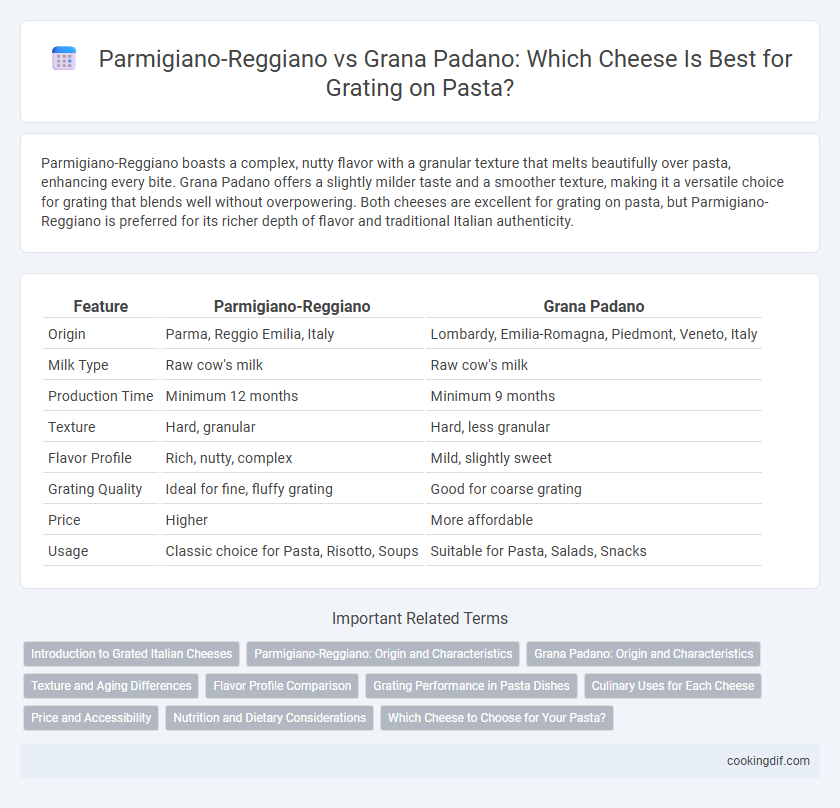
Parmigiano-Reggiano boasts a complex, nutty flavor with a granular texture that melts beautifully over pasta, enhancing every bite. Grana Padano offers a slightly milder taste and a smoother texture, making it a versatile choice for grating that blends well without overpowering. Both cheeses are excellent for grating on pasta, but Parmigiano-Reggiano is preferred for its richer depth of flavor and traditional Italian authenticity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Parmigiano-Reggiano | Grana Padano |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Parma, Reggio Emilia, Italy | Lombardy, Emilia-Romagna, Piedmont, Veneto, Italy |
| Milk Type | Raw cow's milk | Raw cow's milk |
| Production Time | Minimum 12 months | Minimum 9 months |
| Texture | Hard, granular | Hard, less granular |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, nutty, complex | Mild, slightly sweet |
| Grating Quality | Ideal for fine, fluffy grating | Good for coarse grating |
| Price | Higher | More affordable |
| Usage | Classic choice for Pasta, Risotto, Soups | Suitable for Pasta, Salads, Snacks |
Introduction to Grated Italian Cheeses
Parmigiano-Reggiano and Grana Padano are two iconic grated Italian cheeses renowned for their rich umami flavor and granular texture, perfect for enhancing pasta dishes. Parmigiano-Reggiano, aged a minimum of 12 months, offers a complex, nutty taste with a dry, crumbly consistency, while Grana Padano matures for at least 9 months, delivering a milder, creamier profile. Both cheeses originate from northern Italy's dairy regions and provide essential depth and savory intensity when freshly grated over traditional pasta recipes.
Parmigiano-Reggiano: Origin and Characteristics
Parmigiano-Reggiano, originating from the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy, is renowned for its rich, nutty flavor and granular texture, making it ideal for grating over pasta dishes. Produced under strict regulations, this cheese ages for a minimum of 12 months, developing a complex taste profile with hints of fruit and savory notes. Its crystalline structure enhances grating efficiency, creating a fluffy topping that melts beautifully into hot pasta, distinguishing it from the milder and less granular Grana Padano.
Grana Padano: Origin and Characteristics
Grana Padano, originating from the Po River Valley in Northern Italy, is a semi-fat hard cheese aged between 9 to 24 months, offering a slightly milder and sweeter flavor compared to Parmigiano-Reggiano. Made from partially skimmed raw milk, its granular texture makes it ideal for grating over pasta dishes, enhancing flavor without overpowering. The cheese's Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) status ensures traditional production methods and regional authenticity, making it a favored choice for authentic Italian cuisine.
Texture and Aging Differences
Parmigiano-Reggiano offers a granular, crystalline texture that enhances pasta dishes with a robust, nutty flavor developed through aging periods of 12 to 36 months. Grana Padano, aged between 9 and 24 months, has a slightly softer, less crumbly texture that yields a milder, creamier taste when grated. These textural and aging contrasts influence the cheese's melting properties and depth of flavor, making Parmigiano-Reggiano preferable for sharp, aged intensity and Grana Padano suited for smoother, delicate finishes on pasta.
Flavor Profile Comparison
Parmigiano-Reggiano offers a robust, nutty flavor with deep umami notes, making it ideal for enhancing the complexity of pasta dishes. Grana Padano presents a milder, creamier taste with slightly sweet undertones that blend smoothly without overpowering other ingredients. Both cheeses deliver a granular texture perfect for grating, but Parmigiano-Reggiano intensifies savory profiles while Grana Padano provides subtle richness.
Grating Performance in Pasta Dishes
Grana Padano offers a slightly softer texture than Parmigiano-Reggiano, making it easier to grate finely over hot pasta dishes for even flavor distribution. Its balanced saltiness and nutty notes enhance pasta sauces without overpowering the dish, while Parmigiano-Reggiano's sharper and more granular texture delivers a robust taste with a coarser grate. For optimal grating performance, Grana Padano's consistent texture allows for quick melting and smoother integration into creamy pasta preparations.
Culinary Uses for Each Cheese
Parmigiano-Reggiano offers a sharper, nuttier flavor ideal for finishing rich pasta dishes like carbonara and cacio e pepe, enhancing depth and umami. Grana Padano has a milder, creamier taste, making it perfect for melting into risottos, polenta, or lighter pasta sauces where subtle cheese notes complement without overpowering. Both cheeses excel when freshly grated, but Parmigiano-Reggiano's granular texture provides a more robust topping, while Grana Padano's finer crumb melts smoothly, balancing texture and flavor in various culinary applications.
Price and Accessibility
Parmigiano-Reggiano typically commands a higher price due to its strict production regulations and longer aging process, making it a premium choice for grating over pasta. Grana Padano offers a more affordable alternative with widespread availability in supermarkets, providing good quality at a lower cost. Both cheeses deliver rich umami flavors, but Grana Padano is often preferred for budget-conscious consumers seeking easy access without compromising taste.
Nutrition and Dietary Considerations
Parmigiano-Reggiano and Grana Padano both offer rich protein content and essential minerals like calcium and phosphorus, supporting bone health and muscle function in pasta dishes. Parmigiano-Reggiano tends to have a longer aging process, resulting in more concentrated nutrients and a stronger flavor, while Grana Padano generally has lower fat content and slightly fewer calories, beneficial for calorie-conscious diets. Both cheeses are naturally lactose-free due to aging, making them suitable for lactose-intolerant individuals seeking nutritional benefits in their pasta meals.
Which Cheese to Choose for Your Pasta?
Parmigiano-Reggiano offers a robust, nutty flavor with granular texture ideal for grating over pasta, enhancing dishes like spaghetti carbonara and fettuccine Alfredo. Grana Padano presents a milder, creamier taste and a slightly softer texture, perfect for a subtler finish on risotto or penne. For authentic Italian pasta recipes requiring bold seasoning, Parmigiano-Reggiano is preferred; for gentle flavor that complements without overpowering, Grana Padano is a suitable choice.
Parmigiano-Reggiano vs Grana Padano for grating Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com