High hydration doughs, containing more water, yield a crust that is airy, soft, and open-crumbed with a chewy texture, ideal for Neapolitan-style pizzas. Low hydration doughs result in a denser, crispier crust with a more uniform crumb, characteristic of New York-style or thin-crust pizzas. Balancing hydration levels influences fermentation time, dough handling, and final crust texture, making hydration a crucial factor in pizza crust quality.
Table of Comparison
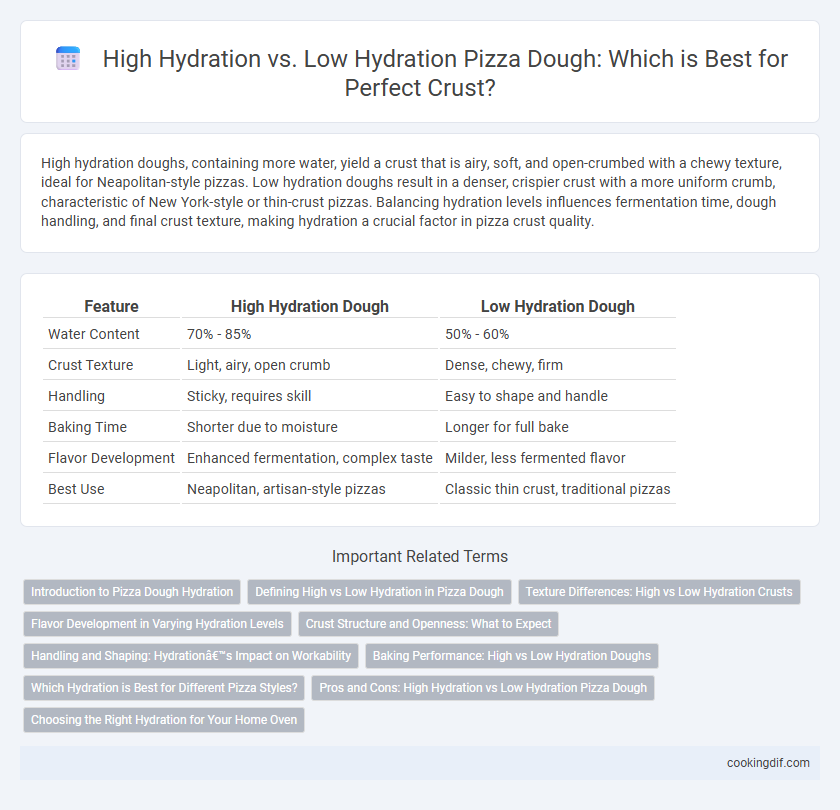
| Feature | High Hydration Dough | Low Hydration Dough |
|---|---|---|
| Water Content | 70% - 85% | 50% - 60% |
| Crust Texture | Light, airy, open crumb | Dense, chewy, firm |
| Handling | Sticky, requires skill | Easy to shape and handle |
| Baking Time | Shorter due to moisture | Longer for full bake |
| Flavor Development | Enhanced fermentation, complex taste | Milder, less fermented flavor |
| Best Use | Neapolitan, artisan-style pizzas | Classic thin crust, traditional pizzas |
Introduction to Pizza Dough Hydration
Pizza dough hydration refers to the percentage of water relative to flour weight, significantly impacting crust texture and baking properties. High hydration dough, often above 70%, creates a lighter, airier crust with larger bubbles and a softer crumb, ideal for Neapolitan-style pizzas. Low hydration dough, typically below 60%, results in a denser, firmer crust with a chewier bite, preferred for traditional New York-style pizzas.
Defining High vs Low Hydration in Pizza Dough
High hydration pizza dough contains 65% to 80% water relative to flour weight, creating a wetter, softer dough that yields an airy, open crumb and a crisp, blistered crust. Low hydration dough ranges from 50% to 60% water, producing a stiffer, denser dough with a tighter crumb and a chewier texture. The hydration level directly affects dough extensibility, fermentation speed, and oven spring, making it a crucial factor in defining crust characteristics.
Texture Differences: High vs Low Hydration Crusts
High hydration pizza dough produces a crust with an open, airy crumb and a chewy, tender texture due to increased water content allowing for better gluten development. Low hydration dough results in a denser, firmer crust with a crispier bite and more structured texture, ideal for thin-crust styles. Hydration levels significantly influence crust elasticity, crustiness, and overall mouthfeel, shaping the final pizza eating experience.
Flavor Development in Varying Hydration Levels
High hydration doughs, typically above 70%, enhance flavor development by allowing extended fermentation and better enzyme activity, which produces complex, tangy flavors and a more open crumb structure in the pizza crust. Low hydration doughs stabilize gluten formation, resulting in a denser texture with more subtle flavor notes due to reduced fermentation byproducts. Balancing hydration levels directly influences crust fermentation dynamics, yeast activity, and enzymatic reactions, ultimately shaping the pizza's taste and texture profile.
Crust Structure and Openness: What to Expect
High hydration doughs, typically containing 70% or more water, produce a crust with a more open crumb structure and larger air pockets, resulting in a light, airy texture. Low hydration doughs, with around 55-60% water, yield a denser, tighter crumb and a crispier crust due to reduced moisture and less gluten development. Expect high hydration crusts to have greater elasticity and irregular holes, while low hydration crusts are more uniform and compact in appearance.
Handling and Shaping: Hydration’s Impact on Workability
High hydration doughs, typically above 70%, create a softer, stickier texture that demands more skillful handling and gentle shaping to maintain structure without tearing. Low hydration doughs, around 55-60%, offer a stiffer, firmer consistency that is easier to stretch and shape, providing greater control for crisp crusts. Adjusting hydration levels directly influences dough elasticity, extensibility, and workability, impacting the final crust texture and overall pizza quality.
Baking Performance: High vs Low Hydration Doughs
High hydration pizza doughs, typically ranging from 70% to 80% water content, create a lighter, airier crust with larger, irregular holes due to increased steam during baking. Low hydration doughs, around 55% to 60%, yield a denser, chewier crust with a more uniform crumb structure and easier handling during shaping and baking. High hydration doughs require higher oven temperatures and longer baking times to achieve optimal crust crispiness and open crumb, while low hydration doughs bake faster and produce a firmer texture but less oven spring.
Which Hydration is Best for Different Pizza Styles?
High hydration dough, typically around 70-85%, produces an open crumb and chewy texture ideal for Neapolitan and artisan-style pizzas, enhancing crispiness and flavor development. Low hydration dough, ranging from 55-60%, results in a denser, firmer crust preferred for New York or Sicilian pizzas, providing a sturdy base capable of holding heavier toppings. Choosing the right hydration percentage depends on the desired crust texture and pizza style, balancing moisture, gluten development, and baking method.
Pros and Cons: High Hydration vs Low Hydration Pizza Dough
High hydration pizza dough, typically above 70%, produces a lighter, airier crust with larger, irregular holes and a crispier exterior due to increased water content allowing better gluten development. However, it is more challenging to handle, sticky, and requires longer fermentation times compared to low hydration dough, which ranges from 55% to 60%, offering easier shaping, a denser, chewier crust, and faster fermentation. Low hydration dough often results in a more uniform crumb structure but may lack the open, airy texture prized in Neapolitan or artisanal-style pizzas.
Choosing the Right Hydration for Your Home Oven
High hydration dough, typically above 70%, creates a lighter, airier crust with open crumb structure ideal for high-temperature ovens that can handle intense steam. Low hydration dough, usually around 60-65%, produces a denser, chewier crust that performs better in home ovens with lower, more controlled heat. Choosing the right hydration depends on your oven's baking environment to balance moisture retention and crust crispiness for optimal pizza quality.
High hydration vs low hydration for crust Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com