Dairy-based ingredients like cream or whole milk enhance frittata creaminess, creating a rich and velvety texture. Non-dairy alternatives such as coconut milk or cashew cream offer a similar smoothness while catering to lactose intolerance or vegan preferences. Choosing the right option depends on dietary needs and desired flavor profiles without compromising the frittata's creamy consistency.
Table of Comparison
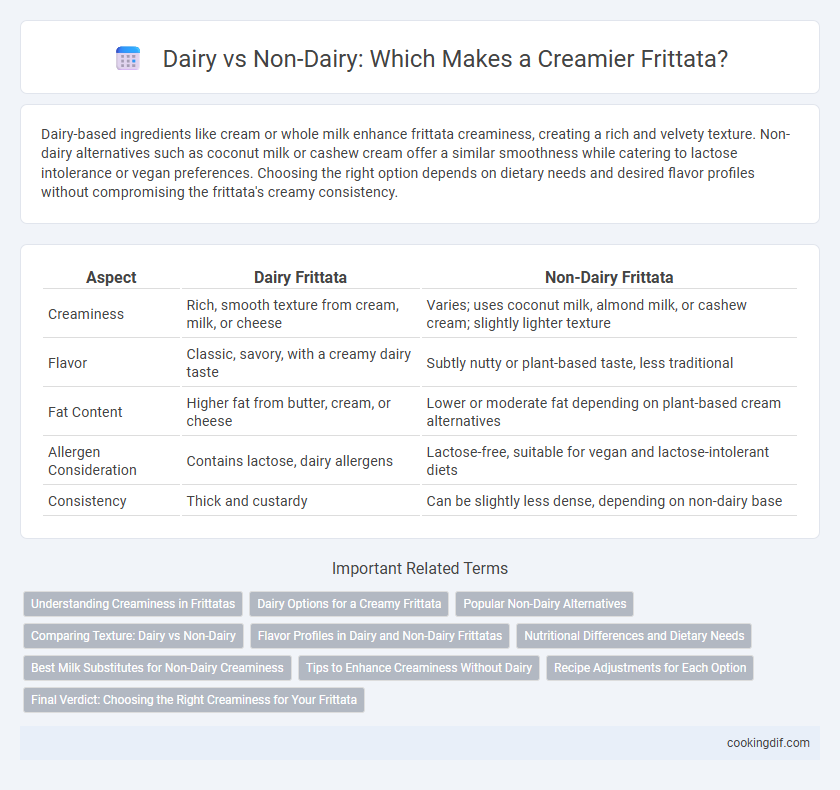
| Aspect | Dairy Frittata | Non-Dairy Frittata |
|---|---|---|
| Creaminess | Rich, smooth texture from cream, milk, or cheese | Varies; uses coconut milk, almond milk, or cashew cream; slightly lighter texture |
| Flavor | Classic, savory, with a creamy dairy taste | Subtly nutty or plant-based taste, less traditional |
| Fat Content | Higher fat from butter, cream, or cheese | Lower or moderate fat depending on plant-based cream alternatives |
| Allergen Consideration | Contains lactose, dairy allergens | Lactose-free, suitable for vegan and lactose-intolerant diets |
| Consistency | Thick and custardy | Can be slightly less dense, depending on non-dairy base |
Understanding Creaminess in Frittatas
Creaminess in frittatas depends largely on the choice between dairy and non-dairy ingredients, where dairy options like heavy cream and whole milk contribute rich fats that enhance smooth texture and mouthfeel. Non-dairy alternatives such as coconut milk or cashew cream provide a creamy consistency while catering to lactose intolerance and vegan preferences, though they may impart distinct flavors or lighter textures. Balancing fat content and moisture is crucial regardless of the type, as it directly influences the frittata's tenderness and overall flavor depth.
Dairy Options for a Creamy Frittata
Dairy options like whole milk, heavy cream, and cream cheese significantly enhance the creaminess of a frittata by adding rich fats and smooth textures. Using heavy cream or half-and-half results in a velvety consistency, while cream cheese imparts a tangy, luscious mouthfeel. Incorporating these dairy ingredients balances the egg mixture, ensuring a creamy and decadent frittata.
Popular Non-Dairy Alternatives
Popular non-dairy alternatives for achieving creaminess in frittatas include coconut milk, almond milk, and cashew cream, each providing distinct textures and subtle flavors. Coconut milk adds a rich, silky texture, while almond milk offers a lighter, nutty undertone without overpowering the dish. Cashew cream is favored for its thickness and smoothness, closely mimicking the creamy consistency of traditional dairy cream in frittatas.
Comparing Texture: Dairy vs Non-Dairy
Dairy creams such as heavy cream and whole milk provide a rich, velvety texture that enhances the frittata's softness and moisture retention, creating a luscious mouthfeel. Non-dairy alternatives like coconut milk or almond milk offer a lighter texture and can introduce subtle nutty or sweet notes, though they may yield a slightly less creamy consistency. Choosing between dairy and non-dairy influences the frittata's overall creaminess and density, impacting the dish's moisture balance and flavor depth.
Flavor Profiles in Dairy and Non-Dairy Frittatas
Dairy-based frittatas typically offer a rich, creamy texture with a slightly tangy flavor from ingredients like heavy cream or cheese, enhancing the overall taste complexity. Non-dairy alternatives, such as coconut milk or cashew cream, provide a smoother, subtler creaminess with unique nutty or sweet undertones that complement plant-based ingredients. Choosing between dairy and non-dairy influences not only the frittata's mouthfeel but also its flavor profile, catering to diverse dietary preferences and culinary styles.
Nutritional Differences and Dietary Needs
Dairy-based creamers in frittatas, such as whole milk or heavy cream, offer higher levels of calcium, vitamin D, and protein, which support bone health and muscle maintenance. Non-dairy alternatives like almond, soy, or oat milk provide varied nutritional profiles, often lower in saturated fat and calories, catering to lactose-intolerant or vegan diets while sometimes lacking comparable amounts of calcium and protein without fortification. Choosing between dairy and non-dairy creamers depends on individual dietary restrictions, nutritional goals, and preferences for plant-based or traditional animal-derived ingredients.
Best Milk Substitutes for Non-Dairy Creaminess
Almond milk, cashew milk, and oat milk serve as excellent dairy-free alternatives to achieve a creamy texture in frittatas, with oat milk providing a naturally sweet and creamy profile comparable to traditional dairy. Coconut milk adds richness and depth, particularly suited for savory frittata variations, while soy milk offers a neutral flavor and high protein content that enhances the dish's structure. Blending non-dairy milks with a small amount of nutritional yeast or soaked cashews can further improve creaminess, creating a satisfying and textured frittata without relying on dairy products.
Tips to Enhance Creaminess Without Dairy
Using aquafaba or blended silken tofu can replicate the creamy texture in a frittata without dairy. Incorporating mashed avocado or a splash of coconut milk adds richness and moistness, enhancing overall creaminess. Nutritional yeast also boosts flavor while maintaining a smooth consistency.
Recipe Adjustments for Each Option
Using dairy products like heavy cream or whole milk enhances frittata creaminess through rich fats and smooth texture, allowing for a more custard-like consistency and easier seasoning adjustments. Non-dairy alternatives such as almond, soy, or oat milk require careful selection to maintain moisture without sacrificing flavor, often necessitating added nutritional yeast or plant-based cream to achieve similar richness. Adjusting cooking time and whisking technique helps balance the moisture levels for both dairy and non-dairy options, ensuring a perfectly creamy frittata.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Creaminess for Your Frittata
Dairy options like heavy cream or whole milk provide a rich, velvety texture that enhances the classic frittata's creaminess and depth of flavor. Non-dairy alternatives such as coconut milk, almond milk, or cashew cream offer a lighter, dairy-free creaminess suitable for vegan or lactose-intolerant diets without sacrificing moisture. The final verdict depends on dietary preferences and desired texture, with dairy delivering traditional silkiness and non-dairy creating a subtle, wholesome creaminess that complements various flavor profiles.
Dairy vs Non-dairy for Frittata creaminess Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com