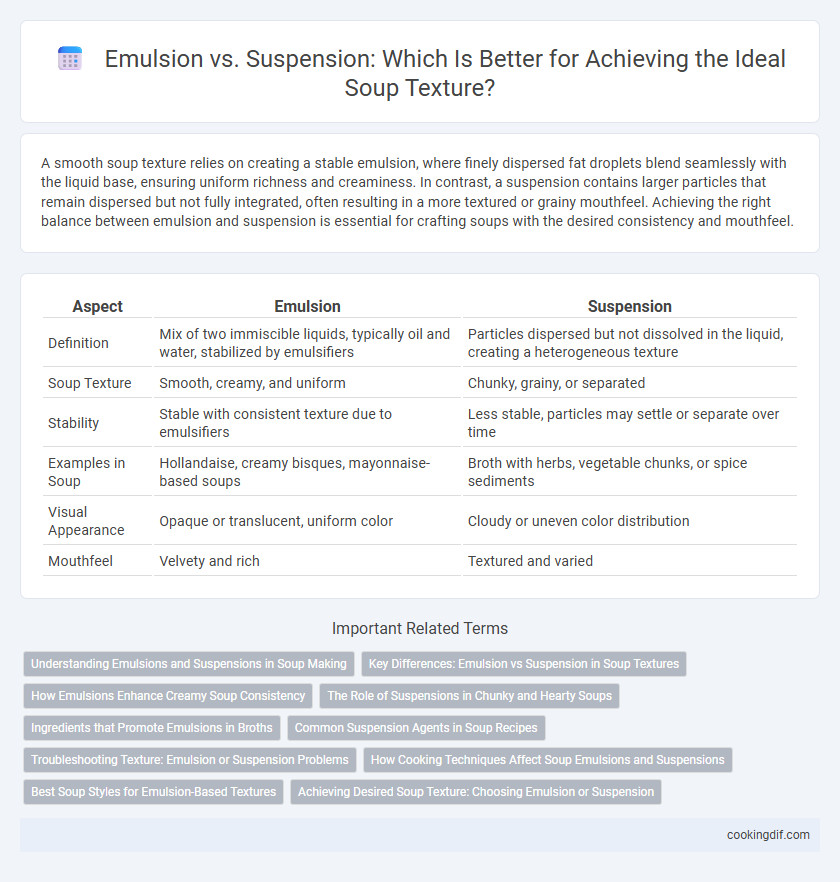
A smooth soup texture relies on creating a stable emulsion, where finely dispersed fat droplets blend seamlessly with the liquid base, ensuring uniform richness and creaminess. In contrast, a suspension contains larger particles that remain dispersed but not fully integrated, often resulting in a more textured or grainy mouthfeel. Achieving the right balance between emulsion and suspension is essential for crafting soups with the desired consistency and mouthfeel.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Emulsion | Suspension |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mix of two immiscible liquids, typically oil and water, stabilized by emulsifiers | Particles dispersed but not dissolved in the liquid, creating a heterogeneous texture |
| Soup Texture | Smooth, creamy, and uniform | Chunky, grainy, or separated |
| Stability | Stable with consistent texture due to emulsifiers | Less stable, particles may settle or separate over time |
| Examples in Soup | Hollandaise, creamy bisques, mayonnaise-based soups | Broth with herbs, vegetable chunks, or spice sediments |
| Visual Appearance | Opaque or translucent, uniform color | Cloudy or uneven color distribution |
| Mouthfeel | Velvety and rich | Textured and varied |
Understanding Emulsions and Suspensions in Soup Making
Emulsions in soup involve blending two immiscible liquids like oil and water into a stable mixture, creating a smooth, creamy texture essential in creamy soups and vinaigrettes. Suspensions occur when solid particles, such as herbs or spices, are dispersed throughout the liquid but remain visibly distinct, contributing to a textured and hearty mouthfeel typical in chunky vegetable or lentil soups. Understanding the science behind emulsions and suspensions helps chefs control soup consistency, enhancing flavor release and overall sensory experience.
Key Differences: Emulsion vs Suspension in Soup Textures
Emulsions in soup consist of finely dispersed fat droplets within a water-based broth, creating a smooth, creamy texture commonly seen in creamy bisques or chowders. Suspensions contain larger solid particles like vegetable chunks or herbs suspended in the liquid, resulting in a chunkier, more textured mouthfeel typical of minestrone or vegetable soup. The key difference lies in particle size and stability, where emulsions offer a uniform mixture and suspension provides visible, separate ingredients.
How Emulsions Enhance Creamy Soup Consistency
Emulsions improve creamy soup texture by evenly dispersing fat droplets into water, creating a smooth and stable blend that resists separation. This microscopic integration of oil and water phases enhances mouthfeel, giving soups a rich, velvety consistency often sought in bisques and cream-based recipes. Emulsifying agents like lecithin or mustard act as stabilizers, ensuring uniform texture and preventing curdling during heating.
The Role of Suspensions in Chunky and Hearty Soups
Suspensions play a crucial role in creating chunky and hearty soups by evenly dispersing solid particles such as vegetables, meat, or grains throughout the broth. This texture contrast enhances the sensory experience and provides a satisfying mouthfeel distinct from the smooth consistency achieved by emulsions. Maintaining a stable suspension prevents ingredient settling, ensuring each spoonful delivers robust chunks and rich flavor.
Ingredients that Promote Emulsions in Broths
Ingredients like egg yolks, mustard, and lecithin-rich foods such as soy or sunflower seeds promote emulsions in broths by stabilizing oil and water mixtures, resulting in a smooth, creamy texture. Emulsifiers reduce surface tension, preventing separation and enhancing the soup's mouthfeel and appearance. Using these natural emulsifiers creates rich, velvety soups without the need for added thickeners or stabilizers.
Common Suspension Agents in Soup Recipes
Common suspension agents in soup recipes include starches such as cornstarch and flour, which help maintain a uniform texture by preventing ingredient separation. Hydrocolloids like xanthan gum and guar gum are also frequently used to stabilize emulsions and disperse particles evenly throughout the broth. These agents improve mouthfeel and consistency, ensuring a smooth and appealing soup texture.
Troubleshooting Texture: Emulsion or Suspension Problems
Troubleshooting texture issues in soup often involves differentiating between emulsion and suspension problems. An emulsion failure results in separation of oil and water phases, causing oily patches and uneven mouthfeel, while suspension problems lead to settling or clumping of solids, resulting in a grainy or watery texture. Stabilizing agents like lecithin for emulsions and proper agitation or hydrocolloids for suspensions can restore a smooth, consistent soup texture.
How Cooking Techniques Affect Soup Emulsions and Suspensions
Cooking techniques significantly influence soup texture by altering the properties of emulsions and suspensions; vigorous blending creates stable emulsions by evenly dispersing fat droplets within a liquid base, resulting in smooth, creamy soups. Conversely, gentle simmering without agitation maintains suspensions, where solid particles remain dispersed but separate over time, producing soups with chunkier textures and visible ingredient layers. Proper temperature control and stirring intensity are essential to achieving the desired balance between emulsion stability and suspension clarity in various soup recipes.
Best Soup Styles for Emulsion-Based Textures
Emulsion-based soup textures, characterized by smooth, creamy consistency without separation, excel in styles like bisques, cream soups, and veloutes, where finely blended fats and liquids create a stable mixture. Techniques involving vigorous blending and the use of emulsifiers such as egg yolk or cream ensure homogeneity and richness, enhancing mouthfeel and flavor integration. These soups benefit from the controlled distribution of fat droplets, which stabilizes the emulsion and delivers satisfying, silky textures preferred in gourmet and classic French cuisine.
Achieving Desired Soup Texture: Choosing Emulsion or Suspension
Achieving the desired soup texture depends on choosing between emulsion and suspension techniques. Emulsions create a smooth, creamy texture by blending two immiscible liquids, such as oil and water, stabilized by emulsifiers like lecithin or mustard. Suspensions maintain solid particles evenly distributed in the liquid, resulting in a chunkier, more textured soup experience.
Emulsion vs Suspension for soup texture Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com