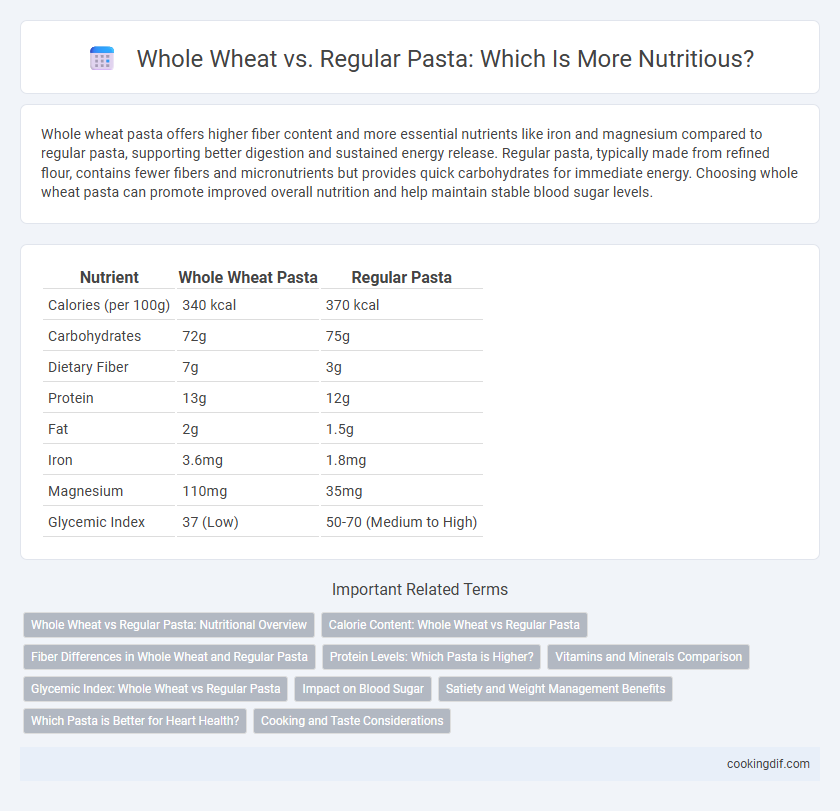
Whole wheat pasta offers higher fiber content and more essential nutrients like iron and magnesium compared to regular pasta, supporting better digestion and sustained energy release. Regular pasta, typically made from refined flour, contains fewer fibers and micronutrients but provides quick carbohydrates for immediate energy. Choosing whole wheat pasta can promote improved overall nutrition and help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Table of Comparison
| Nutrient | Whole Wheat Pasta | Regular Pasta |
|---|---|---|
| Calories (per 100g) | 340 kcal | 370 kcal |
| Carbohydrates | 72g | 75g |
| Dietary Fiber | 7g | 3g |
| Protein | 13g | 12g |
| Fat | 2g | 1.5g |
| Iron | 3.6mg | 1.8mg |
| Magnesium | 110mg | 35mg |
| Glycemic Index | 37 (Low) | 50-70 (Medium to High) |
Whole Wheat vs Regular Pasta: Nutritional Overview
Whole wheat pasta contains higher fiber content, typically around 6-8 grams per serving, compared to 2 grams in regular pasta, supporting better digestive health and prolonged satiety. It also offers increased levels of essential nutrients such as magnesium, zinc, and B vitamins, while regular pasta is often enriched but lacks the same natural nutrient density. The glycemic index of whole wheat pasta is lower, contributing to more stable blood sugar levels after consumption.
Calorie Content: Whole Wheat vs Regular Pasta
Whole wheat pasta contains approximately 120-140 calories per 2-ounce serving, while regular pasta typically has around 200 calories for the same portion size. The reduced calorie content in whole wheat pasta is due to its higher fiber and protein composition, which also promotes satiety. Choosing whole wheat pasta supports a lower calorie intake and improved nutritional quality compared to regular refined pasta.
Fiber Differences in Whole Wheat and Regular Pasta
Whole wheat pasta contains significantly higher dietary fiber compared to regular pasta, offering around 6-8 grams of fiber per serving versus 2 grams in traditional pasta. This increased fiber content supports better digestive health, aids in blood sugar regulation, and promotes satiety. Choosing whole wheat pasta enhances overall nutrient intake while contributing to improved metabolic outcomes.
Protein Levels: Which Pasta is Higher?
Whole wheat pasta contains approximately 7-8 grams of protein per 2-ounce serving, surpassing regular pasta, which typically offers around 5-6 grams. The increased protein content in whole wheat pasta comes from the bran and germ retained during processing, providing a richer nutritional profile. Choosing whole wheat pasta supports higher protein intake crucial for muscle repair and satiety in balanced diets.
Vitamins and Minerals Comparison
Whole wheat pasta contains higher levels of vitamins and minerals compared to regular pasta, including increased amounts of B vitamins such as thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, and folate. It also provides more essential minerals like iron, magnesium, and zinc, which contribute to improved metabolic functions and immune support. Regular pasta, made from refined wheat, has lower nutrient density due to the removal of bran and germ during processing.
Glycemic Index: Whole Wheat vs Regular Pasta
Whole wheat pasta has a lower glycemic index (GI) compared to regular pasta, typically ranging between 37-50 versus 50-65 for refined pasta. This lower GI means whole wheat pasta causes a slower, more gradual rise in blood glucose levels, beneficial for blood sugar management and sustained energy. Choosing whole wheat pasta supports better glycemic control and may aid in weight management and reducing risk of type 2 diabetes.
Impact on Blood Sugar
Whole wheat pasta has a lower glycemic index compared to regular pasta, leading to slower digestion and a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels. It contains higher fiber content, which helps improve insulin sensitivity and supports stable glucose metabolism. Choosing whole wheat pasta can benefit individuals managing blood sugar and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Satiety and Weight Management Benefits
Whole wheat pasta contains higher fiber content compared to regular pasta, which enhances satiety and helps control appetite by promoting a slower digestive process. The increased fiber and nutrient density in whole wheat pasta contribute to more stable blood sugar levels, supporting effective weight management and reducing cravings. Choosing whole wheat pasta over regular pasta can aid in maintaining a healthy weight due to its ability to keep you fuller for longer and improve overall metabolic health.
Which Pasta is Better for Heart Health?
Whole wheat pasta contains more fiber, antioxidants, and essential nutrients such as magnesium and potassium than regular pasta, which helps reduce cholesterol levels and improve cardiovascular health. Regular pasta, typically made from refined grains, lacks these heart-healthy compounds and can cause quicker spikes in blood sugar. Choosing whole wheat pasta supports better heart health by promoting lower blood pressure and reducing inflammation.
Cooking and Taste Considerations
Whole wheat pasta contains more fiber and nutrients like manganese and magnesium compared to regular pasta, but it requires longer cooking times and careful monitoring to avoid a gritty texture. Regular pasta cooks faster, offering a softer, more neutral taste that complements a wider variety of sauces. Taste preferences often lean toward regular pasta for its familiar texture, while whole wheat pasta appeals to those prioritizing nutritional benefits despite its denser, nuttier flavor.
Whole wheat vs regular pasta for nutrition Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com