Wet masala for curry paste preparation combines fresh ingredients like onions, garlic, ginger, and tomatoes, creating a rich, aromatic base with enhanced moisture and depth of flavor. Dry masala, made from ground spices and dehydrated herbs, offers a concentrated, long-lasting seasoning that intensifies the curry's heat and complexity without adding extra liquid. Choosing between wet and dry masala depends on the desired texture and taste, with wet masala providing a smoother, saucier curry and dry masala delivering a drier, spiced finish.
Table of Comparison
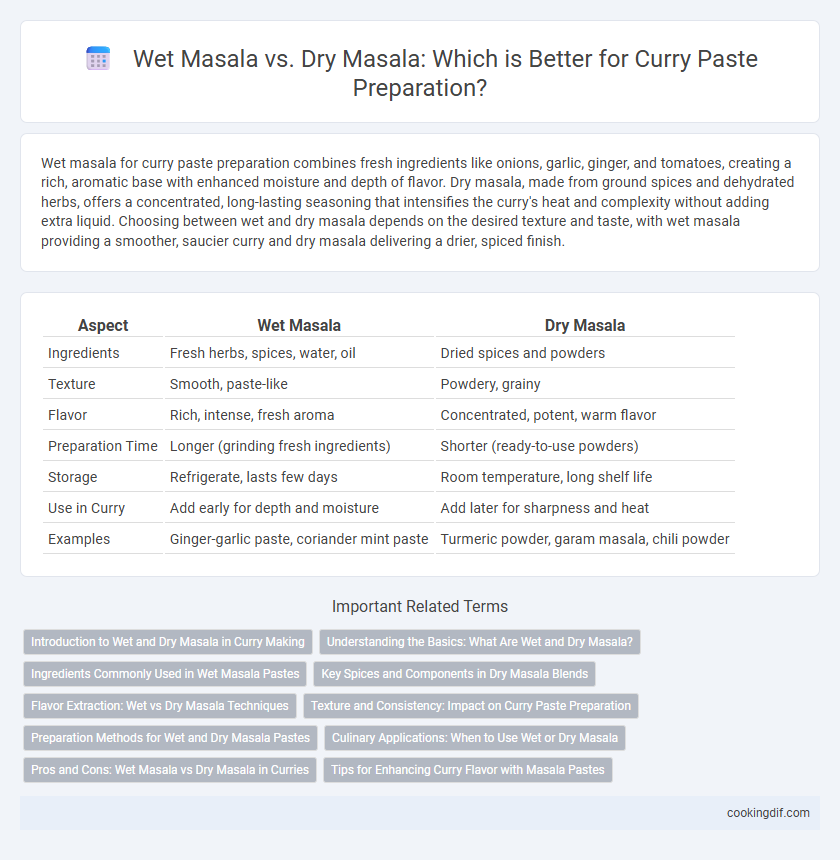
| Aspect | Wet Masala | Dry Masala |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | Fresh herbs, spices, water, oil | Dried spices and powders |
| Texture | Smooth, paste-like | Powdery, grainy |
| Flavor | Rich, intense, fresh aroma | Concentrated, potent, warm flavor |
| Preparation Time | Longer (grinding fresh ingredients) | Shorter (ready-to-use powders) |
| Storage | Refrigerate, lasts few days | Room temperature, long shelf life |
| Use in Curry | Add early for depth and moisture | Add later for sharpness and heat |
| Examples | Ginger-garlic paste, coriander mint paste | Turmeric powder, garam masala, chili powder |
Introduction to Wet and Dry Masala in Curry Making
Wet masala, typically made by grinding fresh ingredients such as onions, garlic, ginger, and spices along with water or oil, forms the base paste for many traditional curries, enhancing flavor and texture. Dry masala involves roasting and grinding dried spices into a fine powder, providing a concentrated and aromatic spice blend that can be tempered or added directly to dishes. Both wet and dry masalas are essential in curry making, offering distinct layers of taste and aroma fundamental to authentic Indian cuisine.
Understanding the Basics: What Are Wet and Dry Masala?
Wet masala consists of ground spices blended with liquids such as water, yogurt, or oil, creating a moist paste that enhances flavor absorption in curries. Dry masala is a powdered spice mix made from roasted and ground spices without any added moisture, ideal for dry rubs or tempering. Understanding the differences helps in selecting the appropriate masala type for desired curry textures and flavor intensity.
Ingredients Commonly Used in Wet Masala Pastes
Wet masala pastes typically include ingredients such as fresh garlic, ginger, green chilies, onions, and tomatoes, blended with whole spices like cumin seeds, coriander seeds, and cardamom pods to create a rich and aromatic base. The moisture from these fresh ingredients helps release essential oils and flavors, resulting in a vibrant and flavorful curry foundation. This contrasts with dry masala powders, which rely solely on ground dried spices without the fresh aromatic elements found in wet pastes.
Key Spices and Components in Dry Masala Blends
Dry masala blends for curry pastes primarily include key spices such as cumin seeds, coriander seeds, fennel seeds, mustard seeds, and dried red chilies, which offer concentrated flavor and enhanced shelf stability. These spices are typically roasted and ground finely to release essential oils, intensifying the curry's aroma and taste compared to wet masalas that might dilute spice potency with moisture. Incorporating dry masala blends ensures a balanced, robust base for curry pastes, maintaining vibrant flavor profiles during cooking.
Flavor Extraction: Wet vs Dry Masala Techniques
Wet masala techniques enhance flavor extraction by releasing essential oils and aromatic compounds through the use of water, oil, or yogurt, intensifying the curry's overall taste and richness. Dry masala methods rely on roasting spices to amplify their natural flavors and create a deeper, smokier profile, which adds complexity without added moisture. Combining both approaches strategically maximizes flavor depth and authenticity in curry paste preparation.
Texture and Consistency: Impact on Curry Paste Preparation
Wet masala contains moisture-rich ingredients like tomatoes, onions, or yogurt, resulting in a smooth, thick paste ideal for creating creamy and luscious curry textures. Dry masala, composed of powdered spices without added liquids, produces a coarse, grainy consistency that intensifies aromatic flavors but requires oil or water for blending in curry preparation. Selecting wet or dry masala directly influences the curry paste's texture and consistency, impacting cooking time and the release of essential oils for flavor infusion.
Preparation Methods for Wet and Dry Masala Pastes
Wet masala pastes are prepared by grinding fresh ingredients like onions, garlic, ginger, and green chilies with water or oil, resulting in a smooth, aromatic blend that enhances curry flavor. Dry masala pastes involve roasting whole or ground spices such as cumin, coriander, and turmeric before grinding them into a powder, then mixing with minimal liquid to form a concentrated paste. Both methods influence the texture and intensity of the curry, with wet masalas offering moisture and richness, while dry masalas provide a robust, toasted spice profile.
Culinary Applications: When to Use Wet or Dry Masala
Wet masala, containing fresh ingredients like ginger, garlic, and onions, is ideal for gravies and curries that require rich, smooth textures and intensified flavors. Dry masala powders are preferred for dry-cooked dishes, stir-fries, and spice rubs, offering concentrated aroma without adding moisture. Choosing the right masala type enhances the dish's texture and flavor complexity, aligning with specific culinary techniques and regional recipes.
Pros and Cons: Wet Masala vs Dry Masala in Curries
Wet masala enhances curries with a rich, intense flavor and smooth texture by using fresh ingredients blended with water or oil, allowing spices to release essential oils effectively. However, wet masala has a shorter shelf life due to moisture content, increasing the risk of spoilage and requiring refrigeration. Dry masala offers longer preservation, convenient storage, and ease of use but may lack the deep, vibrant taste and texture that wet masala imparts to curry dishes.
Tips for Enhancing Curry Flavor with Masala Pastes
Wet masala pastes, made by blending fresh ingredients like onions, garlic, ginger, and spices with water or oil, deliver a more vibrant and aromatic curry base compared to dry masalas. Using freshly ground whole spices and roasting them before grinding enhances the depth and complexity of the masala paste, intensifying the curry's flavor profile. Incorporating ingredients like yogurt or coconut milk when preparing wet masala can add richness and balance the heat, creating a well-rounded, creamy curry.
Wet masala vs Dry masala for paste preparation Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com