Cold-proofing dough enhances flavor and texture by allowing slower fermentation, resulting in a chewier crust and more complex taste. Room-temperature proofing accelerates yeast activity for faster rise but may produce less depth in flavor and a softer texture. Choosing between methods depends on desired dough characteristics and available preparation time.
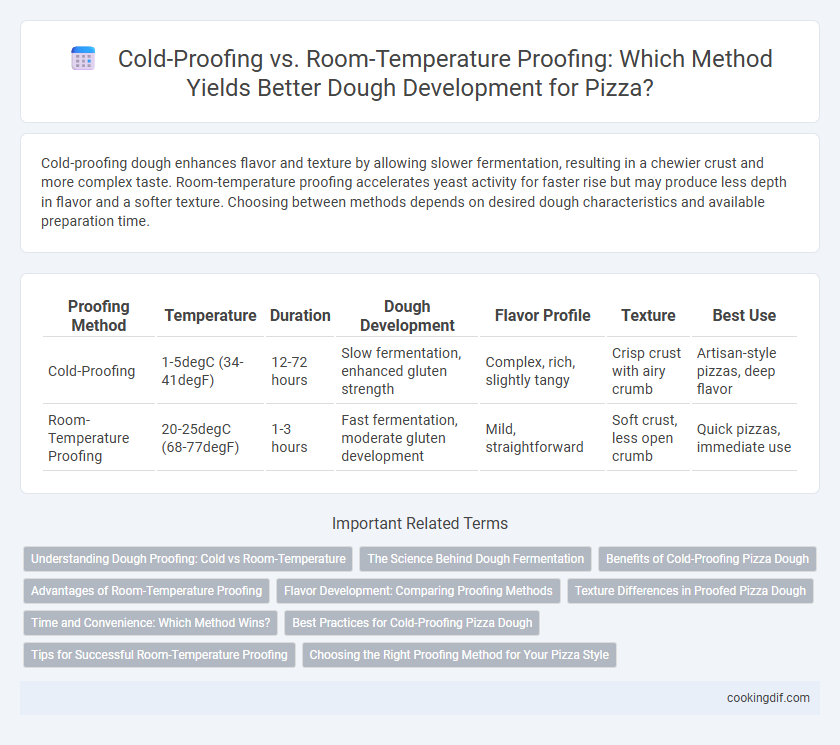
Table of Comparison
| Proofing Method | Temperature | Duration | Dough Development | Flavor Profile | Texture | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold-Proofing | 1-5degC (34-41degF) | 12-72 hours | Slow fermentation, enhanced gluten strength | Complex, rich, slightly tangy | Crisp crust with airy crumb | Artisan-style pizzas, deep flavor |
| Room-Temperature Proofing | 20-25degC (68-77degF) | 1-3 hours | Fast fermentation, moderate gluten development | Mild, straightforward | Soft crust, less open crumb | Quick pizzas, immediate use |
Understanding Dough Proofing: Cold vs Room-Temperature
Cold-proofing pizza dough involves fermenting it in the refrigerator at temperatures between 35degF and 45degF, resulting in enhanced flavor development and improved dough texture due to slower yeast activity. Room-temperature proofing occurs at around 70degF to 75degF, accelerating fermentation and resulting in faster dough rise but potentially less complex flavor. Understanding the balance between cold-proofing and room-temperature proofing helps optimize gluten network formation and yeast metabolism for preferred crust characteristics.
The Science Behind Dough Fermentation
Cold-proofing dough involves slow fermentation at low temperatures, enhancing flavor complexity and texture through extended yeast activity and enzyme reactions. Room-temperature proofing accelerates fermentation, producing faster gas production that results in a lighter crumb but less developed flavor. Understanding the balance of temperature and time affects gluten structure, yeast metabolism, and overall dough consistency crucial for optimal pizza crust quality.
Benefits of Cold-Proofing Pizza Dough
Cold-proofing pizza dough enhances flavor complexity by allowing slow fermentation, which develops richer, tangier taste profiles through extended yeast activity. This method improves dough texture, yielding a chewier crust with better gluten structure and higher moisture retention during baking. Cold-proofing also offers practical benefits, such as extended dough shelf life and increased flexibility for home cooks and pizzerias to manage preparation timing efficiently.
Advantages of Room-Temperature Proofing
Room-temperature proofing accelerates yeast activity, leading to faster dough fermentation and enhanced gluten development compared to cold-proofing. This method improves dough elasticity and rise, resulting in a lighter, airier crust with better texture and flavor complexity. It also allows for more predictable timing in pizza preparation, benefiting both home cooks and professional pizzerias.
Flavor Development: Comparing Proofing Methods
Cold-proofing pizza dough enhances flavor complexity by allowing slow fermentation at low temperatures, promoting the development of organic acids and deeper aromatic profiles. Room-temperature proofing speeds up fermentation but can result in less nuanced flavors due to rapid yeast activity and reduced acid production. Bakers seeking rich, well-rounded taste often prefer cold-proofing to achieve a balance of tanginess and aromatic depth in the crust.
Texture Differences in Proofed Pizza Dough
Cold-proofing pizza dough slows fermentation, resulting in a chewier texture with enhanced flavor complexity and a more open crumb structure. Room-temperature proofing produces a softer, more tender crust with a uniform crumb but less depth in flavor due to faster yeast activity. Choosing between these methods depends on desired texture, with cold-proofed dough preferred for artisanal pizzas and room-temperature proofing suited for quick preparation.
Time and Convenience: Which Method Wins?
Cold-proofing pizza dough requires 12 to 72 hours in the refrigerator, allowing for slow fermentation that enhances flavor and improves texture without constant monitoring. Room-temperature proofing typically takes 1 to 3 hours, offering faster dough readiness but less depth of flavor compared to cold-fermented dough. For convenience and time efficiency, room-temperature proofing wins, while cold-proofing excels in flavor development with extended time commitment.
Best Practices for Cold-Proofing Pizza Dough
Cold-proofing pizza dough slows fermentation by storing it in a refrigerator at 35-40degF (2-4degC) for 24-72 hours, enhancing flavor complexity and dough strength through gradual yeast activity. Optimal cold-proofing allows gluten development and enzyme activity without over-fermentation, producing a chewy crust with better texture and a more pronounced yeast aroma. Best practices include tightly covering the dough to prevent drying and allowing it to reach room temperature before shaping for easier handling and optimal oven spring.
Tips for Successful Room-Temperature Proofing
Room-temperature proofing enhances dough fermentation by maintaining an optimal 70-75degF (21-24degC) environment, encouraging yeast activity and gluten development for a flavorful crust. To ensure successful room-temperature proofing, cover the dough with a damp cloth or plastic wrap to prevent drying and place it in a draft-free area for consistent rising. Monitoring the dough's volume, which should typically double within 1 to 2 hours, helps determine readiness for shaping and baking.
Choosing the Right Proofing Method for Your Pizza Style
Cold-proofing dough in the refrigerator slows fermentation, enhancing flavor complexity and creating a chewier crust ideal for Neapolitan or artisan-style pizzas. Room-temperature proofing accelerates yeast activity, producing a softer, airy dough perfect for classic American or Sicilian-style pizzas with a lighter texture. Selecting the right proofing method depends on the desired crust texture and flavor profile, balancing fermentation time and temperature to achieve optimal dough development.
Cold-proofing vs Room-temperature proofing for dough development Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com