Dairy milk offers a rich, creamy texture and natural sweetness that enhances the smoothness of pudding, providing a traditional flavor profile. Plant-based milk alternatives, such as almond, oat, or coconut milk, deliver diverse flavors and cater to lactose intolerance or vegan preferences while sometimes requiring thickeners to achieve the desired consistency. Choosing between dairy and plant-based milk affects the pudding's taste, texture, and nutritional content, making it essential to select based on dietary needs and flavor preferences.
Table of Comparison
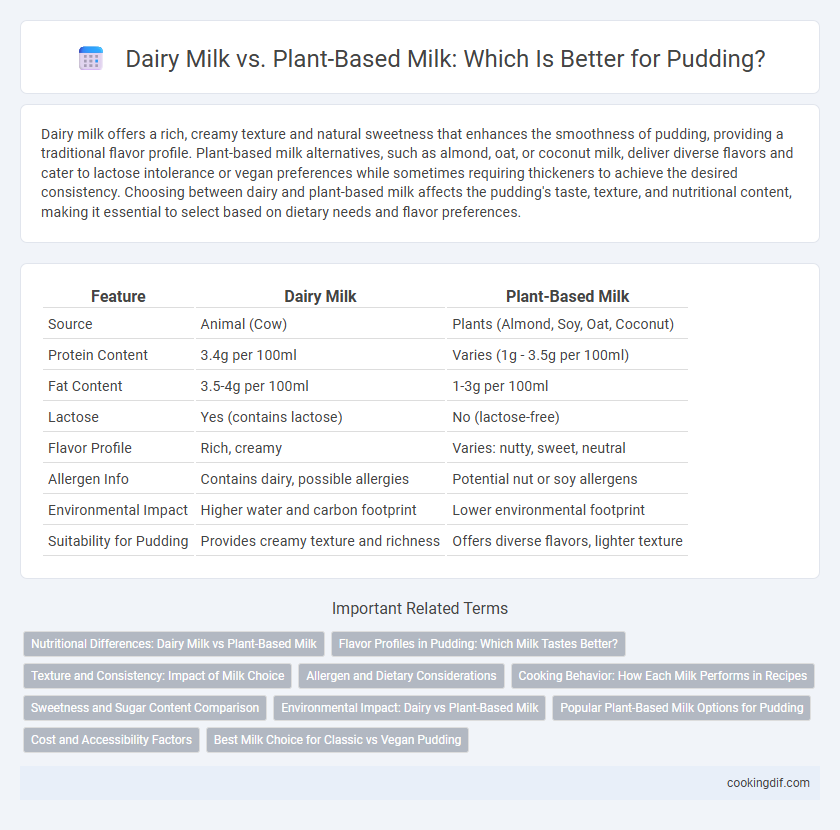
| Feature | Dairy Milk | Plant-Based Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Animal (Cow) | Plants (Almond, Soy, Oat, Coconut) |
| Protein Content | 3.4g per 100ml | Varies (1g - 3.5g per 100ml) |
| Fat Content | 3.5-4g per 100ml | 1-3g per 100ml |
| Lactose | Yes (contains lactose) | No (lactose-free) |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, creamy | Varies: nutty, sweet, neutral |
| Allergen Info | Contains dairy, possible allergies | Potential nut or soy allergens |
| Environmental Impact | Higher water and carbon footprint | Lower environmental footprint |
| Suitability for Pudding | Provides creamy texture and richness | Offers diverse flavors, lighter texture |
Nutritional Differences: Dairy Milk vs Plant-Based Milk
Dairy milk provides higher levels of protein, calcium, and vitamin B12 compared to most plant-based milks, which often lack these nutrients unless fortified. Plant-based milks such as almond, soy, and oat varieties typically contain fewer calories and less saturated fat, benefiting those seeking lower fat intake. Nutritional profiles vary widely among plant-based options, with soy milk offering protein content closest to dairy, while almond and rice milks are usually lower in protein and enriched with vitamins D and B12.
Flavor Profiles in Pudding: Which Milk Tastes Better?
Dairy milk offers a rich, creamy texture with naturally sweet and buttery flavor notes that enhance traditional pudding recipes, creating a smooth, indulgent taste experience. Plant-based milks such as almond, coconut, or oat provide diverse flavor profiles ranging from nutty and earthy to subtly sweet, which can add unique layers without overpowering the pudding's base. The choice between dairy and plant-based milk for pudding ultimately depends on desired flavor intensity and dietary preferences, with dairy milk favored for classic creaminess and plant-based milks praised for their distinctive, health-conscious options.
Texture and Consistency: Impact of Milk Choice
Dairy milk provides a creamy texture and smooth consistency to pudding due to its natural fat and protein content, which helps achieve a rich mouthfeel and stable gel formation. Plant-based milks, such as almond, soy, or oat, often vary in thickness and can produce a thinner or slightly grainy texture depending on their fat and protein levels. Selecting the appropriate milk type directly influences the pudding's final creaminess and firmness, with dairy milk generally delivering a more consistent and luxurious texture.
Allergen and Dietary Considerations
Dairy milk contains lactose and casein, common allergens that can trigger reactions in individuals with lactose intolerance or milk protein allergies, making it unsuitable for those dietary needs. Plant-based milk alternatives like almond, soy, and oat milk provide allergen-friendly options, although soy and nut variants may pose allergy risks for some consumers. Choosing the appropriate base for pudding depends on allergen sensitivity and dietary restrictions, prioritizing hypoallergenic and vegan-friendly ingredients.
Cooking Behavior: How Each Milk Performs in Recipes
Dairy milk offers a rich, creamy texture and consistent protein content that enhances pudding's smoothness and thickening during cooking. Plant-based milks, such as almond or oat, vary widely in fat and protein levels, which can result in a thinner consistency and sometimes require additives like thickeners or emulsifiers to replicate traditional pudding textures. The Maillard reaction and caramelization processes are more pronounced with dairy milk due to its natural sugars and proteins, influencing flavor development in baked or cooked puddings.
Sweetness and Sugar Content Comparison
Dairy milk typically contains 12 grams of natural sugar per cup, contributing to its mildly sweet flavor, while plant-based milks like almond or oat milk often have added sugars ranging from 7 to 15 grams per cup, depending on the brand and variety. The sweetness in dairy milk comes from lactose, a natural sugar, whereas plant-based milks may include sweeteners like cane sugar or agave to enhance flavor. When choosing a pudding base, the sugar content significantly impacts the overall sweetness, making it essential to compare labels for sugar levels to achieve the desired taste and nutritional profile.
Environmental Impact: Dairy vs Plant-Based Milk
Plant-based milk typically has a lower environmental impact compared to dairy milk, requiring significantly less water and land while producing fewer greenhouse gas emissions. Almond, oat, and soy milks generate less carbon dioxide equivalent per liter than traditional cow's milk, making them more sustainable options for pudding bases. Choosing plant-based milk reduces the ecological footprint, supporting efforts to mitigate climate change and resource depletion.
Popular Plant-Based Milk Options for Pudding
Popular plant-based milk options for pudding include almond milk, coconut milk, and oat milk, each offering unique flavors and textures that enhance the dessert's appeal. Almond milk provides a subtle nutty taste and a light, creamy consistency, while coconut milk adds rich creaminess and a tropical twist perfect for indulgent puddings. Oat milk is favored for its naturally sweet flavor and smooth texture, making it an excellent base for dairy-free pudding recipes that maintain a satisfying mouthfeel.
Cost and Accessibility Factors
Dairy milk generally offers lower costs due to established supply chains and widespread production, making it more accessible in most regions compared to plant-based alternatives. Plant-based milks like almond, soy, and oat tend to have higher prices influenced by specialized farming and processing methods, often limiting availability in lower-income markets. Accessibility varies with urban areas providing more plant-based options, while rural locations rely heavily on affordable dairy milk for pudding bases.
Best Milk Choice for Classic vs Vegan Pudding
Dairy milk offers a rich, creamy texture ideal for classic pudding recipes, providing a natural sweetness and strong protein content that enhances thickening and mouthfeel. Plant-based milks like almond, oat, or coconut provide a versatile, lactose-free alternative perfect for vegan puddings, with oat milk favored for its neutral flavor and creamy consistency. Choosing the best milk depends on dietary preferences, with dairy milk excelling in traditional taste and plant-based options supporting vegan and lactose-intolerant diets without compromising texture.
Dairy milk vs Plant-based milk for base Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com