Single cream offers a lighter texture for puddings, creating a smooth but less rich consistency that allows the dessert's flavors to shine without overwhelming creaminess. Double cream, with its higher fat content, produces a thicker, indulgent texture that enhances the pudding's richness and provides a velvety mouthfeel. Choosing between single and double cream depends on whether a lighter or more decadent pudding experience is desired.
Table of Comparison
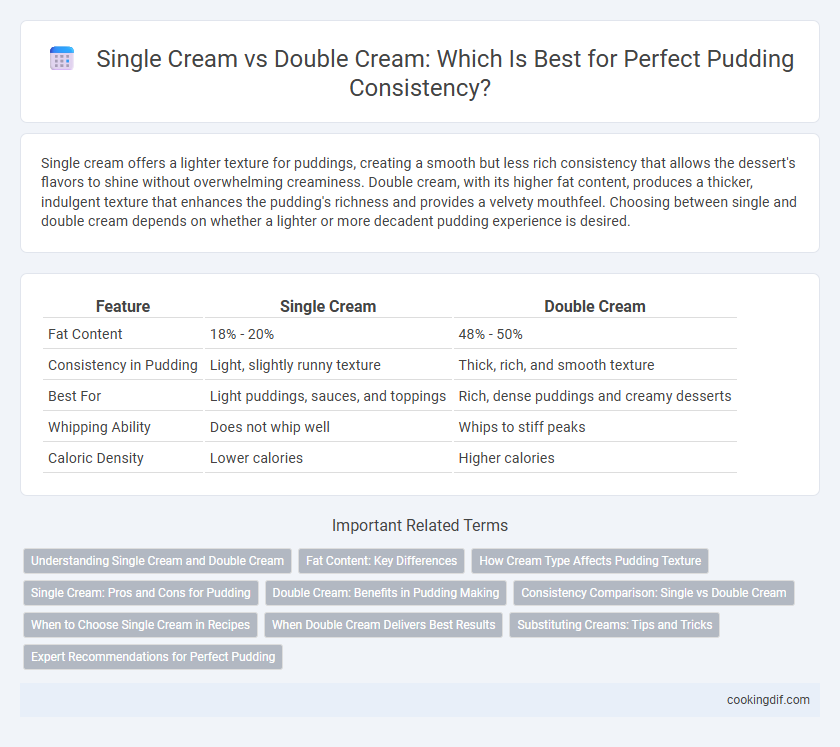
| Feature | Single Cream | Double Cream |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | 18% - 20% | 48% - 50% |
| Consistency in Pudding | Light, slightly runny texture | Thick, rich, and smooth texture |
| Best For | Light puddings, sauces, and toppings | Rich, dense puddings and creamy desserts |
| Whipping Ability | Does not whip well | Whips to stiff peaks |
| Caloric Density | Lower calories | Higher calories |
Understanding Single Cream and Double Cream
Single cream contains around 18-20% fat, providing a lighter, smoother texture in puddings without overwhelming richness. Double cream, with approximately 48% fat, delivers a thicker, richer consistency that enhances the pudding's creaminess and adds indulgence. Choosing between single and double cream affects the pudding's mouthfeel and richness, depending on the desired final texture and flavor intensity.
Fat Content: Key Differences
Single cream typically contains 18-20% fat, resulting in a lighter, thinner texture that adds creaminess without overwhelming pudding's consistency. Double cream has a higher fat content of about 48%, providing a rich, indulgent thickness that enhances pudding's smoothness and body. Selecting between single and double cream depends on the desired creaminess and richness, with double cream offering a denser, more luxurious mouthfeel.
How Cream Type Affects Pudding Texture
Single cream, with its lower fat content of around 18%, produces a lighter, more fluid pudding texture that is less rich and less stable when heated. Double cream contains approximately 48% fat, resulting in a thicker, creamier pudding with a velvety consistency that holds its shape better and adds a luxurious mouthfeel. The higher fat concentration in double cream enhances the pudding's smoothness and richness, making it ideal for recipes requiring a dense, indulgent texture.
Single Cream: Pros and Cons for Pudding
Single cream offers a lighter, less rich texture for pudding, making it suitable for those seeking a lower-fat dessert option without compromising smoothness. Its lower fat content means it may not thicken pudding as effectively as double cream, potentially resulting in a thinner consistency. Using single cream can enhance pudding by providing subtle creaminess while maintaining a delicate mouthfeel, but it may require additional thickening agents to achieve the desired firmness.
Double Cream: Benefits in Pudding Making
Double cream enhances pudding with its rich, velvety texture and higher fat content, creating a luxurious mouthfeel and smoother consistency. Its ability to thicken mixtures more effectively than single cream results in a creamier, more indulgent dessert. This richness also helps stabilize the pudding, preventing separation and ensuring a consistently luscious finish.
Consistency Comparison: Single vs Double Cream
Single cream has a thinner consistency with about 18-20% fat, making pudding lighter and less rich, while double cream contains around 48% fat, resulting in a thicker, creamier texture that enhances the pudding's indulgence. The higher fat content in double cream allows it to whip up more steadily and hold shape, creating a dense and velvety finish ideal for rich puddings. Choosing between single and double cream significantly affects pudding consistency, with single cream providing a more fluid, delicate mouthfeel and double cream delivering luscious thickness and richness.
When to Choose Single Cream in Recipes
Single cream is ideal for puddings requiring a lighter, less rich texture, enhancing creaminess without overwhelming other flavors. It works well in recipes where the pudding should remain smooth and pourable, such as custards or panna cotta, due to its lower fat content around 18%. Choose single cream when a subtler richness is desired or when cream is mixed with other ingredients that provide thickness or structure.
When Double Cream Delivers Best Results
Double cream delivers the best results for pudding when a rich, velvety texture is desired, as its higher fat content (around 48%) creates a thicker, creamier consistency compared to single cream, which contains about 18% fat. Using double cream enhances the smoothness and stability of puddings, especially in recipes like custards or mousse where a luxurious mouthfeel is key. For optimal consistency and indulgence, double cream provides the ideal balance of richness and body that single cream cannot match.
Substituting Creams: Tips and Tricks
Single cream has a lower fat content, around 18-20%, resulting in a thinner, less rich pudding consistency, making it suitable for lighter desserts. Double cream, containing 48% fat or more, creates a thicker, creamier texture ideal for indulgent puddings, but can be substituted by combining single cream with a small amount of butter to mimic richness. Whisking single cream gently to incorporate air or adding a thickening agent like cornflour can also enhance its consistency for pudding recipes.
Expert Recommendations for Perfect Pudding
Expert recommendations for perfect pudding emphasize using double cream over single cream due to its higher fat content, around 48%, which creates a richer, thicker texture essential for a velvety finish. Single cream, with approximately 18% fat, results in a lighter, runnier pudding consistency that may not hold its shape as well. Culinary experts suggest double cream enhances the mouthfeel and stability, ensuring a smooth, indulgent pudding that maintains its structure when chilled.
Single Cream vs Double Cream for pudding consistency Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com