Chia pudding offers a nutrient-dense alternative to traditional pudding by providing high fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and plant-based protein, making it suitable for those seeking healthier or vegan options. Traditional pudding typically contains higher levels of sugar and dairy fats, which may not align with low-calorie or lactose-free diets. Choosing chia pudding supports better digestion and sustained energy levels due to its slow-digesting properties and minimal processed ingredients.
Table of Comparison
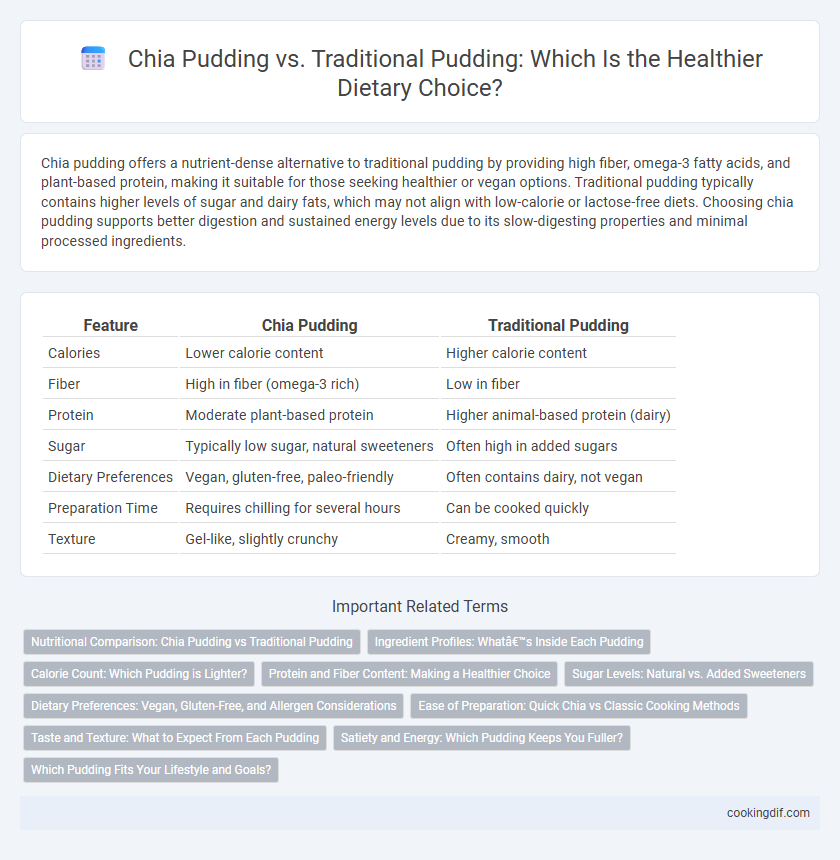
| Feature | Chia Pudding | Traditional Pudding |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | Lower calorie content | Higher calorie content |
| Fiber | High in fiber (omega-3 rich) | Low in fiber |
| Protein | Moderate plant-based protein | Higher animal-based protein (dairy) |
| Sugar | Typically low sugar, natural sweeteners | Often high in added sugars |
| Dietary Preferences | Vegan, gluten-free, paleo-friendly | Often contains dairy, not vegan |
| Preparation Time | Requires chilling for several hours | Can be cooked quickly |
| Texture | Gel-like, slightly crunchy | Creamy, smooth |
Nutritional Comparison: Chia Pudding vs Traditional Pudding
Chia pudding offers a nutrient-dense alternative to traditional pudding, being rich in omega-3 fatty acids, dietary fiber, and plant-based protein, which supports heart health and digestion. Traditional pudding typically contains higher sugars and saturated fats, often derived from dairy and added sweeteners, contributing to increased calorie content and potential blood sugar spikes. Choosing chia pudding aligns with low-calorie, high-fiber diets and provides antioxidants, making it a more balanced option for weight management and sustained energy.
Ingredient Profiles: What’s Inside Each Pudding
Chia pudding features chia seeds soaked in almond milk or coconut milk, providing high fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and plant-based protein, ideal for gluten-free and vegan diets. Traditional pudding typically contains dairy such as milk and eggs, offering calcium and protein but higher in saturated fat and lacking fiber. The ingredient profiles make chia pudding a nutrient-dense, low-sugar option, while traditional pudding focuses on creamy texture from animal-based ingredients.
Calorie Count: Which Pudding is Lighter?
Chia pudding typically contains fewer calories than traditional pudding due to its base of chia seeds and plant-based milk, which are lower in fat and sugar. Traditional pudding often relies on whole milk and sugar, increasing its overall calorie count. For those seeking a lighter dessert option, chia pudding is a more calorie-conscious choice while providing fiber and omega-3 fatty acids.
Protein and Fiber Content: Making a Healthier Choice
Chia pudding offers significantly higher fiber content compared to traditional pudding, with about 10 grams of fiber per serving versus less than 1 gram, aiding digestion and promoting satiety. Protein levels in chia pudding range from 4 to 6 grams per serving, contributed by chia seeds, while traditional pudding typically contains less protein and more added sugars. Choosing chia pudding can enhance dietary fiber and protein intake, supporting weight management and overall digestive health.
Sugar Levels: Natural vs. Added Sweeteners
Chia pudding typically contains lower sugar levels because it relies on natural sweeteners like fruit or honey, unlike traditional pudding that often includes added sugars or artificial sweeteners. The natural fiber content in chia seeds helps moderate blood sugar spikes, making chia pudding a healthier choice for those monitoring sugar intake. Choosing chia pudding can support better glycemic control while still satisfying sweet cravings.
Dietary Preferences: Vegan, Gluten-Free, and Allergen Considerations
Chia pudding offers a plant-based, vegan alternative to traditional pudding, which often contains dairy and eggs. It is naturally gluten-free and free from common allergens like lactose, making it suitable for individuals with dietary restrictions or sensitivities. Traditional pudding may require modifications to accommodate vegan, gluten-free, or allergen-conscious diets, whereas chia pudding inherently meets these requirements.
Ease of Preparation: Quick Chia vs Classic Cooking Methods
Chia pudding requires minimal preparation, often just combining chia seeds with milk or a milk alternative and allowing it to thicken in the refrigerator for a few hours, making it a quick and convenient option. Traditional pudding demands cooking on the stovetop with ingredients like sugar, milk, and thickeners such as cornstarch or eggs, which takes more time and active attention. For individuals seeking a fast, no-cook dessert with flexible customization, chia pudding's simplicity offers a distinct advantage over classic pudding recipes.
Taste and Texture: What to Expect From Each Pudding
Chia pudding offers a unique texture characterized by a gelatinous, slightly crunchy consistency due to the swollen chia seeds, providing a refreshing bite compared to the creamy, smooth texture of traditional pudding made from dairy or starch bases. Taste-wise, chia pudding has a mild, nutty flavor that easily absorbs added ingredients like vanilla or fruit, while traditional pudding features a richer, sweeter profile often enhanced by ingredients such as chocolate or caramel. Consumers seeking a lighter, more nutrient-dense option might prefer chia pudding's subtle taste and distinctive texture, whereas those desiring a classic, indulgent dessert are drawn to the creamy richness of traditional pudding.
Satiety and Energy: Which Pudding Keeps You Fuller?
Chia pudding offers greater satiety compared to traditional pudding due to its high fiber and protein content, which slows digestion and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. Traditional pudding, often high in sugar and low in fiber, can cause rapid spikes and drops in energy, leading to quicker hunger returns. Choosing chia pudding supports longer-lasting energy and fullness, making it a preferable option for sustained dietary satisfaction.
Which Pudding Fits Your Lifestyle and Goals?
Chia pudding offers a nutrient-dense alternative to traditional pudding, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and protein, making it ideal for those seeking weight management or improved digestion. Traditional pudding typically contains higher levels of sugar and saturated fats, aligning better with occasional indulgences rather than daily health goals. Choosing chia pudding supports sustained energy and satiety for active lifestyles, while traditional pudding suits preferences for creamy texture and classic dessert flavors.
Chia pudding vs traditional pudding for dietary choice Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com