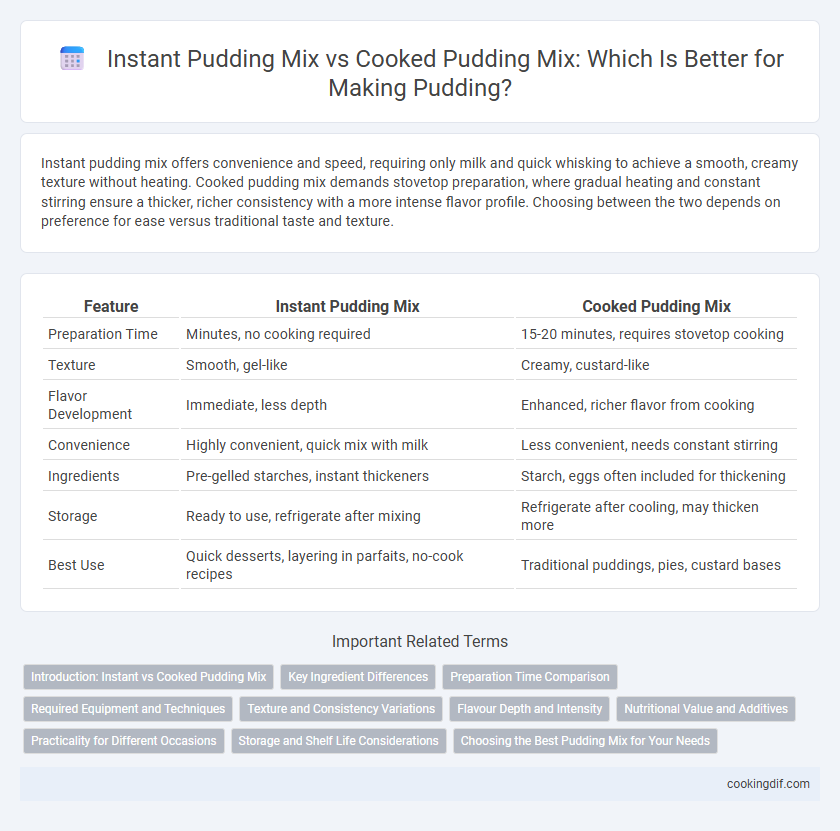
Instant pudding mix offers convenience and speed, requiring only milk and quick whisking to achieve a smooth, creamy texture without heating. Cooked pudding mix demands stovetop preparation, where gradual heating and constant stirring ensure a thicker, richer consistency with a more intense flavor profile. Choosing between the two depends on preference for ease versus traditional taste and texture.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Instant Pudding Mix | Cooked Pudding Mix |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation Time | Minutes, no cooking required | 15-20 minutes, requires stovetop cooking |
| Texture | Smooth, gel-like | Creamy, custard-like |
| Flavor Development | Immediate, less depth | Enhanced, richer flavor from cooking |
| Convenience | Highly convenient, quick mix with milk | Less convenient, needs constant stirring |
| Ingredients | Pre-gelled starches, instant thickeners | Starch, eggs often included for thickening |
| Storage | Ready to use, refrigerate after mixing | Refrigerate after cooling, may thicken more |
| Best Use | Quick desserts, layering in parfaits, no-cook recipes | Traditional puddings, pies, custard bases |
Introduction: Instant vs Cooked Pudding Mix
Instant pudding mix offers quick preparation by simply whisking with cold milk, making it convenient for immediate serving. Cooked pudding mix requires heating and constant stirring to achieve the desired texture, often resulting in a thicker, creamier consistency. Choosing between instant and cooked pudding depends on the time available and the texture preference for the final dessert.
Key Ingredient Differences
Instant pudding mix contains pre-gelatinized starches and thickeners that allow it to set quickly when mixed with cold milk, eliminating the need for cooking. Cooked pudding mix, on the other hand, relies on raw starches that require heating to activate thickening properties, resulting in a smoother, creamier texture. Key ingredients like cornstarch in cooked mixes necessitate cooking, whereas modified starches in instant mixes provide convenience without sacrificing flavor.
Preparation Time Comparison
Instant pudding mix requires significantly less preparation time, as it only needs to be whisked with cold milk and set for a few minutes. Cooked pudding mix demands longer preparation, involving heating milk on the stove, stirring continuously for about 5-10 minutes until thickened, and then cooling. Choosing instant mix saves around 10-15 minutes in total preparation time compared to traditional cooked pudding.
Required Equipment and Techniques
Instant pudding mix requires minimal equipment, typically just a mixing bowl and a whisk, as it can be prepared by simply combining the powder with cold milk and whisking until thickened. Cooked pudding mix demands more specialized tools such as a saucepan and a stove for heating, along with constant stirring using a whisk or spatula to prevent lumps and ensure smooth texture. Techniques for instant pudding focus on quick mixing and chilling, whereas cooked pudding involves precise temperature control and gradual cooking to develop the desired creamy consistency.
Texture and Consistency Variations
Instant pudding mix offers a smooth, creamy texture with a light consistency that sets quickly due to pre-gelatinized starches, making it ideal for quick desserts. Cooked pudding mix requires heating, resulting in a thicker, denser texture with a richer mouthfeel as the starch granules swell fully during cooking. Variations in texture and consistency between the two mixes largely depend on preparation methods, where instant mix yields a softer, more gelatinous consistency and cooked mix produces a firm, custard-like finish.
Flavour Depth and Intensity
Instant pudding mix offers a quicker preparation time but tends to have a lighter flavor profile and less intensity compared to cooked pudding mix. Cooked pudding mix develops richer, deeper flavors through the cooking process, which allows starches and sugars to interact, enhancing taste complexity and mouthfeel. For recipes prioritizing robust flavor depth, cooked pudding mix is the preferred choice despite longer preparation requirements.
Nutritional Value and Additives
Instant pudding mix typically contains stabilizers, emulsifiers, and artificial flavors to ensure quick preparation and consistent texture, which can add unnecessary additives and reduce nutritional quality. Cooked pudding mix, on the other hand, often uses simpler ingredients and fewer preservatives, potentially offering a more natural nutritional profile with less processed additives. Choosing cooked pudding mix may result in higher-quality nutrients and fewer synthetic additives compared to instant options.
Practicality for Different Occasions
Instant pudding mix offers unmatched practicality for quick desserts and casual gatherings due to its no-cook process and minimal preparation time. Cooked pudding mix, requiring stovetop heating and longer cooling, suits occasions where texture and richness are prioritized, such as formal dinners or layered desserts. Choosing between the two depends on the event's time constraints and desired pudding consistency, with instant mixes favoring convenience and cooked mixes enhancing flavor depth.
Storage and Shelf Life Considerations
Instant pudding mix offers a longer shelf life, typically up to two years when stored in a cool, dry place, making it convenient for long-term storage without refrigeration. Cooked pudding mix, once prepared, requires refrigeration and has a shorter shelf life of about 3 to 4 days due to its fresh dairy content. Proper sealing and airtight containers are essential for both types to maintain freshness and prevent contamination.
Choosing the Best Pudding Mix for Your Needs
Instant pudding mix offers a quick, no-cook solution ideal for busy schedules and immediate desserts, while cooked pudding mix provides a richer texture and deeper flavor through stovetop preparation. When choosing the best pudding mix, consider factors like time availability, desired pudding consistency, and flavor intensity, as cooked mixes allow for customization with added ingredients. Nutritional content and the type of dish being prepared also influence the choice between instant and cooked pudding options.
Instant pudding mix vs cooked pudding mix for preparation Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com