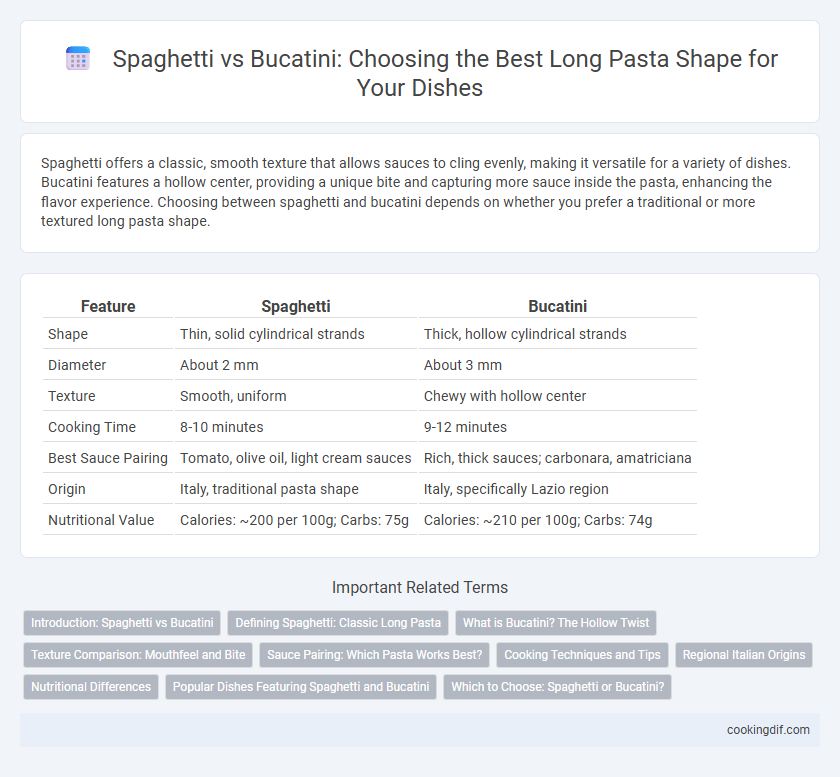
Spaghetti offers a classic, smooth texture that allows sauces to cling evenly, making it versatile for a variety of dishes. Bucatini features a hollow center, providing a unique bite and capturing more sauce inside the pasta, enhancing the flavor experience. Choosing between spaghetti and bucatini depends on whether you prefer a traditional or more textured long pasta shape.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spaghetti | Bucatini |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Thin, solid cylindrical strands | Thick, hollow cylindrical strands |
| Diameter | About 2 mm | About 3 mm |
| Texture | Smooth, uniform | Chewy with hollow center |
| Cooking Time | 8-10 minutes | 9-12 minutes |
| Best Sauce Pairing | Tomato, olive oil, light cream sauces | Rich, thick sauces; carbonara, amatriciana |
| Origin | Italy, traditional pasta shape | Italy, specifically Lazio region |
| Nutritional Value | Calories: ~200 per 100g; Carbs: 75g | Calories: ~210 per 100g; Carbs: 74g |
Introduction: Spaghetti vs Bucatini
Spaghetti and bucatini are both classic Italian long pasta shapes with distinct characteristics. Spaghetti is a thin, round noodle commonly used in a variety of sauces due to its smooth texture, while bucatini features a hollow center, allowing it to hold thicker, chunkier sauces like amatriciana or carbonara more effectively. The unique tubular shape of bucatini enhances sauce absorption, offering a different mouthfeel and cooking experience compared to the solid strands of spaghetti.
Defining Spaghetti: Classic Long Pasta
Spaghetti, a classic long pasta shape, is characterized by its thin, cylindrical strands that cook quickly and hold sauces well. Unlike bucatini, which features a hollow center, spaghetti's solid structure offers a smooth texture and versatility for a variety of Italian dishes. Its precise thickness ranges around 1.8 to 2.0 millimeters, making it ideal for both light olive oil-based sauces and hearty tomato blends.
What is Bucatini? The Hollow Twist
Bucatini is a long pasta shape similar to spaghetti but distinguished by its hollow center, which allows it to hold sauces more effectively. The tubular structure enhances texture and flavor absorption, making it ideal for rich, hearty sauces like carbonara or tomato-based dishes. Unlike solid spaghetti, bucatini's hollow twist provides a unique mouthfeel and an elevated culinary experience in traditional Italian cuisine.
Texture Comparison: Mouthfeel and Bite
Spaghetti offers a smooth, slightly elastic texture that provides a balanced bite and easily absorbs sauces, enhancing the overall mouthfeel. Bucatini features a hollow center, creating a unique contrast between the firm outer layer and the tender interior, resulting in a more dynamic texture and satisfying chew. This hollow structure allows bucatini to capture thicker sauces inside, intensifying flavor delivery with every bite.
Sauce Pairing: Which Pasta Works Best?
Spaghetti's thin, smooth strands pair exceptionally well with lighter sauces like marinara or aglio e olio, allowing flavors to coat evenly without overwhelming the pasta. Bucatini, with its hollow center, captures thicker sauces such as carbonara or amatriciana, providing a burst of flavor inside each bite. Choosing between spaghetti and bucatini ultimately depends on the sauce's consistency and texture, optimizing the dining experience.
Cooking Techniques and Tips
Spaghetti and bucatini differ significantly in texture and cooking requirements; spaghetti cooks faster due to its thin, solid structure, while bucatini, with its hollow center, needs slightly longer to achieve an al dente bite. Cooking bucatini benefits from ample boiling water and occasional stirring to prevent the tubes from sticking together, ensuring even heat distribution inside and out. For both, draining just before fully cooked and finishing the pasta in the sauce allows the starches to thicken the dish and enhance flavor absorption.
Regional Italian Origins
Spaghetti, originating from Southern Italy, particularly Naples, is the most iconic long pasta shape characterized by its thin, cylindrical strands ideal for versatile sauces. Bucatini, hailing from the Lazio region around Rome, features a hollow center that allows sauces to penetrate the pasta, offering a unique texture and flavor experience. Both pastas reflect their regional culinary traditions, with spaghetti commonly paired with tomato-based sauces and bucatini favored in dishes like Amatriciana.
Nutritional Differences
Spaghetti and bucatini share similar calorie counts, averaging around 200 calories per cooked cup, but bucatini contains slightly more dietary fiber due to its hollow center. Both pastas provide roughly 7 grams of protein per serving, but bucatini's structure increases its carbohydrate content slightly, impacting glycemic response. Micronutrient levels such as iron and B vitamins remain comparable, making both shapes nutritionally balanced options within the long pasta category.
Popular Dishes Featuring Spaghetti and Bucatini
Spaghetti is a staple in classic dishes such as Spaghetti Carbonara and Spaghetti Bolognese, prized for its thin, cylindrical shape that effortlessly holds light to moderate sauces. Bucatini stands out in dishes like Bucatini all'Amatriciana, where its hollow center allows rich, tomato-based sauces to permeate each strand, enhancing flavor intensity. Both pasta types complement diverse sauces but differ in texture and sauce retention, making them versatile choices for authentic Italian recipes.
Which to Choose: Spaghetti or Bucatini?
Spaghetti offers a classic, thin, and smooth texture that pairs well with light tomato sauces and olive oil-based dishes, making it versatile for everyday meals. Bucatini features a thicker, hollow center that traps richer sauces like Amatriciana or carbonara, providing a more intense flavor experience. Choosing between spaghetti and bucatini depends on your sauce preference and desired texture, with spaghetti best for delicate flavors and bucatini ideal for hearty, sauce-rich recipes.
Spaghetti vs bucatini for long pasta shapes Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com