Peanut oil offers a higher smoke point than most vegetable oils, making it ideal for high-heat stir-frying without burning or smoking. Its slightly nutty flavor enhances the overall taste of stir-fry dishes, adding depth and richness. Vegetable oils, such as canola or soybean oil, tend to have a more neutral flavor but may have lower smoke points, which can affect cooking performance and taste.
Table of Comparison
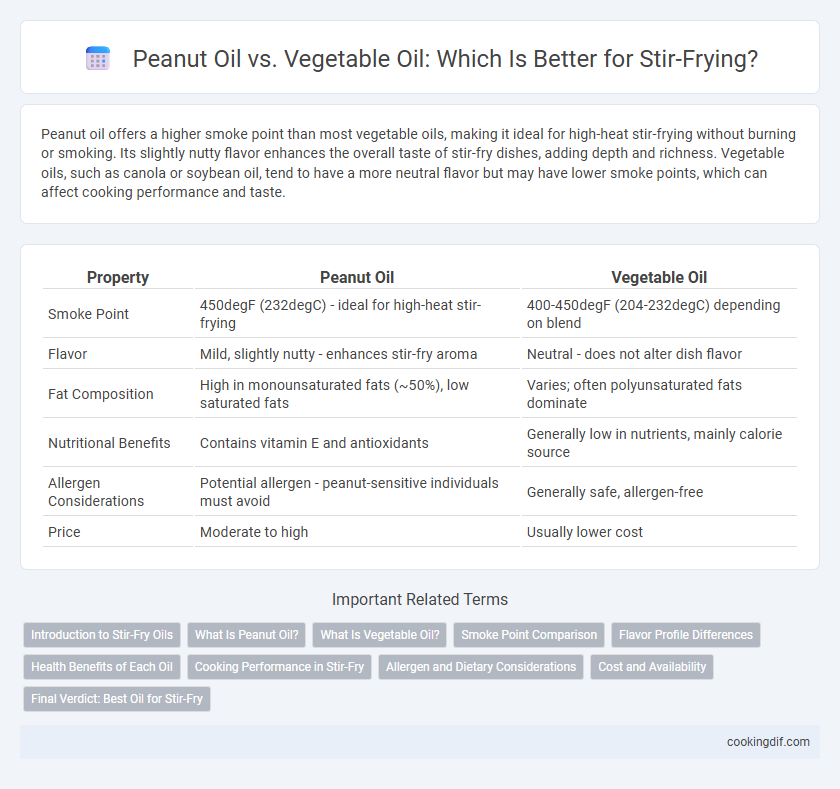
| Property | Peanut Oil | Vegetable Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Smoke Point | 450degF (232degC) - ideal for high-heat stir-frying | 400-450degF (204-232degC) depending on blend |
| Flavor | Mild, slightly nutty - enhances stir-fry aroma | Neutral - does not alter dish flavor |
| Fat Composition | High in monounsaturated fats (~50%), low saturated fats | Varies; often polyunsaturated fats dominate |
| Nutritional Benefits | Contains vitamin E and antioxidants | Generally low in nutrients, mainly calorie source |
| Allergen Considerations | Potential allergen - peanut-sensitive individuals must avoid | Generally safe, allergen-free |
| Price | Moderate to high | Usually lower cost |
Introduction to Stir-Fry Oils
Peanut oil offers a high smoke point of about 450degF, making it ideal for high-heat stir-fry cooking that preserves food flavor and texture. Vegetable oil, with a slightly lower smoke point around 400degF, provides a neutral taste and versatility for various stir-fry dishes. Both oils supply healthy fats, but peanut oil's stable fatty acid profile enhances browning and crispiness in stir-fried meals.
What Is Peanut Oil?
Peanut oil, extracted from peanuts, is a popular cooking oil known for its high smoke point of approximately 450degF (232degC), making it ideal for stir-frying at high temperatures without breaking down. It offers a mild, slightly nutty flavor that enhances the taste of stir-fried dishes while providing heart-healthy monounsaturated fats and antioxidants. Compared to vegetable oils, peanut oil has better stability under heat and a more distinctive flavor profile, contributing to both the texture and aroma of stir-fry meals.
What Is Vegetable Oil?
Vegetable oil is a generic term for oils extracted from various plant sources such as soybeans, corn, sunflower seeds, and canola, commonly used for cooking due to its neutral flavor and high smoke point. Peanut oil is a specific type of vegetable oil derived from peanuts, prized in stir-fry for its slightly nutty flavor and similar high smoke point, which can enhance the dish's taste and cooking performance. Choosing between peanut oil and generic vegetable oil depends on flavor preference and allergen considerations, with both oils offering suitable heat stability for stir-frying.
Smoke Point Comparison
Peanut oil has a high smoke point of around 450degF (232degC), making it ideal for stir-frying at high temperatures without burning or producing harmful compounds. Vegetable oil typically has a lower smoke point, averaging between 400degF (204degC) and 420degF (216degC), which may limit its use in intense stir-fry cooking. Choosing peanut oil ensures better heat tolerance and preserves flavor during quick, high-heat stir-fry methods.
Flavor Profile Differences
Peanut oil delivers a rich, nutty flavor that enhances the depth of stir-fried dishes, making it ideal for Asian-inspired recipes. Vegetable oil has a more neutral taste, allowing the natural flavors of ingredients to shine without overpowering the dish. Choosing peanut oil brings a distinctive aroma and subtle complexity, while vegetable oil offers versatility and a lighter taste profile.
Health Benefits of Each Oil
Peanut oil offers a high smoking point and contains heart-healthy monounsaturated fats along with vitamin E antioxidants, supporting cardiovascular health and reducing inflammation. Vegetable oil, typically a blend of soybean, corn, or sunflower oils, provides a balance of polyunsaturated fats rich in omega-6 fatty acids, which promote brain function and cell growth but should be consumed in moderation. Selecting peanut oil for stir-frying helps maintain nutrient integrity at high heat, while vegetable oil can be beneficial for its essential fatty acids when used at moderate temperatures.
Cooking Performance in Stir-Fry
Peanut oil offers a high smoke point around 450degF, making it ideal for high-heat stir-fry cooking as it maintains stability and resists oxidation better than most vegetable oils. Vegetable oil, often a blend of soybean, corn, and canola oils, typically has a lower smoke point near 400degF, which can lead to faster breakdown and off-flavors in intense stir-fry heat. The choice influences flavor profile and cooking efficiency, with peanut oil providing a nuttier taste and superior performance for crispy, evenly cooked stir-fry dishes.
Allergen and Dietary Considerations
Peanut oil, commonly used in stir-fry, is a potential allergen that can trigger severe reactions for individuals with peanut allergies, making vegetable oil a safer alternative for allergen-sensitive diets. Vegetable oils such as canola, soybean, or sunflower typically have a neutral taste and lower allergenic risk, appealing to a broader range of dietary needs. For those with nut allergies or seeking hypoallergenic options, choosing vegetable oil for stir-fry reduces the risk of allergic reactions while maintaining high smoke points for optimal cooking performance.
Cost and Availability
Peanut oil generally commands a higher price than vegetable oil due to its specialized extraction process and limited supply, making it less cost-effective for everyday stir-fry cooking. Vegetable oil, widely available and produced from multiple sources like soybean, corn, and sunflower, offers a more budget-friendly and accessible fat option for most households. Its consistent availability across global markets ensures that home cooks can easily maintain their stir-fry routines without frequent restocking issues.
Final Verdict: Best Oil for Stir-Fry
Peanut oil, with its high smoke point around 450degF, offers superior heat stability ideal for stir-frying, preserving flavor without breaking down. Vegetable oil also provides a neutral taste but typically has a lower smoke point near 400degF, making it less optimal for high-heat cooking. For the best stir-fry results, peanut oil is generally preferred due to its heat resilience and subtle nutty flavor that enhances the dish.
Peanut oil vs Vegetable oil for stir-fry fats Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com