Melted butter adds a rich, creamy flavor and tender texture to pancake batter, enhancing overall taste and mouthfeel. Vegetable oil, on the other hand, provides a lighter, more neutral fat that helps pancakes stay moist without overpowering other flavors. Choosing between the two depends on whether a buttery richness or a lighter, more delicate texture is preferred in the final pancake.
Table of Comparison
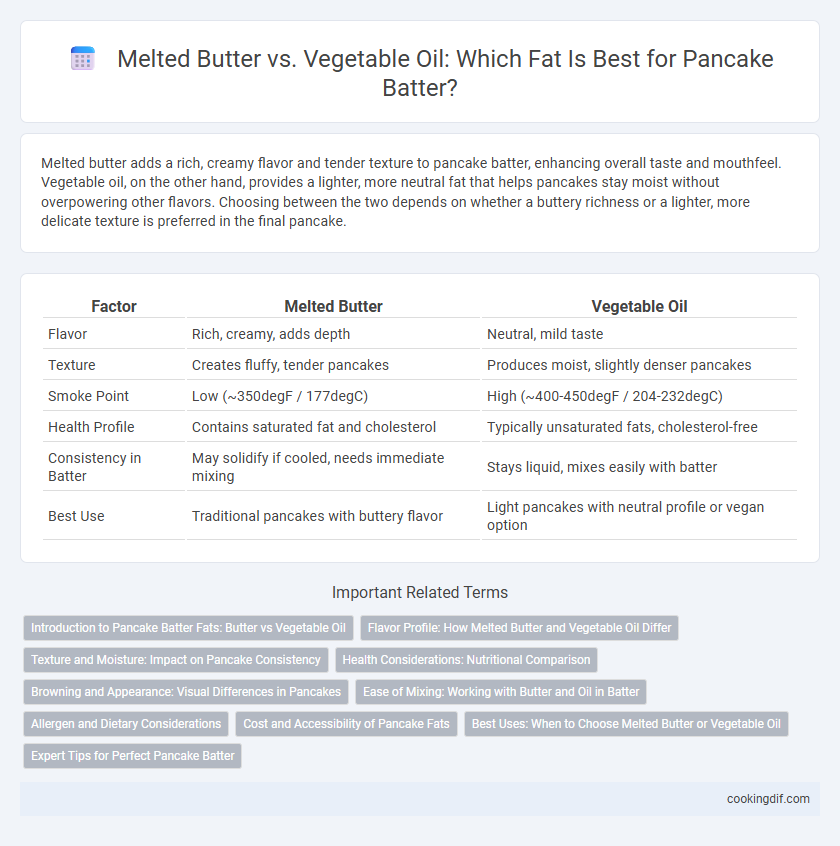
| Factor | Melted Butter | Vegetable Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor | Rich, creamy, adds depth | Neutral, mild taste |
| Texture | Creates fluffy, tender pancakes | Produces moist, slightly denser pancakes |
| Smoke Point | Low (~350degF / 177degC) | High (~400-450degF / 204-232degC) |
| Health Profile | Contains saturated fat and cholesterol | Typically unsaturated fats, cholesterol-free |
| Consistency in Batter | May solidify if cooled, needs immediate mixing | Stays liquid, mixes easily with batter |
| Best Use | Traditional pancakes with buttery flavor | Light pancakes with neutral profile or vegan option |
Introduction to Pancake Batter Fats: Butter vs Vegetable Oil
Butter provides rich flavor and a tender texture to pancake batter due to its milk solids and natural fats, enhancing browning and taste complexity. Vegetable oil offers a neutral flavor and maintains moisture, producing lighter, fluffier pancakes without added butter's richness. Choosing between melted butter and vegetable oil depends on desired pancake texture and flavor profile, with butter favoring indulgence and oil emphasizing simplicity and lightness.
Flavor Profile: How Melted Butter and Vegetable Oil Differ
Melted butter imparts a rich, creamy flavor and a slightly nutty aroma to pancake batter, enhancing the overall taste with its natural dairy notes. Vegetable oil offers a more neutral, subtle flavor that allows other ingredients like vanilla or spices to stand out without adding any distinct taste of its own. Choosing melted butter results in a more indulgent and flavorful pancake, while vegetable oil yields a lighter flavor profile suitable for those preferring less richness.
Texture and Moisture: Impact on Pancake Consistency
Melted butter imparts a rich, creamy texture and enhances moisture retention in pancakes, resulting in a tender, fluffy consistency. Vegetable oil creates a lighter, slightly more elastic batter that yields pancakes with a softer crumb and subtle moisture. The choice between melted butter and vegetable oil directly affects the overall mouthfeel and moistness of the final pancake, influencing its appeal and texture.
Health Considerations: Nutritional Comparison
Melted butter adds saturated fats and fat-soluble vitamins like A and E to pancake batter, which may raise LDL cholesterol levels. Vegetable oil, typically containing unsaturated fats, supports heart health by reducing bad cholesterol and providing essential fatty acids. Choosing vegetable oil over butter can offer a healthier fat profile for pancake recipes without compromising texture.
Browning and Appearance: Visual Differences in Pancakes
Melted butter in pancake batter enhances browning due to its milk solids caramelizing, resulting in a richer golden hue and a slightly crispier edge. Vegetable oil yields a more uniform, lighter color, lacking the deeper caramelization that butter provides. Appearance-wise, butter-based pancakes often display small brown speckles and a more inviting, appetizing look compared to the paler, smoother finish of oil-based pancakes.
Ease of Mixing: Working with Butter and Oil in Batter
Melted butter creates a denser batter that can require more thorough mixing to achieve a smooth consistency, as it solidifies slightly when cooled. Vegetable oil blends seamlessly into the batter, resulting in easier mixing and a more uniform texture without the risk of clumping. Choosing vegetable oil often simplifies the batter preparation process due to its consistent liquid state at room temperature.
Allergen and Dietary Considerations
Melted butter provides a rich flavor but contains dairy allergens, making it unsuitable for those with lactose intolerance or milk allergies. Vegetable oil is a dairy-free alternative, ideal for vegan diets and individuals with milk sensitivities, while also offering a neutral taste that does not overpower the pancake batter. Choosing between butter and vegetable oil for pancake batter depends on dietary restrictions and allergen concerns to ensure safe and enjoyable consumption.
Cost and Accessibility of Pancake Fats
Melted butter offers rich flavor but tends to be pricier and less shelf-stable compared to vegetable oil, impacting overall pancake cost efficiency. Vegetable oil is widely available, budget-friendly, and has a longer shelf life, making it a practical choice for consistent pancake preparation. Selecting between these fats balances cost considerations with desired taste and pantry accessibility.
Best Uses: When to Choose Melted Butter or Vegetable Oil
Melted butter enhances pancake batter with rich flavor and a tender crumb, making it ideal for recipes aiming for a classic, buttery taste and softer texture. Vegetable oil provides a neutral taste and promotes a moist, fluffy pancake, best suited for when a lighter flavor is desired or for allergy-friendly, dairy-free options. Choosing between melted butter and vegetable oil depends on the flavor preference and dietary requirements, with butter favored for richness and oil preferred for moisture and neutrality.
Expert Tips for Perfect Pancake Batter
Melted butter enhances pancake batter by adding rich flavor and a tender crumb due to its milk solids, whereas vegetable oil provides a neutral taste and maintains a lighter texture. Experts recommend using clarified butter to avoid sogginess or substituting with vegetable oil for a dairy-free option, ensuring optimal batter consistency. Balancing fat type and quantity in the batter is crucial for achieving golden, fluffy pancakes with a moist interior.
Melted butter vs vegetable oil for batter fat Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com