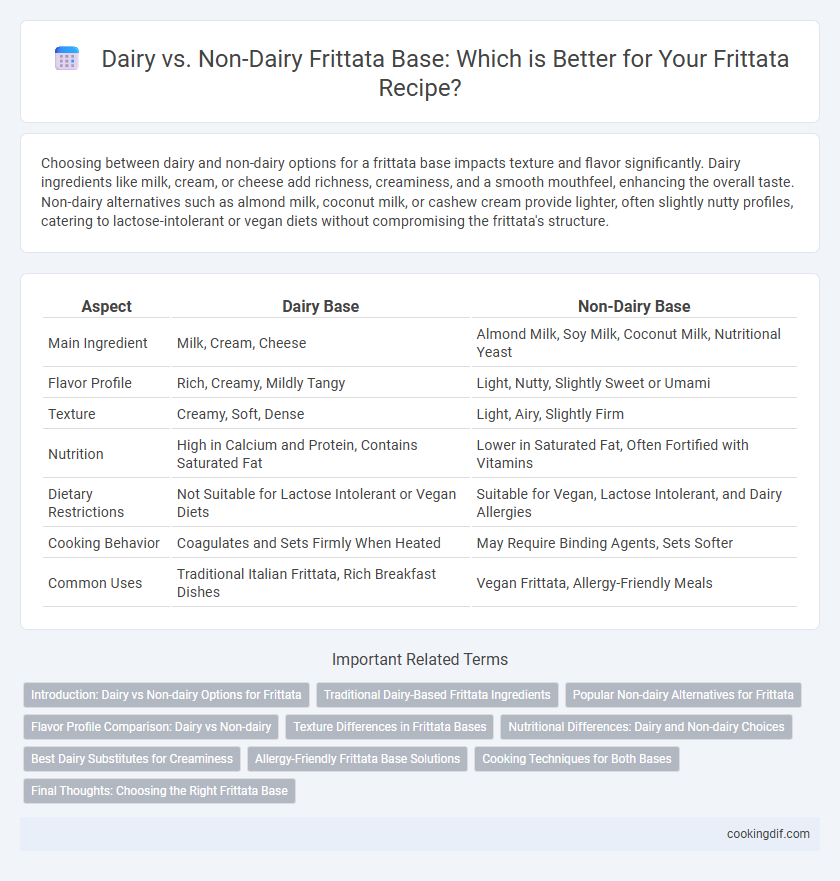
Choosing between dairy and non-dairy options for a frittata base impacts texture and flavor significantly. Dairy ingredients like milk, cream, or cheese add richness, creaminess, and a smooth mouthfeel, enhancing the overall taste. Non-dairy alternatives such as almond milk, coconut milk, or cashew cream provide lighter, often slightly nutty profiles, catering to lactose-intolerant or vegan diets without compromising the frittata's structure.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Dairy Base | Non-Dairy Base |
|---|---|---|
| Main Ingredient | Milk, Cream, Cheese | Almond Milk, Soy Milk, Coconut Milk, Nutritional Yeast |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, Creamy, Mildly Tangy | Light, Nutty, Slightly Sweet or Umami |
| Texture | Creamy, Soft, Dense | Light, Airy, Slightly Firm |
| Nutrition | High in Calcium and Protein, Contains Saturated Fat | Lower in Saturated Fat, Often Fortified with Vitamins |
| Dietary Restrictions | Not Suitable for Lactose Intolerant or Vegan Diets | Suitable for Vegan, Lactose Intolerant, and Dairy Allergies |
| Cooking Behavior | Coagulates and Sets Firmly When Heated | May Require Binding Agents, Sets Softer |
| Common Uses | Traditional Italian Frittata, Rich Breakfast Dishes | Vegan Frittata, Allergy-Friendly Meals |
Introduction: Dairy vs Non-dairy Options for Frittata
Selecting between dairy and non-dairy bases for frittatas significantly influences texture and flavor profiles. Dairy options like milk, cream, or cheese provide richness and creaminess, contributing to a smooth and velvety consistency. Non-dairy alternatives such as almond milk, coconut milk, or soy milk offer lactose-free choices that can create lighter or subtly nutty undertones while accommodating dietary restrictions.
Traditional Dairy-Based Frittata Ingredients
Traditional dairy-based frittata ingredients primarily include whole milk, heavy cream, or full-fat ricotta, which contribute to a rich, creamy texture and enhanced flavor profile. These dairy components help achieve a smooth, custard-like consistency when combined with beaten eggs and baked, distinguishing the frittata from other egg dishes. The use of high-fat dairy products balances the savory fillings and promotes a tender, moist interior, essential for an authentic Italian frittata experience.
Popular Non-dairy Alternatives for Frittata
Popular non-dairy alternatives for a frittata base include almond milk, coconut milk, and cashew cream, each providing a creamy texture without the lactose. These plant-based options maintain moisture and flavor while accommodating vegan or lactose-intolerant diets. Nutritional yeast often enhances the savory profile, mimicking the richness of dairy-based frittatas.
Flavor Profile Comparison: Dairy vs Non-dairy
Dairy-based frittatas deliver a rich, creamy texture with a subtle tang from ingredients like cheese or milk, enhancing the overall savory depth. Non-dairy alternatives, such as almond or oat milk, contribute a lighter, often slightly nutty or sweet undertone, which can brighten the flavor profile without overpowering. The choice between dairy and non-dairy bases significantly influences the mouthfeel and aroma, tailoring the frittata experience to dietary preferences and desired taste nuances.
Texture Differences in Frittata Bases
Using dairy such as milk, cream, or cheese in a frittata base creates a rich, creamy texture that enhances the softness and moisture of the dish. Non-dairy alternatives like almond milk or coconut milk produce a lighter, slightly firmer texture, often resulting in a less creamy but more delicate frittata. The choice between dairy and non-dairy influences both the mouthfeel and the final consistency, with dairy contributing to a smooth, custard-like interior while non-dairy options yield a drier, more set structure.
Nutritional Differences: Dairy and Non-dairy Choices
Dairy-based frittatas typically offer higher protein and calcium content due to ingredients like milk, cheese, and cream, which also contribute to a richer texture and flavor profile. Non-dairy alternatives such as almond milk, coconut milk, or cashew cream provide lower saturated fat and fewer calories, making them suitable for lactose-intolerant individuals or those seeking plant-based options. Both choices impact the nutritional profile, with dairy enriching vitamin D and riboflavin levels, while non-dairy versions often provide added vitamins from fortified plant milks.
Best Dairy Substitutes for Creaminess
Using dairy alternatives like coconut cream, cashew cream, or almond milk enhances frittata creaminess while catering to lactose intolerance or vegan diets. Coconut cream provides a rich texture and subtle sweetness, closely mimicking heavy cream's mouthfeel. Cashew cream offers a smooth, neutral flavor that blends seamlessly with eggs, while almond milk adds lightness without overpowering the dish.
Allergy-Friendly Frittata Base Solutions
Choosing a non-dairy base like almond milk or coconut milk ensures an allergy-friendly frittata suitable for lactose-intolerant or dairy-allergic individuals. Nutrient-rich options such as cashew cream or tofu blends enhance texture while maintaining protein content without traditional dairy. These alternatives provide versatile, inclusive solutions for crafting delicious frittatas that accommodate diverse dietary needs.
Cooking Techniques for Both Bases
Using dairy products such as milk, cream, or cheese in a frittata base results in a richer, creamier texture that firms up smoothly during baking or stovetop cooking. Non-dairy alternatives like almond milk, coconut milk, or cashew cream require careful heat management to prevent curdling and often benefit from lower cooking temperatures and slower heat application to ensure even setting. Mastery of these techniques ensures the frittata holds together with a tender crumb regardless of the chosen dairy or non-dairy base.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Frittata Base
Selecting the right frittata base depends on dietary preferences and desired texture, with dairy options like milk or cream providing a rich, creamy consistency, while non-dairy alternatives such as almond or oat milk offer a lighter, vegan-friendly result. Dairy enriches flavor and helps achieve a fluffy texture, whereas non-dairy bases cater to lactose intolerance and plant-based diets without compromising moisture. Balancing taste, dietary needs, and texture ensures a perfect frittata tailored to individual preferences.
Dairy vs Non-dairy for frittata base Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com