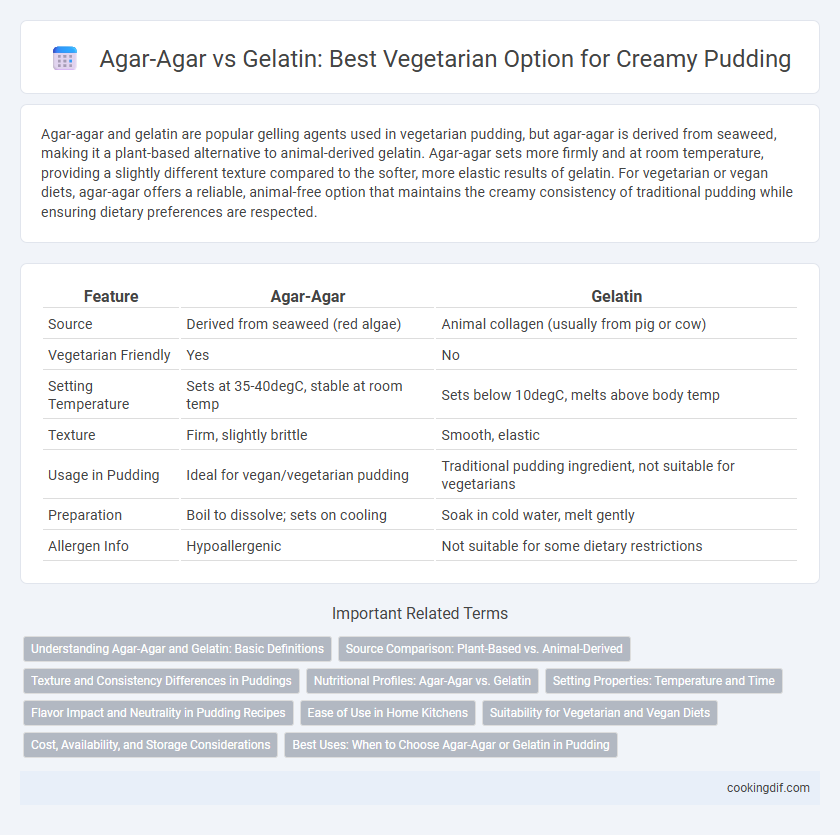
Agar-agar and gelatin are popular gelling agents used in vegetarian pudding, but agar-agar is derived from seaweed, making it a plant-based alternative to animal-derived gelatin. Agar-agar sets more firmly and at room temperature, providing a slightly different texture compared to the softer, more elastic results of gelatin. For vegetarian or vegan diets, agar-agar offers a reliable, animal-free option that maintains the creamy consistency of traditional pudding while ensuring dietary preferences are respected.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Agar-Agar | Gelatin |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from seaweed (red algae) | Animal collagen (usually from pig or cow) |
| Vegetarian Friendly | Yes | No |
| Setting Temperature | Sets at 35-40degC, stable at room temp | Sets below 10degC, melts above body temp |
| Texture | Firm, slightly brittle | Smooth, elastic |
| Usage in Pudding | Ideal for vegan/vegetarian pudding | Traditional pudding ingredient, not suitable for vegetarians |
| Preparation | Boil to dissolve; sets on cooling | Soak in cold water, melt gently |
| Allergen Info | Hypoallergenic | Not suitable for some dietary restrictions |
Understanding Agar-Agar and Gelatin: Basic Definitions
Agar-agar is a plant-based gelling agent derived from red seaweed, commonly used as a vegetarian alternative to gelatin, which is an animal-derived protein obtained from collagen in animal bones and skin. Agar-agar sets pudding more firmly than gelatin and remains stable at higher temperatures, making it ideal for vegan desserts. Gelatin produces a softer, melt-in-the-mouth texture preferred for traditional puddings but is unsuitable for vegetarians due to its animal origin.
Source Comparison: Plant-Based vs. Animal-Derived
Agar-agar, derived from red seaweed, serves as a plant-based alternative to gelatin, which is extracted from animal collagen primarily found in bones and skin. Agar-agar offers a firmer texture and sets more quickly at room temperature, making it ideal for vegetarian pudding recipes seeking a natural gelling agent. Its plant-origin ensures suitability for vegans and vegetarians, contrasting with gelatin's animal-derived composition that limits its use in plant-based diets.
Texture and Consistency Differences in Puddings
Agar-agar creates a firmer, more brittle texture in vegetarian puddings, while gelatin produces a smoother, creamier consistency with a delicate wobble. Agar-agar sets more quickly and remains stable at room temperature, making it ideal for puddings that require a firm hold. Gelatin's melting point is lower, resulting in a softer, melt-in-the-mouth texture that enhances the creaminess of dairy-based puddings.
Nutritional Profiles: Agar-Agar vs. Gelatin
Agar-agar offers a higher fiber content and zero cholesterol, making it a favorable choice for vegetarian pudding with added digestive benefits. Gelatin provides more protein and essential amino acids but contains animal-derived components unsuitable for vegetarians. Nutritionally, agar-agar supports a low-calorie, plant-based diet, while gelatin contributes to collagen intake and muscle repair.
Setting Properties: Temperature and Time
Agar-agar sets rapidly at room temperature, typically firming within 15 to 30 minutes, and remains stable up to 85degC, making it ideal for firm vegetarian puddings. Gelatin requires refrigeration to set, usually taking 2 to 4 hours, and melts at body temperature around 35degC, resulting in a softer texture. The temperature stability and quick setting time of agar-agar provide a reliable alternative for vegetarian pudding that needs to maintain shape without refrigeration.
Flavor Impact and Neutrality in Pudding Recipes
Agar-agar offers a neutral flavor profile that preserves the original taste of puddings, making it ideal for vegetarian recipes where flavor fidelity is essential. Gelatin can impart a slight animal-based taste, which may alter the delicate flavors in puddings. Choosing agar-agar ensures a clean, unaltered flavor impact, enhancing the natural ingredients without masking them.
Ease of Use in Home Kitchens
Agar-agar offers a straightforward preparation process in home kitchens, dissolving quickly in boiling water and setting at room temperature, eliminating the need for refrigeration. Gelatin requires careful blooming in cold water before heating, which can be more time-consuming and sensitive to precise temperatures. For vegetarian pudding, agar-agar's ease of use and reliability make it a preferred choice among home cooks.
Suitability for Vegetarian and Vegan Diets
Agar-agar, derived from red algae, is a plant-based gelling agent ideal for vegetarian and vegan pudding recipes due to its natural origin and ability to set firm gels without animal products. Gelatin, in contrast, is sourced from animal collagen, making it unsuitable for vegan diets and limiting its use to vegetarian preparations only if sourced from non-strict vegetarian animals. Choosing agar-agar ensures a fully plant-based pudding, meeting strict vegetarian and vegan dietary requirements while providing a comparable texture to gelatin-based desserts.
Cost, Availability, and Storage Considerations
Agar-agar, derived from seaweed, is a cost-effective and widely available vegetarian alternative to gelatin, which is animal-based and generally pricier. Agar-agar has a longer shelf life and can be stored at room temperature without refrigeration, unlike gelatin that requires cool, dry storage to maintain its gelling properties. Cost efficiency and ease of storage make agar-agar preferable for vegetarian pudding recipes, especially in regions where plant-based ingredients are more accessible.
Best Uses: When to Choose Agar-Agar or Gelatin in Pudding
Agar-agar is ideal for vegetarian pudding recipes that require a firm, jelly-like texture and withstand higher temperatures without melting, making it perfect for fruit-based or Asian-style puddings. Gelatin, derived from animal collagen, offers a smooth, creamy texture suited for traditional Western-style puddings with a delicate, melt-in-the-mouth quality best served chilled. Choose agar-agar for vegan or vegetarian dishes and gelatin when aiming for a softer set and richer mouthfeel in dairy-based puddings.
Agar-Agar vs Gelatin for vegetarian pudding Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com