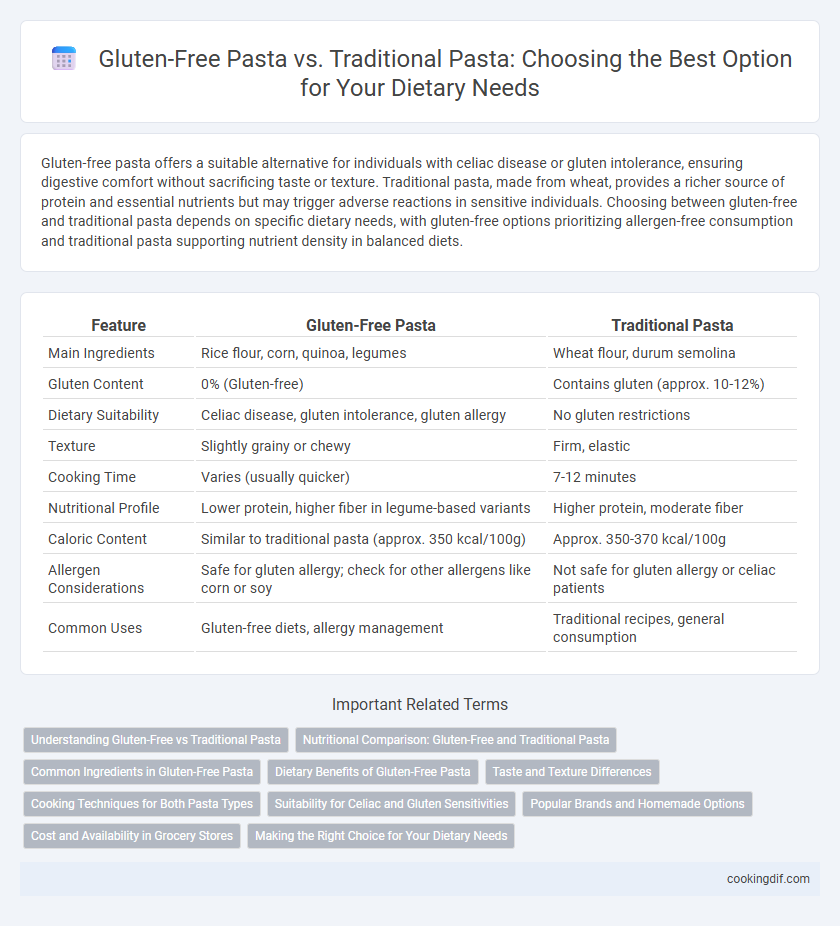
Gluten-free pasta offers a suitable alternative for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance, ensuring digestive comfort without sacrificing taste or texture. Traditional pasta, made from wheat, provides a richer source of protein and essential nutrients but may trigger adverse reactions in sensitive individuals. Choosing between gluten-free and traditional pasta depends on specific dietary needs, with gluten-free options prioritizing allergen-free consumption and traditional pasta supporting nutrient density in balanced diets.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gluten-Free Pasta | Traditional Pasta |
|---|---|---|
| Main Ingredients | Rice flour, corn, quinoa, legumes | Wheat flour, durum semolina |
| Gluten Content | 0% (Gluten-free) | Contains gluten (approx. 10-12%) |
| Dietary Suitability | Celiac disease, gluten intolerance, gluten allergy | No gluten restrictions |
| Texture | Slightly grainy or chewy | Firm, elastic |
| Cooking Time | Varies (usually quicker) | 7-12 minutes |
| Nutritional Profile | Lower protein, higher fiber in legume-based variants | Higher protein, moderate fiber |
| Caloric Content | Similar to traditional pasta (approx. 350 kcal/100g) | Approx. 350-370 kcal/100g |
| Allergen Considerations | Safe for gluten allergy; check for other allergens like corn or soy | Not safe for gluten allergy or celiac patients |
| Common Uses | Gluten-free diets, allergy management | Traditional recipes, general consumption |
Understanding Gluten-Free vs Traditional Pasta
Gluten-free pasta is made from alternative grains like rice, corn, or legumes, catering specifically to individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity who must avoid gluten to prevent adverse health effects. Traditional pasta, typically made from durum wheat semolina, contains gluten, which provides elasticity and a firm texture preferred by many but unsuitable for those with gluten-related disorders. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate pasta to meet dietary needs while maintaining taste and nutritional balance.
Nutritional Comparison: Gluten-Free and Traditional Pasta
Gluten-free pasta, typically made from rice, corn, or legumes, offers a suitable alternative for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, often providing higher protein and fiber content compared to traditional wheat-based pasta. Traditional pasta is rich in complex carbohydrates and provides essential nutrients like B vitamins and iron, but contains gluten, which can cause adverse reactions in sensitive individuals. Comparing both types helps cater to specific dietary requirements, especially for those seeking gluten-free options without compromising on nutritional value.
Common Ingredients in Gluten-Free Pasta
Gluten-free pasta commonly includes rice flour, corn flour, quinoa, and chickpea flour, providing alternatives suitable for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. These ingredients offer different textures and nutritional profiles compared to traditional wheat-based pasta, often contributing higher protein and fiber content. Choosing gluten-free options supports dietary restrictions while maintaining the enjoyment of pasta dishes.
Dietary Benefits of Gluten-Free Pasta
Gluten-free pasta caters to individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity by eliminating gluten, which can cause digestive distress and inflammation in these populations. It often contains alternative ingredients like rice, corn, or quinoa, providing a nutrient profile that supports digestive health and reduces the risk of gluten-related autoimmune reactions. Choosing gluten-free pasta can enhance overall gut health and energy levels for those with dietary restrictions, making it a beneficial option for gluten-intolerant individuals.
Taste and Texture Differences
Gluten-free pasta often features ingredients like rice, corn, or quinoa, resulting in a slightly different taste and a firmer, sometimes grainier texture compared to traditional wheat-based pasta. Traditional pasta offers a chewy, elastic bite due to gluten, enhancing the overall mouthfeel and sauce absorption. Taste preferences vary widely, with gluten-free options popular among those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, while traditional pasta remains preferred for its classic texture and flavor.
Cooking Techniques for Both Pasta Types
Gluten-free pasta requires careful attention to cooking time to avoid mushiness, often needing a shorter boil and immediate draining to maintain texture. Traditional pasta benefits from salted boiling water and stirring during cooking to prevent sticking and achieve al dente firmness. Both types improve in texture when rinsed briefly after cooking; however, gluten-free varieties may need gentle handling to preserve shape and prevent breakage.
Suitability for Celiac and Gluten Sensitivities
Gluten-free pasta is specifically designed for individuals with celiac disease and gluten sensitivities, as it eliminates wheat gluten, preventing adverse digestive reactions and autoimmune responses. Traditional pasta, made primarily from wheat flour, contains gluten and can trigger symptoms such as intestinal inflammation, bloating, and nutrient malabsorption in sensitive individuals. Choosing gluten-free pasta made from rice, corn, quinoa, or legumes supports a safe and balanced diet for those requiring strict gluten avoidance.
Popular Brands and Homemade Options
Gluten-free pasta from popular brands like Barilla and Tinkyada offers reliable alternatives for those with gluten sensitivities, made from ingredients such as rice, corn, or quinoa to mimic traditional pasta texture and flavor. Homemade gluten-free pasta recipes often utilize blends of almond flour, tapioca starch, and xanthan gum to achieve a similar elasticity and bite, catering to personalized dietary requirements. Traditional pasta brands like De Cecco and Barilla remain favored for their durum wheat composition, which provides essential nutrients and a classic taste for non-restricted diets.
Cost and Availability in Grocery Stores
Gluten-free pasta often costs significantly more than traditional pasta, with prices varying depending on the brand and ingredients like rice, corn, or quinoa flours. Availability of gluten-free pasta has improved but remains limited in many grocery stores compared to the wide variety of traditional wheat-based pasta options. For consumers with dietary needs or gluten intolerance, this price disparity and reduced shelf presence can impact shopping convenience and budget planning.
Making the Right Choice for Your Dietary Needs
Gluten-free pasta, made from alternative flours such as rice, corn, or quinoa, offers a suitable option for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, providing similar texture and taste without triggering adverse reactions. Traditional pasta, typically made from wheat flour, contains gluten, which supports elasticity and chewiness but must be avoided by those with gluten-related disorders. Selecting the right pasta depends on dietary restrictions, nutritional goals, and personal preferences, ensuring a balanced and safe meal choice.
Gluten-free pasta vs traditional pasta for dietary needs Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com