Vanilla extract offers a smooth, concentrated flavor with easy mixing, making it a convenient choice for pudding recipes. Vanilla bean provides a richer, more intense taste and visible specks, enhancing both flavor and presentation. Choosing between them depends on whether you prefer convenience or a gourmet touch in your pudding.
Table of Comparison
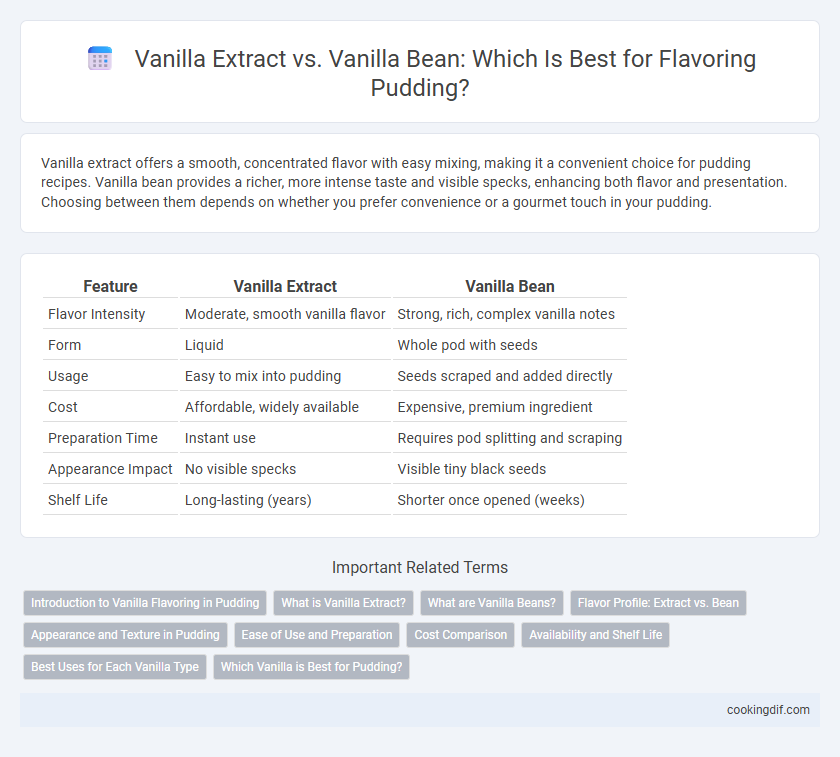
| Feature | Vanilla Extract | Vanilla Bean |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor Intensity | Moderate, smooth vanilla flavor | Strong, rich, complex vanilla notes |
| Form | Liquid | Whole pod with seeds |
| Usage | Easy to mix into pudding | Seeds scraped and added directly |
| Cost | Affordable, widely available | Expensive, premium ingredient |
| Preparation Time | Instant use | Requires pod splitting and scraping |
| Appearance Impact | No visible specks | Visible tiny black seeds |
| Shelf Life | Long-lasting (years) | Shorter once opened (weeks) |
Introduction to Vanilla Flavoring in Pudding
Vanilla bean offers a natural, rich flavor with tiny seeds that add texture and depth to pudding, while vanilla extract delivers a more uniform and convenient vanilla essence derived from soaking beans in alcohol. Using vanilla beans can enhance the visual appeal and elevate the sensory experience, whereas vanilla extract provides consistent flavor strength and easier incorporation. Pudding recipes often balance these options depending on desired intensity, cost, and preparation time.
What is Vanilla Extract?
Vanilla extract is a concentrated liquid flavoring made by soaking vanilla beans in alcohol and water, capturing the beans' aromatic compounds and essential oils. It provides a consistent and potent vanilla taste that blends smoothly into puddings, enhancing their creamy texture without the granular presence of vanilla bean seeds. Unlike whole vanilla beans, extract offers convenience and longer shelf life while maintaining the characteristic sweet and floral vanilla flavor.
What are Vanilla Beans?
Vanilla beans are the fruit of the vanilla orchid, containing tiny seeds that deliver a rich, aromatic flavor far more complex and intense than vanilla extract. These beans are often split and scraped to release the flavorful seeds, which infuse puddings with a natural, creamy vanilla essence. Unlike vanilla extract, which is made by soaking beans in alcohol, whole vanilla beans provide a purer, more robust taste and visual appeal with their characteristic speckles.
Flavor Profile: Extract vs. Bean
Vanilla extract offers a consistent, smooth flavor with subtle floral and sweet notes due to its alcohol-based infusion, making it ideal for evenly sweet puddings. Vanilla bean provides a more intense, complex profile featuring rich, creamy, and slightly spicy undertones from the whole pod's seeds and pod itself. Choosing between extract and bean depends on the desired depth and authenticity of vanilla flavor in pudding recipes.
Appearance and Texture in Pudding
Vanilla bean adds visible black specks to pudding, creating an artisanal and natural appearance that vanilla extract lacks. The bean's fresh, creamy seeds can slightly enhance pudding's texture, contributing to a subtle graininess compared to the smooth finish from extract. Using vanilla bean often results in a more rustic and textured pudding, whereas vanilla extract maintains a uniformly silky consistency.
Ease of Use and Preparation
Vanilla extract offers a convenient and quick way to infuse pudding with rich vanilla flavor, requiring no additional preparation beyond measuring and mixing. Vanilla beans demand more effort, involving splitting the bean and scraping out the seeds, which enhances flavor complexity but increases preparation time. For ease of use and fast preparation, vanilla extract remains the preferred choice in pudding making.
Cost Comparison
Vanilla extract generally costs significantly less than vanilla beans, making it a more budget-friendly option for flavoring pudding in large quantities. While vanilla beans provide a richer, more intense flavor, their premium price--often several times higher than extract per unit--can impact overall recipe costs. Choosing extract allows for consistent vanilla taste without the high expenses associated with whole beans, ideal for cost-conscious cooking.
Availability and Shelf Life
Vanilla extract is widely available in most grocery stores and has a shelf life of up to four years when stored in a cool, dark place. Vanilla beans, while less commonly found and often more expensive, offer a more intense flavor but have a shorter shelf life of about six months to one year if kept properly sealed and refrigerated. Choosing between the two depends on accessibility and how long you intend to store the flavoring for your pudding recipes.
Best Uses for Each Vanilla Type
Vanilla extract offers a smooth, consistent flavor ideal for baking and blending into puddings where uniform taste is crucial. Vanilla beans provide a more intense, aromatic essence with visible specks, enhancing gourmet puddings and custards that benefit from a richer texture and appearance. Use vanilla extract for everyday recipes and vanilla beans for specialty desserts requiring a pronounced, natural vanilla character.
Which Vanilla is Best for Pudding?
Vanilla beans provide a rich, aromatic flavor with natural vanilla specks that enhance pudding's texture and presentation, while vanilla extract offers convenience and a more subtle vanilla essence. The choice depends on the desired intensity and authenticity of vanilla taste; vanilla beans are preferred for a deep, complex flavor profile, whereas extract suits quick recipes or milder vanilla notes. High-quality Madagascar vanilla beans consistently deliver premium flavor, making them the best option for gourmet pudding.
Vanilla extract vs vanilla bean for flavoring Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com