Sauce reduction intensifies flavors by simmering the sauce to evaporate water, resulting in a thicker, more concentrated consistency ideal for bold pasta dishes. Sauce emulsification involves blending fat and liquid to create a smooth, creamy texture that evenly coats the pasta, enhancing mouthfeel and balance. Mastering these techniques ensures a perfect sauce texture and flavor harmony in every plate.
Table of Comparison
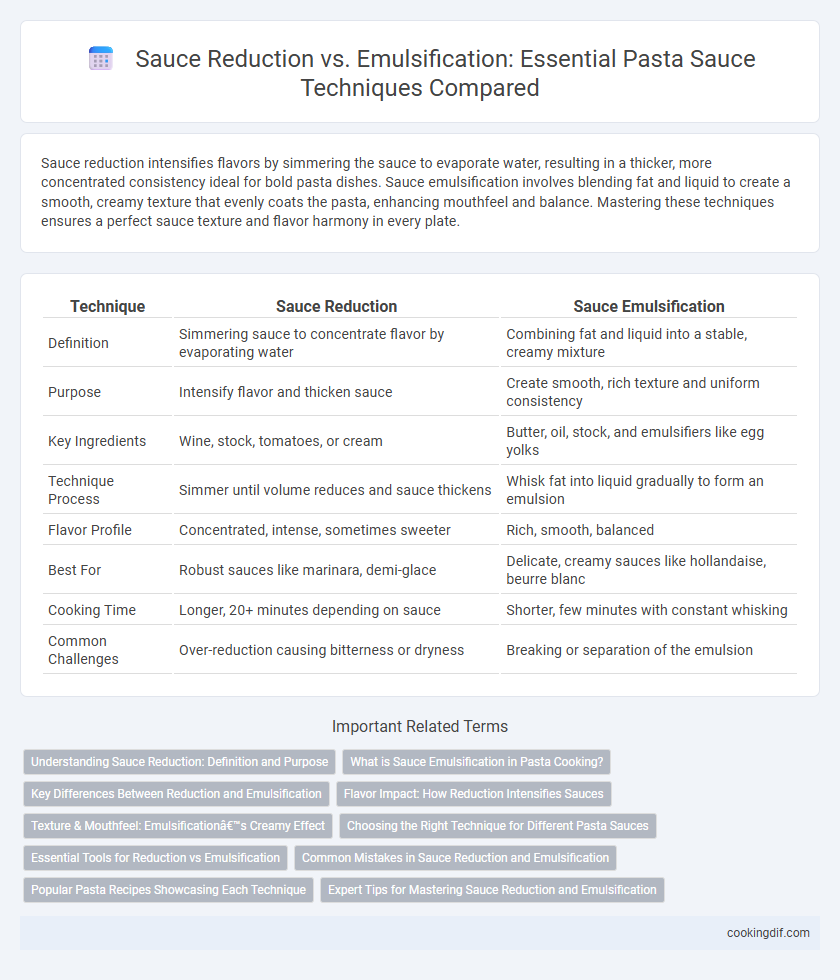
| Technique | Sauce Reduction | Sauce Emulsification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simmering sauce to concentrate flavor by evaporating water | Combining fat and liquid into a stable, creamy mixture |
| Purpose | Intensify flavor and thicken sauce | Create smooth, rich texture and uniform consistency |
| Key Ingredients | Wine, stock, tomatoes, or cream | Butter, oil, stock, and emulsifiers like egg yolks |
| Technique Process | Simmer until volume reduces and sauce thickens | Whisk fat into liquid gradually to form an emulsion |
| Flavor Profile | Concentrated, intense, sometimes sweeter | Rich, smooth, balanced |
| Best For | Robust sauces like marinara, demi-glace | Delicate, creamy sauces like hollandaise, beurre blanc |
| Cooking Time | Longer, 20+ minutes depending on sauce | Shorter, few minutes with constant whisking |
| Common Challenges | Over-reduction causing bitterness or dryness | Breaking or separation of the emulsion |
Understanding Sauce Reduction: Definition and Purpose
Sauce reduction involves simmering a liquid to concentrate flavors and thicken its consistency, essential for enhancing pasta dishes. This technique intensifies taste by evaporating water content, resulting in a richer, more robust sauce that clings well to noodles. Understanding reduction is crucial for achieving the perfect balance between viscosity and flavor depth in classic Italian pasta sauces.
What is Sauce Emulsification in Pasta Cooking?
Sauce emulsification in pasta cooking involves blending fat, such as olive oil or butter, with starchy pasta water to create a smooth, creamy sauce that clings perfectly to the pasta strands. This technique enhances flavor integration and texture without relying on heavy cream, resulting in a lighter, silkier coating. Unlike sauce reduction which concentrates flavors by simmering, emulsification binds ingredients at a molecular level, producing a cohesive, velvety finish.
Key Differences Between Reduction and Emulsification
Sauce reduction intensifies flavor by simmering to evaporate water content, resulting in a thicker and more concentrated consistency. Emulsification blends two immiscible liquids, such as oil and vinegar or butter and stock, into a stable, creamy sauce through vigorous mixing or whisking. While reduction relies on heat and time to enhance flavor, emulsification depends on mechanical agitation and the presence of emulsifying agents to create texture and stability.
Flavor Impact: How Reduction Intensifies Sauces
Sauce reduction concentrates flavors by simmering the sauce to evaporate water, resulting in a thicker texture and intensified taste essential for pasta dishes. Emulsification, by contrast, blends fats and liquids to create a smooth, creamy consistency without significantly altering flavor intensity. Reduction enhances robustness and depth of sauces, making it a preferred technique to elevate pasta experience through rich, bold flavors.
Texture & Mouthfeel: Emulsification’s Creamy Effect
Sauce emulsification creates a creamy, velvety texture by evenly blending fat and liquid, enhancing mouthfeel without the thickness of reduction. Reduction intensifies flavors by evaporating water, resulting in a thicker, more concentrated sauce but can lead to a heavier mouthfeel. Emulsified pasta sauces like Alfredo or Carbonara deliver a smoother, silkier coating that clings delicately to noodles, improving overall texture and eating experience.
Choosing the Right Technique for Different Pasta Sauces
Sauce reduction concentrates flavors by simmering liquids until thickened, ideal for hearty tomato or wine-based pasta sauces. Sauce emulsification creates a creamy, stable mixture by blending fat with liquids, perfect for rich butter or cream-based sauces like Alfredo. Selecting the right technique enhances texture and flavor, ensuring each pasta sauce complements its specific ingredients perfectly.
Essential Tools for Reduction vs Emulsification
Sauce reduction requires a wide, shallow pan such as a saute pan to maximize surface area and facilitate rapid evaporation of liquids, concentrating flavors efficiently. Emulsification demands a whisk or immersion blender to vigorously combine fat and liquid components into a stable, creamy texture. Mastering these essential tools enhances control over sauce consistency and flavor intensity in pasta preparations.
Common Mistakes in Sauce Reduction and Emulsification
Common mistakes in sauce reduction include overcooking, which causes bitterness and loss of vibrant flavors, and not stirring frequently, leading to uneven consistency and burnt spots. In sauce emulsification, errors such as adding oil too quickly or failing to maintain a consistent temperature result in separation and a broken sauce rather than a smooth, cohesive texture. Proper technique requires careful heat control and gradual incorporation of ingredients to achieve balanced flavor and ideal sauce texture.
Popular Pasta Recipes Showcasing Each Technique
Classic Italian pasta dishes like Spaghetti alla Carbonara highlight sauce emulsification, where the heat from the pasta combines eggs and cheese into a creamy, smooth sauce without curdling. In contrast, a rich Bolognese sauce showcases sauce reduction, simmered slowly to concentrate flavors and thicken the texture. Both techniques enhance the pasta experience by balancing flavor intensity and sauce consistency in traditional recipes.
Expert Tips for Mastering Sauce Reduction and Emulsification
Mastering sauce reduction involves carefully simmering the sauce to concentrate flavors and achieve the desired thickness, with attention to consistent heat and stirring to prevent burning. Expert chefs emphasize the importance of gradual emulsification, where fat and liquid components are combined through slow whisking to create a smooth, glossy texture without separation. Precision in temperature control and timing ensures that reduction enhances depth while emulsification provides a balanced, cohesive sauce ideal for pasta dishes.
sauce reduction vs sauce emulsification for sauce technique Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com