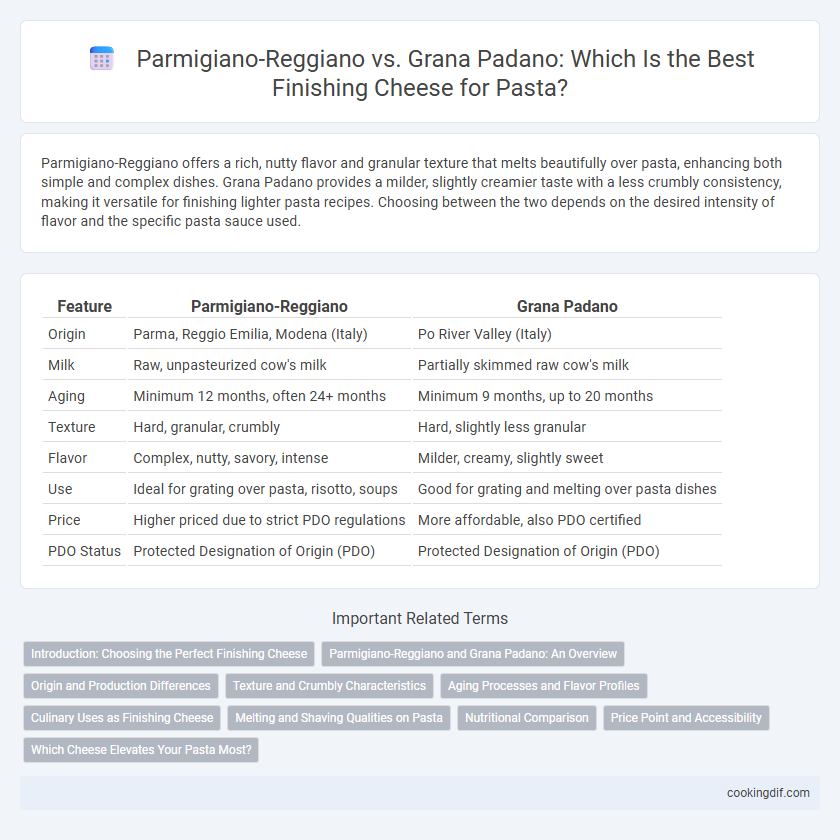
Parmigiano-Reggiano offers a rich, nutty flavor and granular texture that melts beautifully over pasta, enhancing both simple and complex dishes. Grana Padano provides a milder, slightly creamier taste with a less crumbly consistency, making it versatile for finishing lighter pasta recipes. Choosing between the two depends on the desired intensity of flavor and the specific pasta sauce used.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Parmigiano-Reggiano | Grana Padano |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Parma, Reggio Emilia, Modena (Italy) | Po River Valley (Italy) |
| Milk | Raw, unpasteurized cow's milk | Partially skimmed raw cow's milk |
| Aging | Minimum 12 months, often 24+ months | Minimum 9 months, up to 20 months |
| Texture | Hard, granular, crumbly | Hard, slightly less granular |
| Flavor | Complex, nutty, savory, intense | Milder, creamy, slightly sweet |
| Use | Ideal for grating over pasta, risotto, soups | Good for grating and melting over pasta dishes |
| Price | Higher priced due to strict PDO regulations | More affordable, also PDO certified |
| PDO Status | Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) | Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) |
Introduction: Choosing the Perfect Finishing Cheese
Parmigiano-Reggiano and Grana Padano both deliver rich, nutty flavors ideal for finishing pasta dishes, but they differ in texture and aging processes that influence taste intensity. Parmigiano-Reggiano, aged a minimum of 12 months, offers a crystalline, granular texture and a complex umami profile, making it perfect for enhancing hearty sauces. Grana Padano, with a shorter aging period of 9-16 months, provides a milder, creamier flavor that complements lighter pasta preparations without overpowering delicate ingredients.
Parmigiano-Reggiano and Grana Padano: An Overview
Parmigiano-Reggiano and Grana Padano are two premier Italian cheeses often used as finishing touches on pasta dishes. Parmigiano-Reggiano is known for its complex, nutty flavor and granular texture due to a minimum aging period of 12 months, offering a richer taste profile ideal for enhancing the depth of pasta sauces. Grana Padano, aged between 9 to 24 months, provides a milder, slightly sweeter flavor with a smoother texture, making it a versatile alternative for pasta finishing that balances taste and affordability.
Origin and Production Differences
Parmigiano-Reggiano, produced exclusively in specific provinces of Italy such as Parma and Reggio Emilia, undergoes a strict aging process of at least 12 months, contributing to its intense, granular texture. Grana Padano comes from a wider geographic area across the Po River Valley, including Lombardy and Veneto, and typically ages for a minimum of 9 months, resulting in a milder flavor and creamier consistency. The production of Parmigiano-Reggiano excludes the use of any additives like preservatives, whereas Grana Padano permits the addition of lysozyme to control bacteria growth, influencing differences in texture and taste between the two cheeses.
Texture and Crumbly Characteristics
Parmigiano-Reggiano features a granular, slightly crystalline texture that crumbles easily, making it ideal for sprinkling over pasta dishes for a balanced, nutty flavor. Grana Padano offers a smoother, less crumbly texture with a subtler aroma, providing a creamy finish without overpowering the dish. The distinct crumbly characteristic of Parmigiano-Reggiano enhances mouthfeel, while Grana Padano's softer texture melts more readily into pasta sauces.
Aging Processes and Flavor Profiles
Parmigiano-Reggiano undergoes a minimum aging process of 12 months, often extending to 24-36 months, resulting in a complex, nutty flavor with granular texture ideal for finishing pasta dishes. Grana Padano is aged for a minimum of 9 months, sometimes up to 20 months, offering a milder, creamier profile with less intense umami notes. The longer aging in Parmigiano-Reggiano develops sharper, more pronounced savory qualities, making it a preferred choice for robust pasta sauces, while Grana Padano's subtler flavor complements lighter recipes.
Culinary Uses as Finishing Cheese
Parmigiano-Reggiano offers a robust, nutty flavor with granular texture, ideal for grating over pasta dishes to enhance umami depth and complexity. Grana Padano provides a milder, creamier taste with a slightly softer texture, making it suitable for a subtler finish on delicate pasta or risotto recipes. Both cheeses melt well but Parmigiano-Reggiano's intense flavor profile is preferred for bold sauces, while Grana Padano complements lighter culinary preparations.
Melting and Shaving Qualities on Pasta
Parmigiano-Reggiano offers superior melting qualities, creating a creamy texture that enhances pasta dishes, while Grana Padano provides a slightly milder melt with a less granular consistency. The firm texture of Parmigiano-Reggiano allows for cleaner, more delicate shavings that evenly distribute over hot pasta. Grana Padano's softer body makes it easier to grate finely but produces thicker shavings that add a subtle crunch and nutty flavor.
Nutritional Comparison
Parmigiano-Reggiano contains higher protein content, approximately 38 grams per 100 grams, compared to Grana Padano's 33 grams, making it a richer source of essential amino acids. Both cheeses offer comparable calcium levels, around 1100 mg per 100 grams, supporting bone health, but Parmigiano-Reggiano typically has lower fat content and fewer calories per serving. The aging process of Parmigiano-Reggiano also increases its digestibility and concentration of bioactive peptides, enhancing its nutritional profile for finishing pasta dishes.
Price Point and Accessibility
Parmigiano-Reggiano commands a higher price point due to its strict production regulations and longer aging process, making it a premium finishing cheese for pasta dishes. Grana Padano offers a more affordable and widely accessible alternative, with a slightly milder flavor profile and faster aging period. Both cheeses provide authentic Italian taste, but Grana Padano is often preferred for everyday use due to its cost-effectiveness and availability.
Which Cheese Elevates Your Pasta Most?
Parmigiano-Reggiano and Grana Padano both enhance pasta with rich, nutty flavors, but Parmigiano-Reggiano's aged complexity and granular texture offer a more intense umami profile that elevates dishes to a gourmet level. Grana Padano's milder taste and slightly creamier consistency make it a versatile option for a subtle finishing touch. For pasta lovers seeking a robust, savory finish, Parmigiano-Reggiano is the preferred choice to intensify flavor depth.
Parmigiano-Reggiano vs Grana Padano for finishing cheese Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com