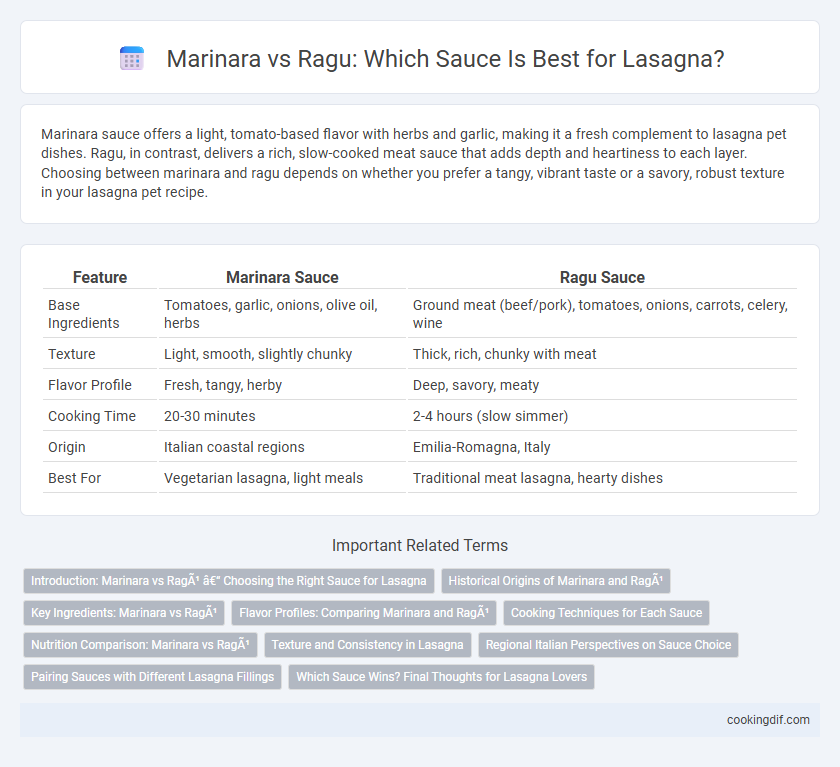
Marinara sauce offers a light, tomato-based flavor with herbs and garlic, making it a fresh complement to lasagna pet dishes. Ragu, in contrast, delivers a rich, slow-cooked meat sauce that adds depth and heartiness to each layer. Choosing between marinara and ragu depends on whether you prefer a tangy, vibrant taste or a savory, robust texture in your lasagna pet recipe.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Marinara Sauce | Ragu Sauce |
|---|---|---|
| Base Ingredients | Tomatoes, garlic, onions, olive oil, herbs | Ground meat (beef/pork), tomatoes, onions, carrots, celery, wine |
| Texture | Light, smooth, slightly chunky | Thick, rich, chunky with meat |
| Flavor Profile | Fresh, tangy, herby | Deep, savory, meaty |
| Cooking Time | 20-30 minutes | 2-4 hours (slow simmer) |
| Origin | Italian coastal regions | Emilia-Romagna, Italy |
| Best For | Vegetarian lasagna, light meals | Traditional meat lasagna, hearty dishes |
Introduction: Marinara vs Ragù – Choosing the Right Sauce for Lasagna
Marinara sauce offers a light, tomato-based flavor with garlic, onions, and herbs, enhancing lasagna with a fresh and vibrant taste. Ragu, a slow-cooked meat sauce typically made from ground beef or pork, tomatoes, and wine, provides a rich, hearty depth that complements the layered pasta and cheese. Selecting between marinara and ragu depends on whether a lighter or more robust sauce is desired to define the overall lasagna experience.
Historical Origins of Marinara and Ragù
Marinara sauce originated in 16th-century Naples, characterized by its simple blend of tomatoes, garlic, herbs, and olive oil, reflecting Mediterranean coastal cuisine. Ragu, with roots tracing back to 18th-century Bologna, is a meat-based sauce slow-cooked with a mix of ground beef, pork, vegetables, and wine, embodying Northern Italian culinary tradition. These sauces underscore regional Italian diversity, with marinara offering a light, tomato-forward profile and ragu delivering a rich, hearty meat flavor.
Key Ingredients: Marinara vs Ragù
Marinara sauce features key ingredients like tomatoes, garlic, onions, and fresh basil, emphasizing a light, herbaceous flavor profile. Ragu includes ground meat, such as beef or pork, combined with tomatoes, onions, carrots, celery, and a slow-cooked reduction, creating a rich, hearty texture. The contrast in ingredients defines marinara as a simple tomato-based sauce and ragu as a meat-based, savory complement essential for traditional lasagna recipes.
Flavor Profiles: Comparing Marinara and Ragù
Marinara sauce offers a bright, tangy flavor with prominent notes of fresh tomatoes, garlic, and herbs like basil and oregano, delivering a light and vibrant base for lasagna. Ragu features a rich, savory profile with slow-cooked meat, tomatoes, onions, and wine, creating deep umami flavors and a hearty, robust texture that complements layered pasta. The choice between marinara and ragu influences the overall taste experience, with marinara emphasizing freshness and ragu providing complexity and fullness.
Cooking Techniques for Each Sauce
Marinara sauce is typically made by quickly simmering tomatoes, garlic, and herbs, allowing the fresh flavors to shine with minimal cooking time, preserving its bright and tangy profile. Ragu requires a slow, extended simmering process where meat, vegetables, and tomatoes meld together over hours, creating a rich, hearty sauce with deep, complex flavors. The contrasting cooking techniques--rapid simmering for marinara and slow braising for ragu--define their distinct textures and taste intensity in lasagna preparation.
Nutrition Comparison: Marinara vs Ragù
Marinara sauce, primarily made from tomatoes, garlic, and herbs, is lower in calories and fat compared to ragu, making it a lighter option rich in vitamins A and C and antioxidants like lycopene. Ragu, a meat-based sauce typically incorporating beef or pork, provides higher protein and iron content but also contains more saturated fat and calories. Choosing marinara promotes a heart-healthier profile, while ragu offers enhanced nutrient density beneficial for muscle repair and energy.
Texture and Consistency in Lasagna
Marinara sauce offers a smooth, slightly chunky texture with a bright tomato flavor that creates a lighter consistency in lasagna. Ragu, often slow-cooked with ground meat and vegetables, provides a rich, thick, and hearty texture that intensifies the dish's overall body and moisture. The choice between marinara and ragu directly impacts the lasagna's mouthfeel, with marinara delivering a fresher bite and ragu adding depth and robustness.
Regional Italian Perspectives on Sauce Choice
Marinara sauce, originating from Southern Italy, is a simple tomato-based sauce featuring garlic, basil, and olive oil, often favored in regions like Naples for its light and fresh flavor. Ragu, a meat-based sauce with slow-cooked minced beef, pork, or veal combined with tomatoes and aromatic vegetables, is traditionally associated with Emilia-Romagna, where it forms the classic base for lasagna alla Bolognese. Regional Italian preferences reflect culinary heritage, with Southern Italians preferring marinara for its vibrant simplicity, while Northern Italians emphasize ragu's rich, hearty depth in their lasagna recipes.
Pairing Sauces with Different Lasagna Fillings
Marinara sauce pairs best with vegetable or cheese-based lasagnas due to its light, tangy flavor that complements rather than overwhelms the fillings. Ragu, a rich meat-based sauce typically made from ground beef, pork, and tomatoes, enhances meat-filled lasagnas by providing depth and robust savory notes. Selecting the appropriate sauce elevates the overall balance, ensuring the layers of pasta, cheese, and filling harmonize perfectly.
Which Sauce Wins? Final Thoughts for Lasagna Lovers
Marinara sauce offers a vibrant, tomato-forward flavor with fresh herbs that enhance the lightness of lasagna, while ragu provides a rich, slow-cooked meatiness that adds depth and heartiness. For traditional lasagna lovers seeking robust, layered complexity, ragu often wins due to its savory texture and balanced seasoning. Marinara suits those preferring a simpler, vegetarian-friendly option with bright acidity and herbal notes, making the choice dependent on personal taste and dietary preference.
Marinara vs ragù for sauce Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com