Oil-blanching noodles prevents them from sticking together and creates a slightly firmer texture ideal for layering in lasagna, while classic boiling allows noodles to fully hydrate and soften, making them easier to fold and less likely to break apart. Pre-cooking pasta with oil-blanching retains more structure during baking, reducing water absorption and preventing soggy layers, unlike boiling which can sometimes lead to overly soft noodles. Choosing oil-blanching enhances the overall texture and appearance of lasagna, yielding distinct, tender noodles that hold their shape throughout cooking.
Table of Comparison
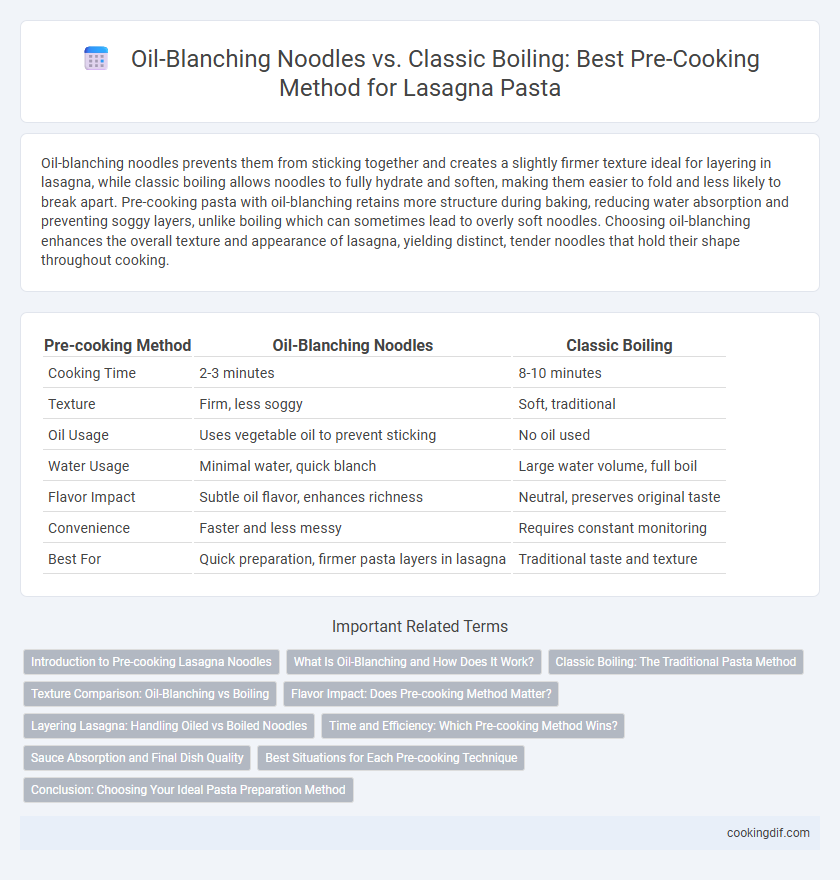
| Pre-cooking Method | Oil-Blanching Noodles | Classic Boiling |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Time | 2-3 minutes | 8-10 minutes |
| Texture | Firm, less soggy | Soft, traditional |
| Oil Usage | Uses vegetable oil to prevent sticking | No oil used |
| Water Usage | Minimal water, quick blanch | Large water volume, full boil |
| Flavor Impact | Subtle oil flavor, enhances richness | Neutral, preserves original taste |
| Convenience | Faster and less messy | Requires constant monitoring |
| Best For | Quick preparation, firmer pasta layers in lasagna | Traditional taste and texture |
Introduction to Pre-cooking Lasagna Noodles
Oil-blanching lasagna noodles involves briefly submerging them in hot oil to create a flexible texture that prevents sticking without over-softening. Classic boiling remains the traditional method, using rapidly boiling water to cook noodles evenly but requiring immediate separation to avoid clumping. Choosing oil-blanching or boiling depends on desired noodle texture and cooking workflow in lasagna preparation.
What Is Oil-Blanching and How Does It Work?
Oil-blanching noodles involves briefly cooking pasta in hot oil rather than boiling water, which creates a protective coating that prevents sticking and overcooking. This method maintains the noodle's texture and enhances flavor by sealing in moisture and allowing a slight browning effect. Unlike classic boiling, oil-blanching reduces water absorption, resulting in firmer, less soggy lasagna layers.
Classic Boiling: The Traditional Pasta Method
Classic boiling remains the traditional pasta method for preparing lasagna noodles, involving submerging them in rapidly boiling water to achieve optimal texture and tenderness. This technique ensures even cooking and prevents noodles from becoming too soft or sticky, enhancing the layered structure of the lasagna. Maintaining a consistent rolling boil and occasional stirring are essential steps to avoid clumping and achieve perfect al dente pasta.
Texture Comparison: Oil-Blanching vs Boiling
Oil-blanching lasagna noodles creates a firmer, less sticky texture by lightly coating the pasta in oil while partially cooking it, resulting in a more structured bite. Classic boiling softens noodles evenly, yielding a more tender and flexible texture that absorbs sauce better but can become mushy if overcooked. Choosing oil-blanching enhances noodle separation and prevents clumping, while boiling ensures uniform softness ideal for traditional layering in lasagna dishes.
Flavor Impact: Does Pre-cooking Method Matter?
Oil-blanching noodles preserves the pasta's surface starches, enhancing sauce adherence and delivering a richer, more robust flavor profile compared to classic boiling, which can dilute flavor by leaching starches into the water. The slight coating of oil also prevents noodles from sticking together without altering taste, allowing the lasagna layers to maintain distinct textures and improved mouthfeel. Preferring oil-blanching as a pre-cooking method significantly elevates the overall palette experience by maintaining the noodles' natural flavor and supporting harmonious sauce integration.
Layering Lasagna: Handling Oiled vs Boiled Noodles
Oil-blanching noodles creates a slightly firmer texture that prevents sticking and allows for easier separation when layering lasagna, resulting in distinct and even layers. Boiled noodles absorb more water, making them softer and more pliable, but can become fragile and prone to tearing during assembly. Proper handling of oiled noodles reduces the risk of clumping, while boiled noodles require gentle placement to maintain structural integrity in the lasagna.
Time and Efficiency: Which Pre-cooking Method Wins?
Oil-blanching noodles significantly reduces pre-cooking time compared to classic boiling, cutting the process from 8-10 minutes to just 3-5 minutes per batch. This method enhances efficiency by preventing noodles from sticking and clumping, eliminating the need for constant stirring during boiling. For large-scale lasagna preparation, oil-blanching offers a faster, more streamlined workflow without compromising texture or quality.
Sauce Absorption and Final Dish Quality
Oil-blanching noodles creates a smoother surface on lasagna sheets, reducing their ability to absorb sauce and resulting in a slightly drier texture. Classic boiling allows pasta to fully hydrate and swell, optimizing sauce absorption and enhancing the final dish's moistness and flavor integration. Chefs aiming for rich, saucy lasagna typically prefer boiling to ensure an evenly cooked, tender pasta layer that melds seamlessly with the sauce.
Best Situations for Each Pre-cooking Technique
Oil-blanching noodles is best for lasagna when aiming to prevent sticking and maintain a slightly firmer texture, making it ideal for layered dishes that require careful assembly without sogginess. Classic boiling suits lasagna recipes that demand fully hydrated noodles for uniform softness and thorough cooking, especially when the pasta will bake with ample sauce and moisture. Choosing oil-blanching benefits heat-sensitive fillings by reducing water absorption, while boiling enhances flavor integration in hearty, sauce-rich lasagna varieties.
Conclusion: Choosing Your Ideal Pasta Preparation Method
Oil-blanching noodles creates a slightly firmer texture and prevents sticking by coating the pasta with a thin layer of oil, ideal for lasagna layers that require distinct separation and reduced moisture absorption. Classic boiling allows noodles to fully hydrate and soften, offering a more traditional pasta texture that melds seamlessly with rich sauces. Selecting the ideal method depends on whether you prioritize pasta firmness and separation or a fully tender, sauce-integrated consistency in your lasagna.
Oil-blanching noodles vs Classic boiling for pre-cooking pasta Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com