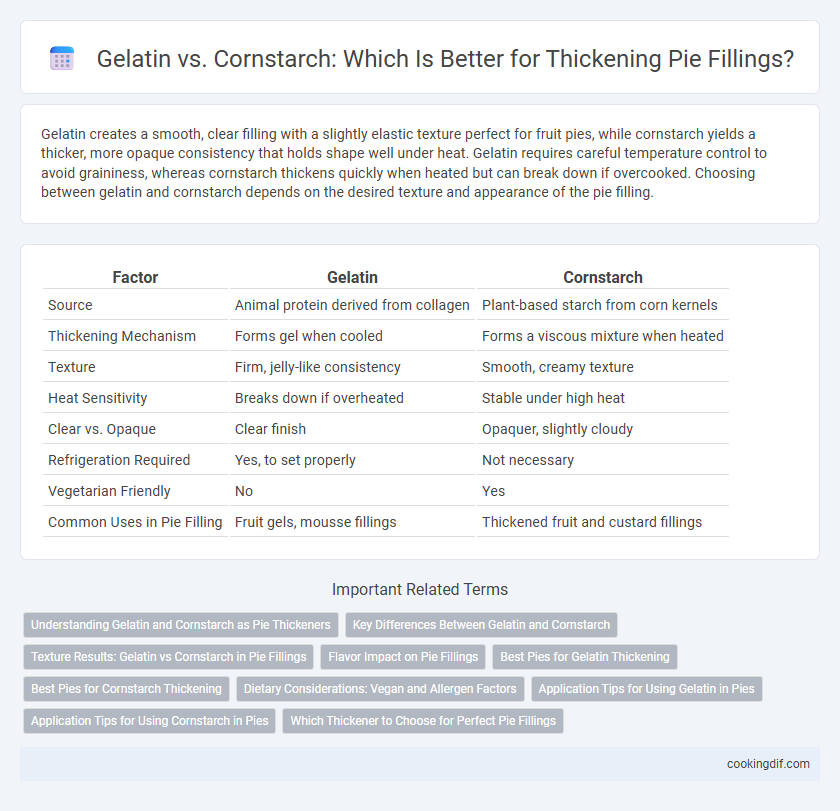
Gelatin creates a smooth, clear filling with a slightly elastic texture perfect for fruit pies, while cornstarch yields a thicker, more opaque consistency that holds shape well under heat. Gelatin requires careful temperature control to avoid graininess, whereas cornstarch thickens quickly when heated but can break down if overcooked. Choosing between gelatin and cornstarch depends on the desired texture and appearance of the pie filling.
Table of Comparison
| Factor | Gelatin | Cornstarch |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Animal protein derived from collagen | Plant-based starch from corn kernels |
| Thickening Mechanism | Forms gel when cooled | Forms a viscous mixture when heated |
| Texture | Firm, jelly-like consistency | Smooth, creamy texture |
| Heat Sensitivity | Breaks down if overheated | Stable under high heat |
| Clear vs. Opaque | Clear finish | Opaquer, slightly cloudy |
| Refrigeration Required | Yes, to set properly | Not necessary |
| Vegetarian Friendly | No | Yes |
| Common Uses in Pie Filling | Fruit gels, mousse fillings | Thickened fruit and custard fillings |
Understanding Gelatin and Cornstarch as Pie Thickeners
Gelatin acts as a protein-based thickener that creates a smooth, gelled texture by binding water molecules, ideal for fruit or cream pie fillings that need a stable set without cloudiness. Cornstarch, a carbohydrate thickener, works through starch granule swelling when heated, producing a glossy, translucent finish and a slightly firmer consistency suitable for traditional baked pies. Understanding the differences in thickening mechanisms and texture outcomes can help bakers choose the best thickener for specific pie fillings and desired mouthfeel.
Key Differences Between Gelatin and Cornstarch
Gelatin and cornstarch differ fundamentally in their thickening properties, with gelatin creating a smooth, jiggly texture that sets firmly when cooled, while cornstarch produces a translucent, glossy, and slightly thickened filling that remains pourable when warm. Gelatin is derived from animal collagen and requires blooming in cold water before melting into the mixture, whereas cornstarch is a plant-based starch that thickens through heat-activated starch granule swelling. The choice between gelatin and cornstarch affects the pie filling's mouthfeel, clarity, and suitability for dietary restrictions such as vegetarianism or veganism.
Texture Results: Gelatin vs Cornstarch in Pie Fillings
Gelatin creates a smooth, jelly-like texture in pie fillings, offering a firm yet tender consistency that holds shape well when chilled. Cornstarch produces a glossy, thickened filling with a slightly softer, more pudding-like texture that remains stable when baked or served warm. Choosing between gelatin and cornstarch depends on the desired firmness and serving temperature of the pie.
Flavor Impact on Pie Fillings
Gelatin provides a smooth, delicate texture with minimal impact on the pie filling's flavor, preserving the fresh, natural taste of fruits or creams. Cornstarch offers a slightly opaque finish and can create a mild, starchy taste that may subtly alter the flavor profile of the pie filling. Choosing gelatin is ideal for maintaining clarity and purity of flavor, while cornstarch adds body but may influence the sweetness and overall mouthfeel.
Best Pies for Gelatin Thickening
Gelatin creates a smooth, glossy texture ideal for creamy or mousse-style pie fillings like key lime or chocolate cream pies, providing a stable set without cloudiness. It works best in no-bake pies that require a firm yet tender consistency, preserving delicate flavors while ensuring a clean slice. Cornstarch, in contrast, suits fruit pies needing a translucent, jelly-like filling but lacks gelatin's silky mouthfeel and firmness.
Best Pies for Cornstarch Thickening
Cornstarch is ideal for thickening pie fillings that require a clear, glossy finish, such as fruit pies like cherry, blueberry, and apple, as it creates a smooth and stable texture without cloudiness. Unlike gelatin, which sets into a firm gel, cornstarch thickens through heat and maintains a soft, sliceable consistency that complements the juicy, tender nature of these pies. For best results, cornstarch should be mixed with sugar before combining with fruit juices to prevent clumping and ensure an even thickening throughout the filling.
Dietary Considerations: Vegan and Allergen Factors
Gelatin, derived from animal collagen, is unsuitable for vegans and those with gelatin allergies, while cornstarch, a plant-based starch, offers a vegan-friendly and hypoallergenic alternative for thickening pie fillings. Cornstarch provides a smooth, clear gelatinous texture without animal ingredients, making it ideal for dietary restrictions related to veganism and common allergens. Choosing cornstarch ensures compatibility with plant-based diets and reduces the risk of allergic reactions, enhancing the accessibility of desserts for diverse dietary needs.
Application Tips for Using Gelatin in Pies
Gelatin provides a clear, stable gel that works best for fruit and creamy pie fillings requiring a smooth texture and glossy finish. For optimal results, dissolve gelatin in cold water before gently heating to prevent clumping and ensure even distribution throughout the filling. Avoid boiling gelatin as it will lose its setting properties; instead, allow the pie to chill thoroughly to achieve a firm, sliceable consistency.
Application Tips for Using Cornstarch in Pies
Cornstarch serves as an effective thickening agent in pie fillings, especially for fruit pies, because it creates a glossy, clear finish that enhances visual appeal. To avoid a starchy taste or cloudy appearance, mix cornstarch with cold water before adding it to hot filling, and cook until the mixture thickens and turns translucent. Use about 1 to 2 tablespoons of cornstarch per cup of liquid, remembering that overcooking can break down the starch and thin the filling.
Which Thickener to Choose for Perfect Pie Fillings
Gelatin creates a smooth, glossy texture ideal for fruit pies that require a stable, jelly-like consistency, while cornstarch offers a sturdier, opaque filling that holds up well under baking heat and delivers a classic pie texture. Choosing gelatin is best for chilled or no-bake pies, as it sets fillings firmly without cloudiness, whereas cornstarch thickens effectively during baking, making it perfect for traditional pies like apple or cherry. Understanding the moisture content and bake time of the filling helps determine the optimal thickener to achieve the perfect pie texture and sliceability.
Gelatin vs Cornstarch for thickening filling Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com