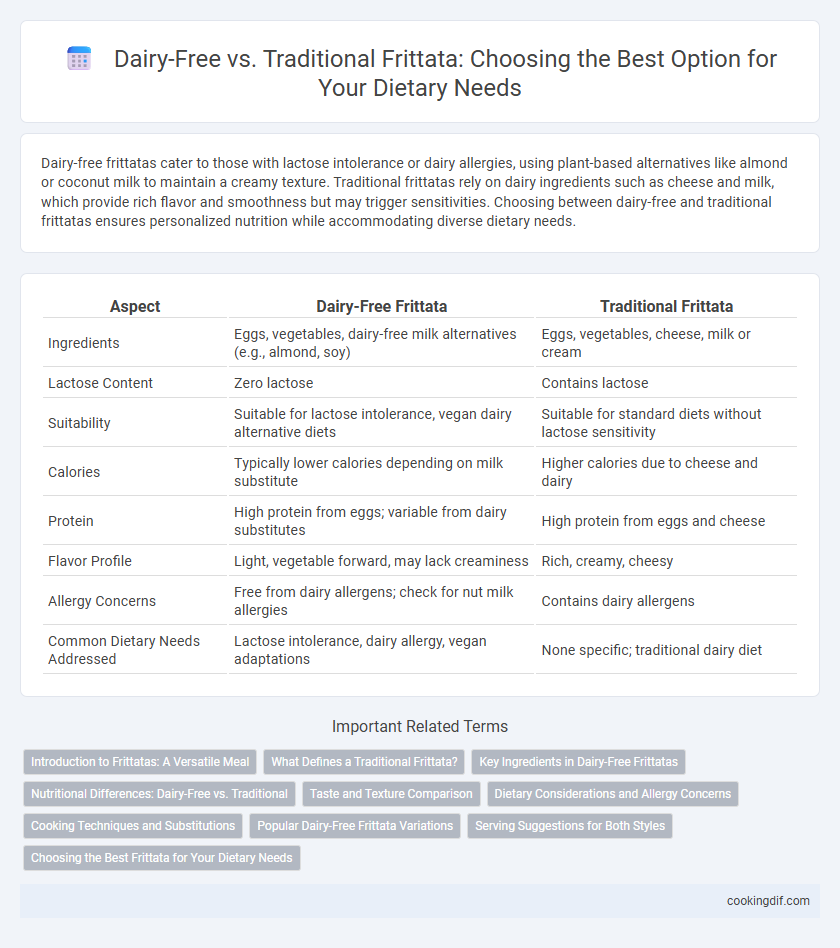
| Aspect | Dairy-Free Frittata | Traditional Frittata |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | Eggs, vegetables, dairy-free milk alternatives (e.g., almond, soy) | Eggs, vegetables, cheese, milk or cream |
| Lactose Content | Zero lactose | Contains lactose |
| Suitability | Suitable for lactose intolerance, vegan dairy alternative diets | Suitable for standard diets without lactose sensitivity |
| Calories | Typically lower calories depending on milk substitute | Higher calories due to cheese and dairy |
| Protein | High protein from eggs; variable from dairy substitutes | High protein from eggs and cheese |
| Flavor Profile | Light, vegetable forward, may lack creaminess | Rich, creamy, cheesy |
| Allergy Concerns | Free from dairy allergens; check for nut milk allergies | Contains dairy allergens |
| Common Dietary Needs Addressed | Lactose intolerance, dairy allergy, vegan adaptations | None specific; traditional dairy diet |
Introduction to Frittatas: A Versatile Meal
Frittatas traditionally blend eggs with dairy products like cheese and milk, creating a rich, creamy texture and savory flavor. Dairy-free frittatas replace these ingredients with plant-based alternatives such as almond milk or cashew cheese, making them suitable for lactose intolerance and vegan diets without compromising taste. This adaptability highlights the frittata's versatility as a nutritious, customizable meal option catering to diverse dietary needs.
What Defines a Traditional Frittata?
A traditional frittata is an Italian egg-based dish typically enriched with dairy ingredients such as cheese, milk, or cream, which contribute to its rich texture and flavor. The use of these dairy components differentiates it from dairy-free versions that replace them with plant-based alternatives like nut milk or tofu to accommodate lactose intolerance or vegan diets. Understanding the role of dairy in a classic frittata is essential for adapting the recipe to meet specific dietary needs without compromising its signature taste and consistency.
Key Ingredients in Dairy-Free Frittatas
Dairy-free frittatas replace traditional ingredients like cheese and milk with alternatives such as coconut milk, almond milk, or nutritional yeast to maintain creaminess and flavor while catering to lactose intolerance and vegan diets. Common key ingredients include silken tofu or cashew cream for texture, along with a blend of vegetables, herbs, and plant-based protein sources like chickpeas or tempeh. These substitutions ensure a nutrient-rich and satisfying meal without compromising on the savory taste characteristic of classic frittatas.
Nutritional Differences: Dairy-Free vs. Traditional
Dairy-free frittatas use plant-based milk or nutritional yeast, reducing saturated fat and cholesterol compared to traditional recipes made with eggs, cheese, and cream. Traditional frittatas are richer in calcium and protein but can contribute to higher calorie and fat intake. For dietary needs, dairy-free options support heart health and lactose intolerance while offering fewer essential nutrients found in dairy products.
Taste and Texture Comparison
Dairy-free frittatas offer a lighter, often slightly less creamy texture compared to traditional versions made with cheese and milk, which deliver a rich, velvety mouthfeel. Taste profiles of dairy-free options tend to be milder and rely more on the natural flavors of vegetables and seasonings, while traditional frittatas feature a savory depth from dairy fats and aged cheeses. For those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies, dairy-free frittatas provide a satisfying alternative without compromising the essential egg-based structure and overall flavor harmony.
Dietary Considerations and Allergy Concerns
Dairy-free frittatas replace traditional cheese and milk with plant-based alternatives like almond milk or nutritional yeast, catering to lactose intolerant and vegan individuals. Traditional frittatas, rich in dairy, provide calcium and protein but can trigger allergies or digestive issues for those sensitive to lactose or casein. Choosing between dairy-free and traditional frittatas depends on specific dietary restrictions and allergy concerns, ensuring safe and nutritious meal options.
Cooking Techniques and Substitutions
Traditional frittata recipes typically rely on eggs and dairy ingredients like cheese and milk for a rich texture, but dairy-free versions substitute plant-based milks, nutritional yeast, and tofu to mimic creaminess and binding properties. Cooking techniques for dairy-free frittatas emphasize careful whisking and gradual heat to achieve a similar fluffy consistency without curdling or drying out the alternative ingredients. These substitutions accommodate lactose intolerance and vegan diets while preserving the signature layered texture and savory flavor of classic frittatas.
Popular Dairy-Free Frittata Variations
Popular dairy-free frittata variations often replace traditional cheese with plant-based alternatives like cashew cream, nutritional yeast, or tofu, maintaining a rich, creamy texture without lactose. Ingredients such as coconut milk or almond milk add moisture and flavor, ensuring the dish suits vegan or lactose-intolerant diets. These modifications make dairy-free frittatas a versatile and nutritious option for those with specific dietary needs or allergies.
Serving Suggestions for Both Styles
Dairy-free frittatas often incorporate creamy alternatives such as coconut milk or cashew cream, providing a rich texture while accommodating lactose intolerance and vegan diets. Traditional frittatas, rich with eggs, cheese, and cream, pair well with crusty bread, fresh herbs, and seasonal vegetables for a hearty meal. Both styles benefit from garnishes like avocado slices, salsa, or microgreens to enhance flavor and presentation without compromising dietary preferences.
Choosing the Best Frittata for Your Dietary Needs
Dairy-free frittatas replace traditional cheese and milk with plant-based alternatives like almond milk or nutritional yeast, catering to lactose intolerance and vegan diets. Traditional frittatas use eggs, milk, and cheese, providing a rich source of protein and calcium but may not suit those with dairy allergies or sensitivities. Selecting the best frittata depends on individual dietary restrictions, nutrient goals, and taste preferences to ensure a balanced and enjoyable meal.
Dairy-free vs traditional frittata for dietary needs Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com