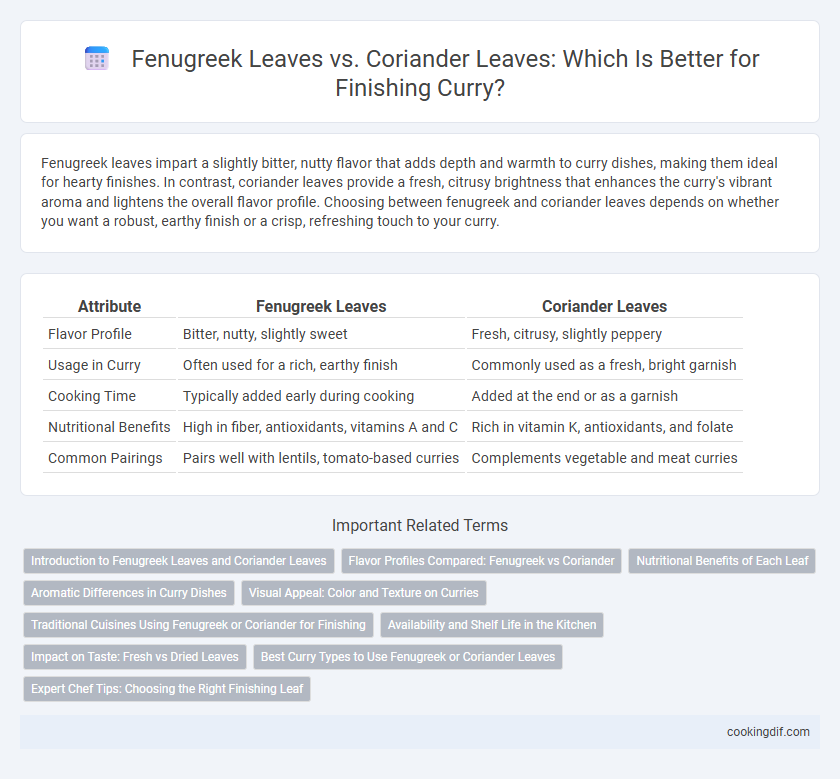
Fenugreek leaves impart a slightly bitter, nutty flavor that adds depth and warmth to curry dishes, making them ideal for hearty finishes. In contrast, coriander leaves provide a fresh, citrusy brightness that enhances the curry's vibrant aroma and lightens the overall flavor profile. Choosing between fenugreek and coriander leaves depends on whether you want a robust, earthy finish or a crisp, refreshing touch to your curry.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Fenugreek Leaves | Coriander Leaves |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor Profile | Bitter, nutty, slightly sweet | Fresh, citrusy, slightly peppery |
| Usage in Curry | Often used for a rich, earthy finish | Commonly used as a fresh, bright garnish |
| Cooking Time | Typically added early during cooking | Added at the end or as a garnish |
| Nutritional Benefits | High in fiber, antioxidants, vitamins A and C | Rich in vitamin K, antioxidants, and folate |
| Common Pairings | Pairs well with lentils, tomato-based curries | Complements vegetable and meat curries |
Introduction to Fenugreek Leaves and Coriander Leaves
Fenugreek leaves, known for their slightly bitter taste and nutty aroma, are rich in vitamins A, C, and K, making them a nutrient-dense option for finishing curries. Coriander leaves, or cilantro, offer a fresh, citrusy flavor and contain antioxidants, vitamin K, and iron, enhancing both the taste and health benefits of a dish. Both herbs serve unique culinary roles, with fenugreek leaves adding depth and bitterness, while coriander leaves provide brightness and a refreshing finish.
Flavor Profiles Compared: Fenugreek vs Coriander
Fenugreek leaves impart a slightly bitter, nutty, and earthy flavor with a hint of sweetness, enhancing depth and complexity in curry dishes. Coriander leaves provide a fresh, citrusy, and slightly peppery taste that brightens and balances rich, spicy curries. Using fenugreek offers warmth and subtle bitterness, while coriander delivers vibrant freshness, making each herb essential for distinct flavor profiles in curry finishing.
Nutritional Benefits of Each Leaf
Fenugreek leaves are rich in dietary fiber, iron, and antioxidants, supporting digestive health and anemia prevention, while coriander leaves provide high levels of vitamin C, vitamin K, and flavonoids that enhance immune function and reduce inflammation. Both herbs contain essential oils with antimicrobial properties but fenugreek has a slightly higher protein content, aiding muscle repair and growth. Incorporating fenugreek and coriander leaves as finishing touches in curry not only enhances flavor but also delivers targeted nutritional benefits for overall well-being.
Aromatic Differences in Curry Dishes
Fenugreek leaves impart a slightly bitter, nutty aroma with subtle maple undertones, creating a warm and earthy finish in curry dishes. Coriander leaves offer a bright, citrusy fragrance with fresh, herbaceous notes that enhance the overall freshness and complexity. The aromatic difference significantly influences the flavor profile, with fenugreek adding depth and richness, while coriander provides a vibrant and refreshing lift.
Visual Appeal: Color and Texture on Curries
Fenugreek leaves add a deep green color and slightly coarse texture, providing a rustic finish to curries, while coriander leaves contribute a vibrant, bright green hue with a delicate, soft texture that enhances visual appeal. The rich, matte appearance of fenugreek leaves contrasts with the glossy, fresh look of coriander, creating distinct visual layers in the dish. Using either herb as a garnish significantly influences the final presentation, with fenugreek offering earthiness and depth, and coriander delivering brightness and freshness.
Traditional Cuisines Using Fenugreek or Coriander for Finishing
In traditional Indian and Middle Eastern cuisines, fenugreek leaves are often used to finish dishes like butter chicken and dal for a slightly bitter, aromatic flavor that enhances depth and richness. Coriander leaves are widely favored in Southeast Asian and Latin American dishes such as curries, salsas, and chutneys, offering a fresh, citrusy finish that brightens the overall taste. Both herbs serve distinct roles in culinary traditions, with fenugreek leaves imparting warmth and complexity while coriander leaves provide vibrant, herbal notes.
Availability and Shelf Life in the Kitchen
Fenugreek leaves are less commonly available in fresh form compared to coriander leaves, which are widely stocked in most grocery stores year-round. Fresh coriander leaves have a shorter shelf life of about 3 to 5 days when refrigerated, whereas fenugreek leaves tend to last slightly longer, maintaining freshness for up to one week under proper storage. Dried fenugreek leaves, known as kasuri methi, offer extended shelf life and can be a convenient substitute when fresh leaves are not accessible.
Impact on Taste: Fresh vs Dried Leaves
Fresh fenugreek leaves impart a slightly bitter, nutty flavor that enhances curry complexity, while dried fenugreek leaves (kasuri methi) offer a concentrated, earthy aroma that intensifies the dish's depth. Coriander leaves, when fresh, provide a bright, citrusy, and herbaceous note that lightens and freshens the curry's taste profile, contrasting with dried coriander leaves, which have a subdued, musty flavor and less impact. Using fresh leaves generally results in a more vibrant finish, while dried leaves contribute deeper, rounded flavors, influencing the final taste intensity and aroma of the curry.
Best Curry Types to Use Fenugreek or Coriander Leaves
Fenugreek leaves, with their slightly bitter and aromatic flavor, are ideal for finishing rich curries like Kerala-style fish curry and Punjabi methi chicken, enhancing depth and complexity. Coriander leaves, offering a fresh and citrusy note, complement lighter curries such as South Indian sambar and North Indian dal tadka, providing a vibrant finishing touch. Choosing fenugreek or coriander leaves depends on the curry's base ingredients and regional flavor profile for optimal taste balance.
Expert Chef Tips: Choosing the Right Finishing Leaf
Fenugreek leaves impart a slightly bitter, nutty flavor that enhances the richness of creamy and tomato-based curries, making them ideal for dishes requiring depth and warmth. Coriander leaves offer a fresh, citrusy aroma that brightens and balances spicy or robust curries, providing a clean, herbal finish. Expert chefs recommend using fenugreek leaves sparingly to avoid overpowering the dish, while coriander leaves can be added generously just before serving to preserve their vibrant flavor and color.
Fenugreek leaves vs coriander leaves for finishing Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com