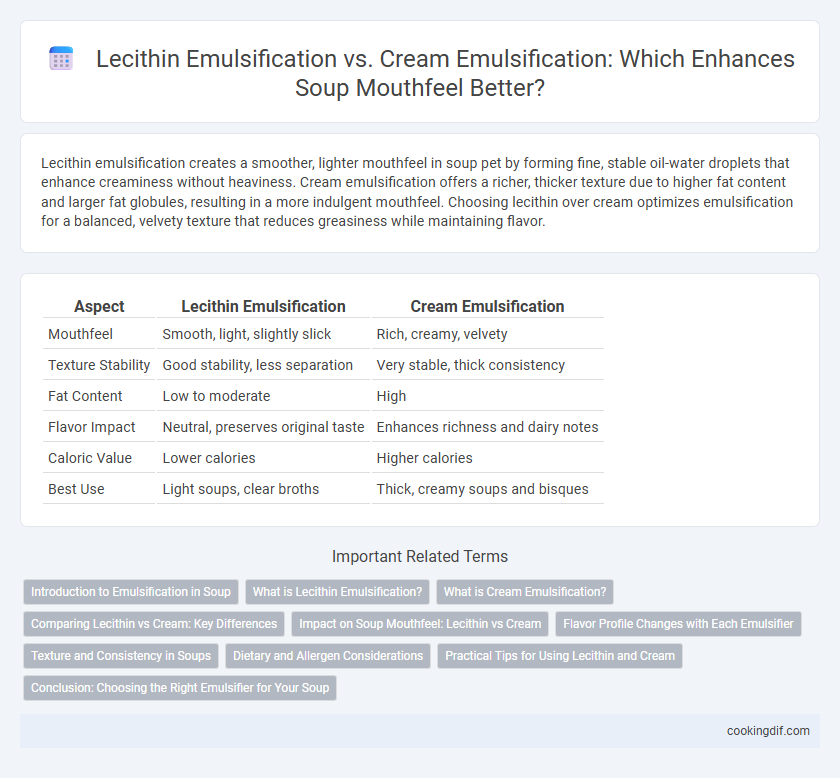
Lecithin emulsification creates a smoother, lighter mouthfeel in soup pet by forming fine, stable oil-water droplets that enhance creaminess without heaviness. Cream emulsification offers a richer, thicker texture due to higher fat content and larger fat globules, resulting in a more indulgent mouthfeel. Choosing lecithin over cream optimizes emulsification for a balanced, velvety texture that reduces greasiness while maintaining flavor.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Lecithin Emulsification | Cream Emulsification |
|---|---|---|
| Mouthfeel | Smooth, light, slightly slick | Rich, creamy, velvety |
| Texture Stability | Good stability, less separation | Very stable, thick consistency |
| Fat Content | Low to moderate | High |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral, preserves original taste | Enhances richness and dairy notes |
| Caloric Value | Lower calories | Higher calories |
| Best Use | Light soups, clear broths | Thick, creamy soups and bisques |
Introduction to Emulsification in Soup
Lecithin emulsification in soup creates a smooth and stable mixture by reducing surface tension between oil and water phases, enhancing mouthfeel through uniform fat dispersion. Cream emulsification relies on milk fat globules that naturally stabilize emulsions, providing a rich, creamy texture and velvety sensation. Both methods influence the soup's consistency and sensory experience, with lecithin offering a lighter, more homogeneous feel compared to the heavier, silkier mouthfeel from cream-based emulsions.
What is Lecithin Emulsification?
Lecithin emulsification involves using lecithin, a natural phospholipid found in soybeans and egg yolks, to stabilize oil and water mixtures in soup, resulting in a smooth and creamy mouthfeel without adding excess fat. Unlike traditional cream emulsification, lecithin forms smaller, more uniform micelles that enhance texture and improve the soup's viscosity and richness while maintaining a lighter profile. This technique optimizes mouthfeel by promoting stable emulsions, reducing separation, and delivering a velvety consistency that enhances flavor release.
What is Cream Emulsification?
Cream emulsification refers to the process of blending fat droplets uniformly into a liquid to create a smooth, rich texture that enhances mouthfeel in soups. This method relies on dairy cream's natural fat content and proteins to stabilize the emulsion, resulting in a velvety, creamy consistency. Compared to lecithin emulsification, which uses soy or egg-based emulsifiers, cream emulsification imparts a fuller, more indulgent sensation ideal for creamy soups.
Comparing Lecithin vs Cream: Key Differences
Lecithin emulsification provides a smooth, lightweight mouthfeel by stabilizing fat and water molecules at a molecular level, resulting in a more uniform texture without heaviness. Cream emulsification contributes to a richer, fuller mouthfeel due to its natural fat content and higher viscosity, which enhances the soup's creaminess and body. Key differences include lecithin's ability to create a cleaner, less oily texture while cream imparts a denser, more indulgent sensation on the palate.
Impact on Soup Mouthfeel: Lecithin vs Cream
Lecithin enhances soup mouthfeel by creating a smooth, velvety texture through effective emulsification of fats and water, resulting in a lighter and less greasy sensation compared to cream. Cream emulsification imparts a rich, creamy mouthfeel due to its higher fat content, adding thickness and a luxurious coating sensation on the palate. The choice between lecithin and cream significantly influences the soup's sensory profile, balancing between lightness and richness to suit different flavor and texture preferences.
Flavor Profile Changes with Each Emulsifier
Lecithin emulsification in soup enhances creaminess while preserving the natural flavors of ingredients, resulting in a smoother, more balanced mouthfeel with subtle nutty undertones. Cream emulsification contributes to a richer, heavier texture, intensifying dairy notes and creating a more indulgent flavor profile. Each emulsifier uniquely modifies the soup's taste and texture, influencing overall flavor depth and mouth coating characteristics.
Texture and Consistency in Soups
Lecithin emulsification in soups creates a smooth, uniform texture by stabilizing fat droplets at the molecular level, enhancing creaminess without heaviness. Cream emulsification relies on fat globules and proteins to produce a rich, velvety mouthfeel but can result in a thicker, sometimes heavier consistency. The choice between lecithin and cream emulsification significantly impacts soup texture, with lecithin offering lighter, more stable emulsions and cream providing a fuller, denser body.
Dietary and Allergen Considerations
Lecithin emulsification enhances soup mouthfeel by creating a smooth, stable texture while being naturally derived from soy or sunflower, catering to vegan and allergen-sensitive diets. Cream emulsification provides a rich, creamy mouthfeel but introduces dairy allergens and higher saturated fat content, limiting suitability for lactose-intolerant or vegan consumers. Opting for lecithin emulsification supports inclusive dietary preferences and allergen management without compromising mouthfeel quality in soups.
Practical Tips for Using Lecithin and Cream
Lecithin emulsification enhances soup mouthfeel by creating a smooth, consistent texture with fine oil dispersion, ideal for lighter, low-fat soups. Cream emulsification contributes to a richer, velvety mouthfeel, adding body and a luxurious mouth-coating effect perfect for hearty, creamy soups. Practical tips include slowly blending lecithin into warm soup to prevent graininess and whisking cream in at the end to avoid curdling and maintain silky texture.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Emulsifier for Your Soup
Lecithin emulsification enhances mouthfeel by creating a smooth, velvety texture through stable oil-in-water emulsions, ideal for clear and light soups. Cream emulsification offers a richer, creamier mouthfeel by incorporating fat globules that add body and a luxurious finish, best suited for thicker, hearty soups. Selecting lecithin or cream depends on the desired texture and richness, balancing the soup's flavor profile with the appropriate emulsifier to achieve the optimal sensory experience.
Lecithin emulsification vs Cream emulsification for mouthfeel Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com