Mozzarella offers a creamy texture and mild flavor that melts smoothly, making it a classic choice for lasagna layers. Provolone provides a sharper, more robust taste with a slightly firmer melt, adding depth and complexity to the dish. Combining both cheeses creates a balanced lasagna with rich creaminess and bold flavor notes.
Table of Comparison
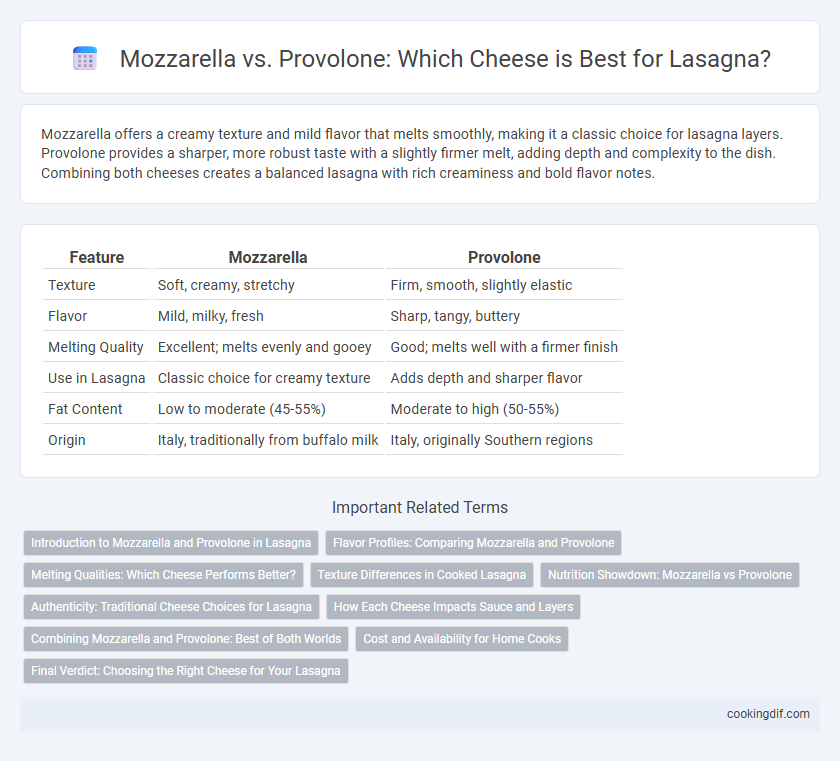
| Feature | Mozzarella | Provolone |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Soft, creamy, stretchy | Firm, smooth, slightly elastic |
| Flavor | Mild, milky, fresh | Sharp, tangy, buttery |
| Melting Quality | Excellent; melts evenly and gooey | Good; melts well with a firmer finish |
| Use in Lasagna | Classic choice for creamy texture | Adds depth and sharper flavor |
| Fat Content | Low to moderate (45-55%) | Moderate to high (50-55%) |
| Origin | Italy, traditionally from buffalo milk | Italy, originally Southern regions |
Introduction to Mozzarella and Provolone in Lasagna
Mozzarella, prized for its creamy texture and excellent melting properties, is a staple cheese in traditional lasagna, providing a rich, gooey layer that enhances the dish's moisture and flavor balance. Provolone offers a sharper, slightly tangy taste with a firmer texture, introducing a distinct depth when blended into lasagna cheese layers or used as a topping. Both cheeses contribute unique flavor profiles and melting characteristics, making them popular choices for customizing authentic Italian lasagna recipes.
Flavor Profiles: Comparing Mozzarella and Provolone
Mozzarella offers a mild, creamy flavor with a smooth texture that melts evenly, making it ideal for the classic, gooey lasagna experience. Provolone delivers a sharper, more tangy taste with a slightly smokier undertone, adding complexity and depth to the dish. Choosing between mozzarella and provolone depends on whether you prefer a subtle, traditional cheese or a bolder, more pronounced flavor profile in your lasagna.
Melting Qualities: Which Cheese Performs Better?
Mozzarella melts more uniformly and creates a smooth, creamy texture that enhances the layers of lasagna, making it the preferred choice for achieving a classic, gooey consistency. Provolone, while also melting well, offers a slightly sharper flavor and a firmer texture that can add complexity but may not provide the same silky melt as mozzarella. For optimal melting performance and the traditional lasagna experience, mozzarella consistently outperforms provolone.
Texture Differences in Cooked Lasagna
Mozzarella offers a creamy, stringy texture that melts smoothly, creating a classic, gooey layer in cooked lasagna. Provolone provides a firmer texture with a slightly sharper bite, which adds a denser and more robust chew to the dish. Choosing mozzarella enhances the lasagna's melt and stretch, while provolone contributes a richer mouthfeel and complexity.
Nutrition Showdown: Mozzarella vs Provolone
Mozzarella contains approximately 280 calories and 22 grams of protein per 100 grams, offering a lower fat content compared to Provolone, which has about 350 calories and 27 grams of protein per 100 grams. Mozzarella is also richer in calcium, providing around 505 mg per serving, essential for bone health, while Provolone offers higher sodium levels, which may affect cardiovascular health concerns. Choosing between these cheeses for lasagna depends on dietary goals, with Mozzarella favored for lower fat and higher calcium intake and Provolone for a stronger flavor coupled with increased protein.
Authenticity: Traditional Cheese Choices for Lasagna
Mozzarella remains the quintessential cheese for authentic lasagna, prized for its creamy meltability and mild flavor that complements the layered pasta and tomato sauce. Provolone, often used as a secondary cheese, provides a sharper, tangier contrast that enhances depth without overpowering the classic taste. Traditional Italian recipes emphasize fresh mozzarella to maintain the dish's genuine texture and flavor profile, while provolone is reserved for variations aiming to add complexity.
How Each Cheese Impacts Sauce and Layers
Mozzarella provides a creamy, melty texture that enhances the sauce's richness and creates smooth, gooey layers in lasagna. Provolone offers a slightly sharper, tangier flavor with a firmer melt, adding depth and a subtle bite to the sauce and distinct, structured layers. Using mozzarella results in a more cohesive, velvety cheese distribution, while provolone introduces a layered complexity that complements hearty tomato sauces.
Combining Mozzarella and Provolone: Best of Both Worlds
Combining mozzarella and provolone in lasagna delivers a rich balance of creamy texture and sharp flavor, enhancing the overall taste profile. Mozzarella's smooth meltability complements provolone's slightly tangy and smoky notes, creating a complex cheese layer that elevates each bite. This blend improves the lasagna's structural integrity and depth, appealing to those seeking a traditional yet flavorful Italian experience.
Cost and Availability for Home Cooks
Mozzarella is typically more affordable and widely available in grocery stores, making it the preferred cheese for home cooks preparing lasagna on a budget. Provolone, while offering a sharper flavor, tends to be pricier and found mainly in specialty or deli sections. Choosing mozzarella ensures easier access and better cost efficiency without compromising the classic texture and melt needed for lasagna.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Cheese for Your Lasagna
Mozzarella offers a creamy, mild texture that melts smoothly, making it a classic choice for traditional lasagna recipes, while provolone provides a sharper, more robust flavor that enhances depth and complexity. Selecting mozzarella results in a balanced, gooey layer that complements tomato sauce and bechamel, whereas provolone adds a bold bite suited for those seeking a rich, tangy profile. The final verdict depends on personal taste preference: mozzarella for a traditional, milder experience, and provolone for a distinctive, flavorful twist.
Mozzarella vs Provolone for cheese Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com