Agar-agar and gelatin are popular setting agents used in pudding making, each offering distinct textural qualities and dietary benefits. Agar-agar, derived from seaweed, sets more firmly and is suitable for vegetarian and vegan diets, while gelatin, made from animal collagen, provides a smoother, more elastic texture. Choosing between them depends on desired pudding consistency, dietary restrictions, and preparation method.
Table of Comparison
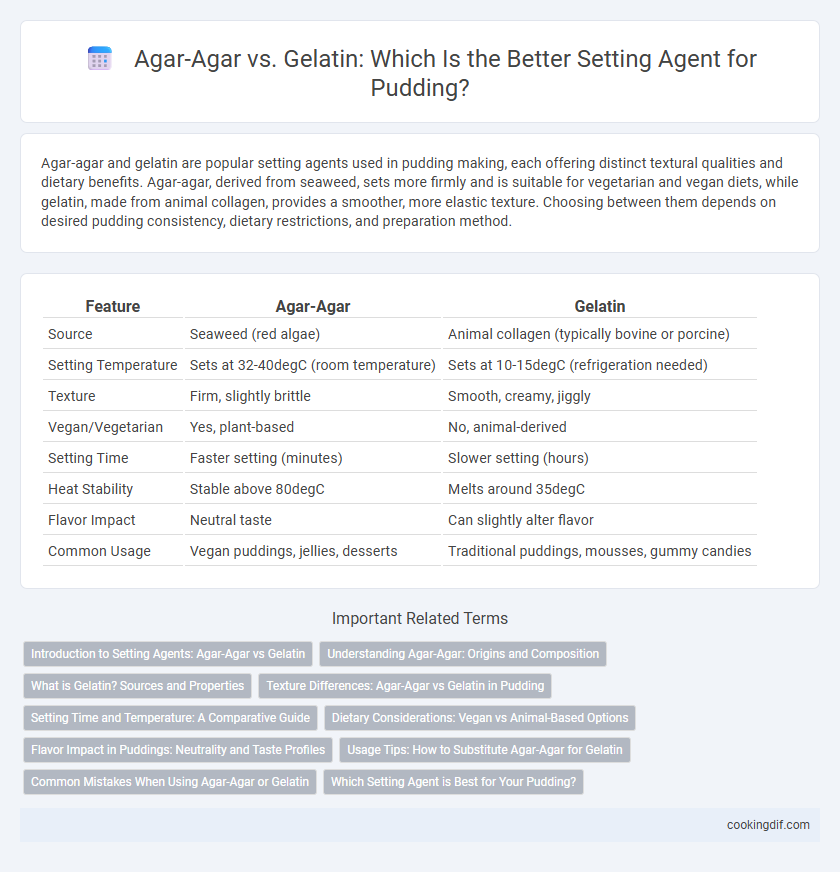
| Feature | Agar-Agar | Gelatin |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Seaweed (red algae) | Animal collagen (typically bovine or porcine) |
| Setting Temperature | Sets at 32-40degC (room temperature) | Sets at 10-15degC (refrigeration needed) |
| Texture | Firm, slightly brittle | Smooth, creamy, jiggly |
| Vegan/Vegetarian | Yes, plant-based | No, animal-derived |
| Setting Time | Faster setting (minutes) | Slower setting (hours) |
| Heat Stability | Stable above 80degC | Melts around 35degC |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral taste | Can slightly alter flavor |
| Common Usage | Vegan puddings, jellies, desserts | Traditional puddings, mousses, gummy candies |
Introduction to Setting Agents: Agar-Agar vs Gelatin
Agar-agar and gelatin are popular setting agents used in puddings, each derived from different natural sources; agar-agar is extracted from red algae, while gelatin comes from animal collagen. Agar-agar sets more firmly and remains stable at room temperature, making it ideal for vegetarian and vegan recipes, whereas gelatin produces a softer, melt-in-the-mouth texture but requires refrigeration to maintain its gel. Understanding their molecular composition and gelling properties allows chefs to select the appropriate agent based on desired texture, dietary restrictions, and preparation conditions.
Understanding Agar-Agar: Origins and Composition
Agar-agar, derived from red algae, serves as a plant-based setting agent distinct from gelatin, which originates from animal collagen. Composed mainly of agarose and agaropectin, agar-agar forms a firm, brittle gel even at room temperature, making it ideal for various pudding recipes. Its unique thermal properties allow it to set quickly without refrigeration, offering a vegan-friendly alternative to traditional gelatin.
What is Gelatin? Sources and Properties
Gelatin is a natural protein derived from collagen found in animal bones, skin, and connective tissues, primarily sourced from pigs and cows. It possesses excellent gelling, thickening, and stabilizing properties, enabling smooth, elastic textures in puddings and other desserts. Unlike plant-based alternatives, gelatin melts at body temperature, offering a unique mouthfeel that enhances the sensory experience of creamy puddings.
Texture Differences: Agar-Agar vs Gelatin in Pudding
Agar-agar creates a firmer, more brittle texture in pudding, offering a slightly grainy mouthfeel due to its plant-based polysaccharides, while gelatin produces a smoother, creamier, and more elastic texture derived from animal collagen. Agar-agar sets at room temperature and remains stable at higher temperatures, making it ideal for puddings that need to hold shape without refrigeration; gelatin requires chilling to gel and can melt at warmer temperatures. The choice between agar-agar and gelatin significantly influences the final pudding's mouthfeel, firmness, and temperature stability, impacting both sensory experience and dietary preferences.
Setting Time and Temperature: A Comparative Guide
Agar-agar sets faster than gelatin, solidifying within 10 to 15 minutes at room temperature, making it ideal for quicker pudding preparation. Gelatin requires refrigeration for 2 to 4 hours to achieve a firm set, as it melts at body temperature around 35degC (95degF), whereas agar-agar remains stable up to 85degC (185degF). These properties make agar-agar suitable for heat-resistant desserts, while gelatin offers a smoother, melt-in-mouth texture but demands longer cooling time.
Dietary Considerations: Vegan vs Animal-Based Options
Agar-agar, derived from red algae, serves as a vegan and plant-based setting agent ideal for dietary restrictions excluding animal products. Gelatin, sourced from animal collagen, is unsuitable for vegans and vegetarians but offers a unique texture favored in traditional pudding recipes. Choosing between agar-agar and gelatin depends on dietary preferences, with agar-agar providing a cruelty-free alternative that sets more firmly and withstands higher temperatures.
Flavor Impact in Puddings: Neutrality and Taste Profiles
Agar-agar and gelatin differ significantly in their flavor impact on puddings, with agar-agar offering a more neutral taste that allows the pudding's natural flavors to shine through without adding any gelatinous aftertaste. Gelatin, derived from animal collagen, can sometimes impart a subtle savory or umami note, potentially altering the intended flavor profile of delicate desserts. For recipes prioritizing pure, clean flavors and vegetarian suitability, agar-agar is the optimal setting agent choice.
Usage Tips: How to Substitute Agar-Agar for Gelatin
When substituting agar-agar for gelatin in pudding recipes, use about one-third the amount of agar powder as gelatin because agar is more potent. Dissolve agar-agar in boiling water and bring it to a simmer to activate its gelling properties, unlike gelatin which dissolves in warm liquid. Note that agar sets faster and at room temperature, producing a firmer texture suitable for vegetarian or vegan diets.
Common Mistakes When Using Agar-Agar or Gelatin
Common mistakes when using agar-agar include overheating it above 90degC, which reduces its gelling strength, and not dissolving it fully before adding to pudding mixtures, resulting in a grainy texture. For gelatin, errors often involve not blooming it properly in cold water before heating, causing uneven setting or a runny pudding. Both setting agents require precise temperature control and proper blooming or dissolution to achieve the desired smooth, firm pudding consistency.
Which Setting Agent is Best for Your Pudding?
Agar-agar and gelatin are popular setting agents for pudding, each with unique properties that influence texture and dietary suitability. Agar-agar, derived from seaweed, provides a firm, slightly brittle texture and is ideal for vegan or vegetarian diets, while gelatin, sourced from animal collagen, yields a smooth, creamy consistency favored in traditional recipes. Choosing the best setting agent depends on dietary preferences, desired firmness, and the specific pudding recipe.
Agar-agar vs Gelatin for setting agent Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com