Thick porridge offers a creamy, dense texture that provides a satisfying mouthfeel and keeps you fuller for longer, making it ideal for those who prefer a hearty breakfast. Runny porridge delivers a lighter, smoother consistency that is easier to digest and can be flavored more evenly with toppings or sweeteners. Choosing between thick and runny porridge depends on personal texture preference and desired meal satiety.
Table of Comparison
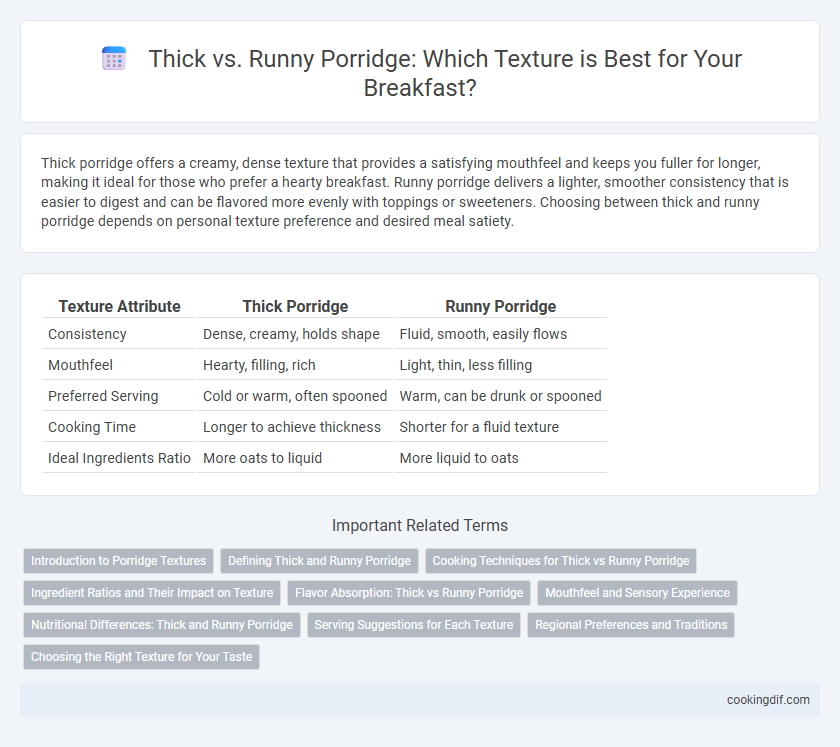
| Texture Attribute | Thick Porridge | Runny Porridge |
|---|---|---|
| Consistency | Dense, creamy, holds shape | Fluid, smooth, easily flows |
| Mouthfeel | Hearty, filling, rich | Light, thin, less filling |
| Preferred Serving | Cold or warm, often spooned | Warm, can be drunk or spooned |
| Cooking Time | Longer to achieve thickness | Shorter for a fluid texture |
| Ideal Ingredients Ratio | More oats to liquid | More liquid to oats |
Introduction to Porridge Textures
Thick porridge offers a dense, creamy texture that provides a satisfying mouthfeel and retains heat longer, making it ideal for hearty breakfasts. Runny porridge has a lighter, more fluid consistency that allows for easier swallowing and absorption of flavors, preferred by those seeking a gentle start to the day. The choice between thick and runny porridge textures depends on personal preference and dietary needs, influencing digestion and satiety.
Defining Thick and Runny Porridge
Thick porridge has a dense, creamy consistency that holds its shape on a spoon, typically achieved by using higher ratios of oats to liquid or longer cooking times to absorb moisture. Runny porridge contains more liquid, resulting in a thinner, more fluid texture that flows easily, often preferred for a lighter, more hydrating breakfast option. The key difference lies in the water-to-oats ratio and cooking duration, which directly influence the porridge's viscosity and mouthfeel.
Cooking Techniques for Thick vs Runny Porridge
Thick porridge requires a longer cooking time and lower heat to allow grains to fully absorb liquid and swell, resulting in a dense, creamy texture. Runny porridge demands higher liquid-to-grain ratios and shorter cooking intervals to maintain a smoother, more fluid consistency. Stirring frequency significantly influences texture, where consistent stirring prevents clumping in thick porridge but is gentler for runny versions to avoid breaking down grains excessively.
Ingredient Ratios and Their Impact on Texture
Thick porridge results from a higher ratio of grains to liquid, creating a dense and creamy texture that holds shape well, ideal for a satisfying, hearty meal. Runny porridge, with more liquid relative to grains, produces a smooth and flowing consistency, making it easier to digest and suitable for those who prefer a lighter texture. Adjusting the ingredient ratios directly impacts the porridge's mouthfeel, with thicker versions often using less water or milk and longer cooking times to absorb moisture fully.
Flavor Absorption: Thick vs Runny Porridge
Thick porridge has a denser texture that allows it to hold flavor compounds more effectively, resulting in a richer and more concentrated taste experience. Runny porridge, with its higher water content, offers a lighter mouthfeel but can dilute flavors, making it less intense and more subtle. Choosing between thick and runny porridge ultimately affects how well the porridge absorbs and delivers seasonings, spices, or sweeteners.
Mouthfeel and Sensory Experience
Thick porridge offers a creamy, dense mouthfeel that provides a satisfying, comforting texture, enhancing the sensory experience with its substantial body. Runny porridge delivers a lighter, smoother sensation on the palate, allowing flavors to be more pronounced and easily refreshed with each spoonful. Texture preferences often depend on individual tastes, where thick porridge appeals to those seeking richness, while runny porridge suits those favoring a delicate, fluid consistency.
Nutritional Differences: Thick and Runny Porridge
Thick porridge typically contains less water, which results in a higher concentration of nutrients such as fiber, protein, and complex carbohydrates per serving compared to runny porridge. The reduced water content in thick porridge can lead to slower digestion and prolonged satiety, making it more suitable for sustained energy release. Runny porridge, due to its higher water content, provides hydration benefits but generally has a lower nutrient density, impacting its overall caloric and nutritional intake.
Serving Suggestions for Each Texture
Thick porridge pairs excellently with robust toppings like nuts, seeds, and rich fruit compotes, offering a hearty, satisfying breakfast. Runny porridge complements lighter add-ins such as fresh berries, honey, or a drizzle of cream, enhancing the smooth, gentle mouthfeel. Each texture's serving suggestions emphasize balancing density with flavor contrasts to elevate the dining experience.
Regional Preferences and Traditions
Thick porridge is favored in Northern European countries like Scotland and Finland, where hearty, dense textures complement colder climates and traditional ingredients such as oats and barley. Runny porridge is more popular in Southern regions like parts of Asia and Africa, where smooth, lighter consistencies pair well with sweeter or spiced flavor profiles and are often consumed as breakfast or comfort food. Regional traditions influence texture preference, with thick porridge aligning with rustic, filling meals and runny porridge suited for easily digestible, warming nourishment.
Choosing the Right Texture for Your Taste
Thick porridge offers a creamy, dense texture that holds shape and is perfect for those who enjoy a hearty, spoonable meal. Runny porridge provides a lighter, smoother consistency that easily mixes with toppings and is preferred by individuals seeking a delicate, easy-to-digest option. Selecting the right porridge texture depends on personal taste preferences and desired mouthfeel, balancing between richness and fluidity.
Thick Porridge vs Runny Porridge for Texture Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com