Classic Italian lasagna features thin layers of pasta, rich bechamel sauce, and a delicate meat ragu, highlighting simplicity and balanced flavors. American lasagna tends to be heartier, with thick layers, generous amounts of ricotta and mozzarella cheese, and often includes ground beef or sausage for a robust taste. Both styles offer distinct approaches to texture and flavor, catering to different preferences for a comforting, satisfying meal.
Table of Comparison
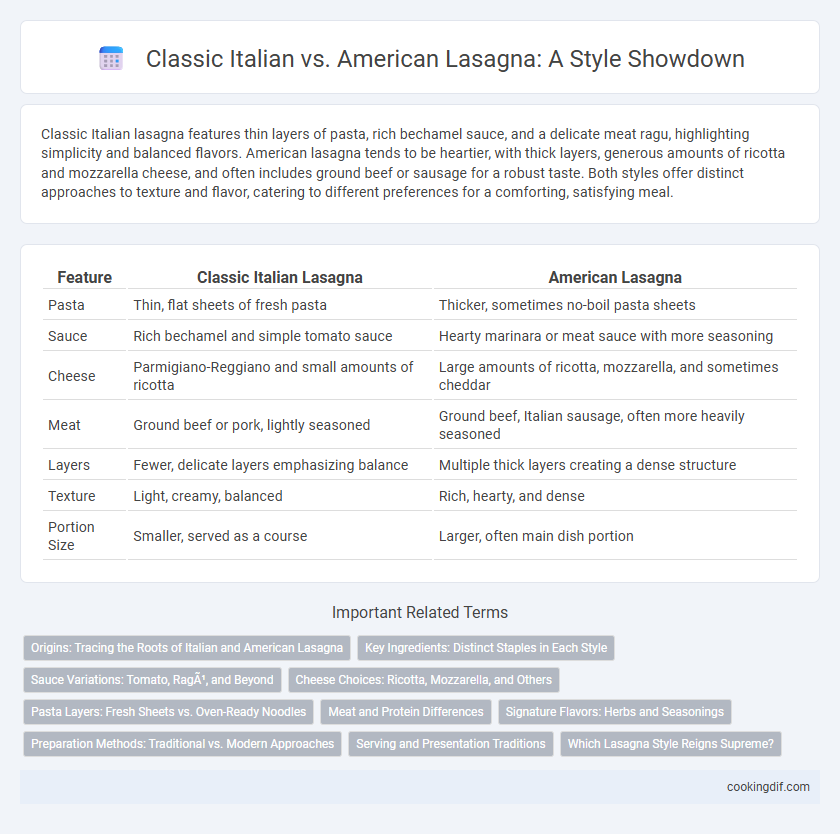
| Feature | Classic Italian Lasagna | American Lasagna |
|---|---|---|
| Pasta | Thin, flat sheets of fresh pasta | Thicker, sometimes no-boil pasta sheets |
| Sauce | Rich bechamel and simple tomato sauce | Hearty marinara or meat sauce with more seasoning |
| Cheese | Parmigiano-Reggiano and small amounts of ricotta | Large amounts of ricotta, mozzarella, and sometimes cheddar |
| Meat | Ground beef or pork, lightly seasoned | Ground beef, Italian sausage, often more heavily seasoned |
| Layers | Fewer, delicate layers emphasizing balance | Multiple thick layers creating a dense structure |
| Texture | Light, creamy, balanced | Rich, hearty, and dense |
| Portion Size | Smaller, served as a course | Larger, often main dish portion |
Origins: Tracing the Roots of Italian and American Lasagna
Classic Italian lasagna, originating from Emilia-Romagna, emphasizes layered pasta sheets with bechamel sauce, ragu alla Bolognese, and Parmigiano-Reggiano, reflecting regional simplicity and rich culinary tradition. American lasagna adapts this foundation by incorporating ricotta cheese, mozzarella, and a variety of meat or vegetable fillings, showcasing a heartier, more customizable style that evolved through Italian immigrant communities. The contrast between traditional Italian and American versions highlights cultural influences on ingredients, cooking techniques, and flavor preferences in lasagna's evolution.
Key Ingredients: Distinct Staples in Each Style
Classic Italian lasagna features thin sheets of pasta layered with ricotta, bechamel sauce, and a rich ragu made from ground beef, pork, or veal combined with tomatoes and herbs, emphasizing delicate flavors and textures. American lasagna typically uses thicker pasta sheets, abundant mozzarella cheese, ricotta, and a robust tomato-based meat sauce often seasoned with garlic and Italian spices for a heartier taste. Key ingredient distinctions highlight Italian lasagna's creamy bechamel and subtle ragu versus American lasagna's emphasis on cheese layers and a more pronounced, spiced tomato sauce.
Sauce Variations: Tomato, Ragù, and Beyond
Classic Italian lasagna typically features a rich ragu made from seasoned ground meat, tomato sauce, and a blend of bechamel and Parmesan cheese, emphasizing balanced layers of flavor and texture. American lasagna often incorporates a thicker tomato sauce, ricotta cheese instead of bechamel, and a heartier, sometimes sweeter, flavor profile with additional ingredients like garlic and Italian sausage. Sauce variations in both styles highlight regional preferences, with Italian ragu focusing on slow-cooked depth, while American versions embrace robust, tomato-heavy sauces.
Cheese Choices: Ricotta, Mozzarella, and Others
Classic Italian lasagna typically features ricotta cheese blended with Parmesan or Pecorino Romano, providing a rich and slightly tangy flavor that complements the bechamel sauce and meat ragu. American lasagna often emphasizes layers of mozzarella for its gooey meltiness, combined with ricotta or cottage cheese to create a creamy texture that balances hearty tomato sauce and ground beef. Variations in cheese choices influence the dish's texture and flavor profile, with Italian versions leaning towards subtlety and complexity, while American styles favor bold, cheesy richness.
Pasta Layers: Fresh Sheets vs. Oven-Ready Noodles
Classic Italian lasagna traditionally features fresh pasta sheets made from flour and eggs, offering a tender texture and subtle flavor that absorbs sauces well. American lasagna often uses oven-ready noodles, which save preparation time but provide a firmer bite and less integration with the layers. The choice between fresh sheets and oven-ready noodles significantly influences the dish's consistency and overall dining experience.
Meat and Protein Differences
Classic Italian lasagna emphasizes a lighter texture using thin layers of pasta, ricotta or bechamel sauce, and a moderate amount of ground beef or pork combined with tomato sauce. American lasagna typically features thicker pasta sheets, generous quantities of ground beef or sausage, and abundant ricotta or mozzarella cheeses, creating a richer and heavier dish. The protein focus in Italian style leans towards balanced flavors with less meat, while American versions prioritize a hearty, protein-dense experience.
Signature Flavors: Herbs and Seasonings
Classic Italian lasagna highlights the robust flavors of fresh basil, oregano, and garlic, blending ricotta cheese with a rich, slow-simmered tomato sauce seasoned with hints of nutmeg and black pepper. American lasagna tends to emphasize heavier seasoning, incorporating Italian sausage, crushed red pepper flakes, and a mix of mozzarella and Parmesan cheeses for a bolder, more pungent profile. The Italian style leans toward subtle herbaceous notes that complement the pasta layers, while the American version delivers a spicier, meat-forward taste with intensified seasoning blends.
Preparation Methods: Traditional vs. Modern Approaches
Classic Italian lasagna emphasizes fresh pasta sheets, a rich bechamel sauce, and a slow-cooked ragu made from high-quality meats and tomatoes, layered meticulously for balanced flavors and textures. In contrast, American lasagna often incorporates pre-cooked noodles, abundant ricotta cheese, and a heavier use of tomato sauce, favoring convenience and a heartier, cheesier profile. Traditional Italian preparation relies on time-honored techniques and carefully selected regional ingredients, whereas modern American approaches adapt recipes for speed and accessibility, sometimes incorporating varied meats and additional cheeses.
Serving and Presentation Traditions
Classic Italian lasagna features thin pasta sheets layered with bechamel sauce, ragu, and Parmesan, emphasizing a delicate, refined presentation often served in modest portions. American lasagna tends to incorporate thicker noodles, ricotta cheese, and abundant mozzarella, creating a hearty, rustic style typically presented in large, generous slices. Serving traditions in Italy prioritize elegance and balance, while American versions focus on comfort and quantity, reflecting distinct culinary values.
Which Lasagna Style Reigns Supreme?
Classic Italian lasagna features thin sheets of pasta layered with bechamel sauce, ricotta, Parmesan, and a rich ragu made from slow-cooked beef and tomatoes, delivering a balanced, elegant flavor profile. American lasagna tends to be heartier, often incorporating thicker pasta, abundant mozzarella, and a more robust meat sauce with Italian sausage, emphasizing bold, comforting taste and generous portion sizes. The ultimate preference depends on whether one favors traditional, refined textures and flavors or a richer, meat-heavy, and cheese-forward experience.
Classic Italian vs American Lasagna for style Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com