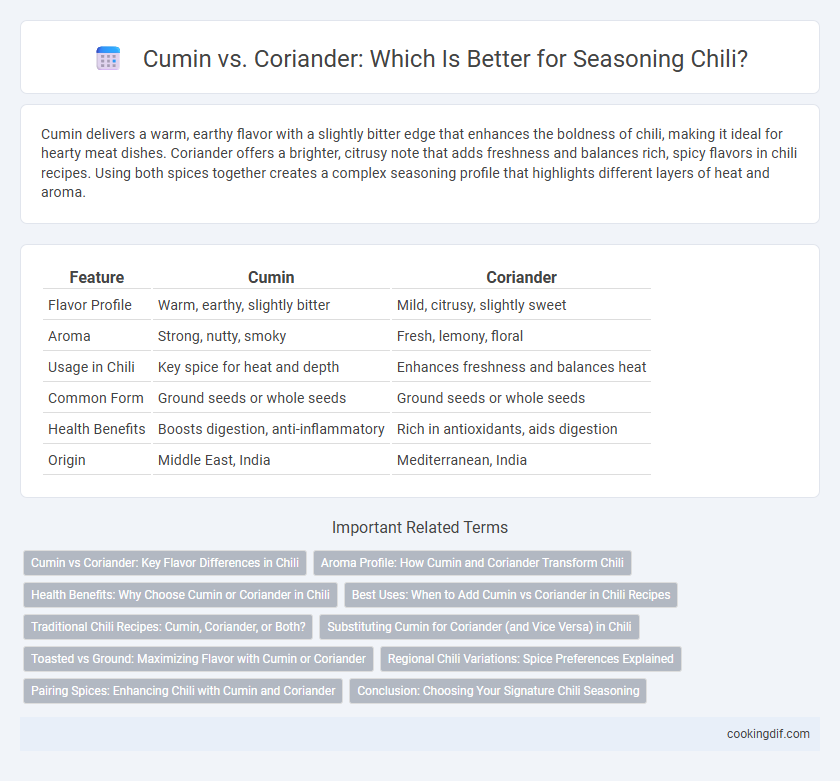
Cumin delivers a warm, earthy flavor with a slightly bitter edge that enhances the boldness of chili, making it ideal for hearty meat dishes. Coriander offers a brighter, citrusy note that adds freshness and balances rich, spicy flavors in chili recipes. Using both spices together creates a complex seasoning profile that highlights different layers of heat and aroma.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cumin | Coriander |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor Profile | Warm, earthy, slightly bitter | Mild, citrusy, slightly sweet |
| Aroma | Strong, nutty, smoky | Fresh, lemony, floral |
| Usage in Chili | Key spice for heat and depth | Enhances freshness and balances heat |
| Common Form | Ground seeds or whole seeds | Ground seeds or whole seeds |
| Health Benefits | Boosts digestion, anti-inflammatory | Rich in antioxidants, aids digestion |
| Origin | Middle East, India | Mediterranean, India |
Cumin vs Coriander: Key Flavor Differences in Chili
Cumin delivers a warm, earthy, and slightly smoky flavor that intensifies the heat and richness of chili, while coriander offers a fresh, citrusy, and slightly sweet taste that brightens and balances the dish's robust spices. Cumin's bold aroma is integral to traditional chili seasoning, enhancing depth and complexity, whereas coriander introduces a subtle, zesty undertone that complements cumin's intensity without overpowering it. Using both spices in chili creates a harmonious blend, with cumin anchoring the savory base and coriander adding a refreshing contrast to the overall flavor profile.
Aroma Profile: How Cumin and Coriander Transform Chili
Cumin imparts a warm, earthy aroma with smoky undertones that deepen the chili's flavor complexity, enhancing its rich and savory character. Coriander offers a bright, citrusy scent with a hint of sweetness, lightening the chili's profile and adding a fresh, vibrant contrast. Together, these spices balance each other, creating a dynamic aroma that elevates the overall sensory experience of chili dishes.
Health Benefits: Why Choose Cumin or Coriander in Chili
Cumin enhances chili with its rich supply of iron, aiding in energy production and immune function, while also promoting digestion through its antioxidant properties. Coriander offers a wealth of vitamins like Vitamin C and K, contributing to heart health and anti-inflammatory effects that can soothe digestive discomfort. Choosing cumin or coriander in chili depends on desired health benefits: cumin supports metabolic processes, whereas coriander delivers essential nutrients and detoxifying effects.
Best Uses: When to Add Cumin vs Coriander in Chili Recipes
Cumin imparts a warm, earthy flavor best added early in chili recipes to enhance the base with deep, smoky notes. Coriander offers a lighter, citrusy aroma and is most effective when added later in cooking to preserve its bright, fresh essence. Balancing these spices strategically elevates chili by blending robust warmth from cumin with the subtle, aromatic lift of coriander.
Traditional Chili Recipes: Cumin, Coriander, or Both?
Traditional chili recipes often incorporate both cumin and coriander to achieve a balanced flavor profile; cumin provides a warm, earthy depth while coriander adds a subtle citrusy brightness. Regions with Mexican and Tex-Mex influences tend to emphasize cumin for its smoky aroma, whereas coriander is favored in some Southwestern variations for its slightly sweet and floral notes. Combining both spices enhances complexity and authenticity in chili seasoning, reflecting diverse culinary traditions.
Substituting Cumin for Coriander (and Vice Versa) in Chili
Substituting cumin for coriander in chili alters the flavor profile, as cumin offers earthy, smoky notes while coriander provides a lighter, citrusy undertone. When replacing coriander with cumin, reduce quantity slightly to prevent overpowering the dish, and when using coriander instead of cumin, increase the amount to retain depth. Both spices complement chili but adjusting their balance is key to maintaining the intended taste complexity and aroma.
Toasted vs Ground: Maximizing Flavor with Cumin or Coriander
Toasted cumin seeds release essential oils that intensify the warm, earthy flavor in chili dishes, while ground cumin offers convenience with a more muted aroma. Coriander achieves a bright, citrusy note when toasted, enhancing chili complexity, whereas ground coriander provides a subtler, sweet undertone. Maximizing flavor in chili depends on balancing toasted spices for depth and ground powders for consistent seasoning.
Regional Chili Variations: Spice Preferences Explained
Regional chili variations highlight distinct spice preferences, with cumin prominently featured in Southwestern and Tex-Mex chilis, imparting a warm, earthy depth that complements smoky meats. Coriander, favored in Mexican and Central American chili recipes, adds a citrusy brightness enhancing the complexity of tomato-based sauces. These regional tendencies reflect cultural influences and ingredient availability, shaping the unique flavor profiles of chili across different areas.
Pairing Spices: Enhancing Chili with Cumin and Coriander
Cumin and coriander both play essential roles in elevating chili's flavor profile, with cumin imparting a warm, earthy bitterness and coriander adding a citrusy, slightly sweet undertone. Pairing these spices balances the chili's heat and richness, creating a depth of flavor that enhances the overall taste experience. Using ground cumin and coriander seeds in combination unlocks a complex aromatic blend, ideal for authentic chili recipes.
Conclusion: Choosing Your Signature Chili Seasoning
Choosing your signature chili seasoning depends on whether you want the warm, earthy, and slightly spicy flavor of cumin or the bright, citrusy, and slightly sweet notes of coriander. Cumin enhances the depth and smokiness in chili, making it ideal for a robust, hearty dish. Coriander adds a fresh, vibrant contrast that complements other spices without overpowering the dish, perfect for a balanced and aromatic chili.
Cumin vs coriander for seasoning Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com