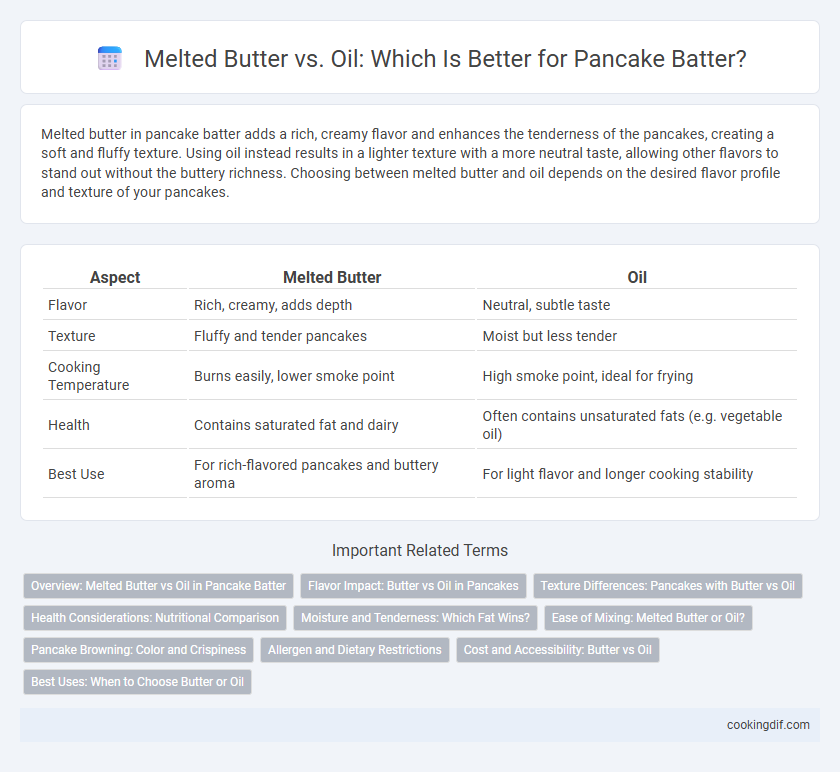
Melted butter in pancake batter adds a rich, creamy flavor and enhances the tenderness of the pancakes, creating a soft and fluffy texture. Using oil instead results in a lighter texture with a more neutral taste, allowing other flavors to stand out without the buttery richness. Choosing between melted butter and oil depends on the desired flavor profile and texture of your pancakes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Melted Butter | Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor | Rich, creamy, adds depth | Neutral, subtle taste |
| Texture | Fluffy and tender pancakes | Moist but less tender |
| Cooking Temperature | Burns easily, lower smoke point | High smoke point, ideal for frying |
| Health | Contains saturated fat and dairy | Often contains unsaturated fats (e.g. vegetable oil) |
| Best Use | For rich-flavored pancakes and buttery aroma | For light flavor and longer cooking stability |
Overview: Melted Butter vs Oil in Pancake Batter
Melted butter adds a rich, creamy flavor and a tender texture to pancake batter, enhancing the overall taste experience. Oil, such as vegetable or canola, creates a lighter, fluffier pancake with a moist interior and often improves batter consistency due to its neutral flavor. Choosing between melted butter and oil depends on desired flavor intensity and texture preferences in the final pancake.
Flavor Impact: Butter vs Oil in Pancakes
Melted butter imparts a rich, creamy flavor and a slightly nutty aroma to pancake batter, enhancing overall taste with its natural dairy notes. Oil, typically neutral in flavor, allows other ingredients to shine without adding complexity but results in a lighter mouthfeel. Choosing butter over oil intensifies the pancake's flavor profile and creates a more indulgent texture, preferred in traditional recipes.
Texture Differences: Pancakes with Butter vs Oil
Melted butter in pancake batter creates a richer, tender texture with a slightly crisp edge due to the milk solids caramelizing during cooking. Oil results in pancakes that are softer and moister, as it coats flour proteins more uniformly, preventing excessive gluten formation. The choice between butter and oil significantly impacts the mouthfeel and density, with butter offering a more delicate crumb and oil producing a denser, chewier pancake.
Health Considerations: Nutritional Comparison
Melted butter in pancake batter offers higher levels of saturated fat and cholesterol compared to vegetable oils, which typically contain healthier unsaturated fats beneficial for heart health. Oils like olive or canola contribute essential fatty acids and vitamin E, supporting cardiovascular function and reducing inflammation. Choosing oil over melted butter can lower calorie density and improve the nutritional profile of pancakes, aligning with heart-healthy dietary guidelines.
Moisture and Tenderness: Which Fat Wins?
Melted butter enhances pancake batter by adding rich moisture and a tender crumb due to its dairy fat and water content, which promotes steam during cooking. Oil contributes a softer texture by coating flour proteins more thoroughly, preventing gluten overdevelopment and yielding tender pancakes. For optimal moisture and tenderness, melted butter offers a flavorful lift, while oil ensures consistently soft, delicate pancakes.
Ease of Mixing: Melted Butter or Oil?
Melted butter incorporates more easily into pancake batter due to its creamy texture, promoting a smoother and more consistent blend compared to oil. Oil tends to separate from the batter without vigorous mixing, potentially causing uneven distribution. Choosing melted butter enhances batter homogeneity, resulting in fluffier and more evenly cooked pancakes.
Pancake Browning: Color and Crispiness
Melted butter in pancake batter enhances browning due to its milk solids, which caramelize and create a rich golden color and crisp texture. Oil, lacking these solids, results in lighter-colored pancakes with a softer, less crispy surface. For optimal pancake browning and crispiness, melted butter provides superior Maillard reaction benefits compared to oil.
Allergen and Dietary Restrictions
Melted butter in pancake batter contains dairy allergens, potentially triggering reactions in individuals with lactose intolerance or milk allergies, while oil offers a dairy-free alternative suitable for vegan and lactose-sensitive diets. Choosing oil, such as canola or vegetable oil, supports allergen-free pancake preparation, reducing the risk for those with milk protein allergens. This substitution ensures adherence to dietary restrictions without compromising batter texture or flavor.
Cost and Accessibility: Butter vs Oil
Butter typically costs more than most cooking oils, making oil a more budget-friendly option for pancake batter. Widely available vegetable or canola oils offer consistent accessibility in stores year-round, whereas butter may be seasonal or subject to price fluctuations. Both options provide convenient sources of fat, but oil's lower price and broader availability make it ideal for frequent pancake preparation.
Best Uses: When to Choose Butter or Oil
Melted butter in pancake batter enhances flavor with a rich, creamy taste and promotes a tender, fluffy texture, ideal for classic or buttermilk pancakes where taste is paramount. Oil contributes to a lighter, moister pancake with a slightly crisp edge, making it suitable for recipes needing a neutral flavor or when dairy-free options are preferred. Choose butter for indulgent, buttery pancakes and oil for healthier or vegan variations that emphasize moisture and softness.
Melted butter vs oil for pancake batter Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com