Single grain porridge blends offer a pure, consistent flavor and texture that highlight the natural taste of one cereal, making them ideal for those seeking simplicity and specific nutritional benefits. Multi-grain porridge blends combine diverse grains such as oats, barley, and quinoa, providing a richer nutrient profile with increased fiber, protein, and essential vitamins that support digestive health and sustained energy. Choosing between single grain and multi-grain blends depends on dietary goals and taste preferences, balancing flavor intensity with nutritional variety.
Table of Comparison
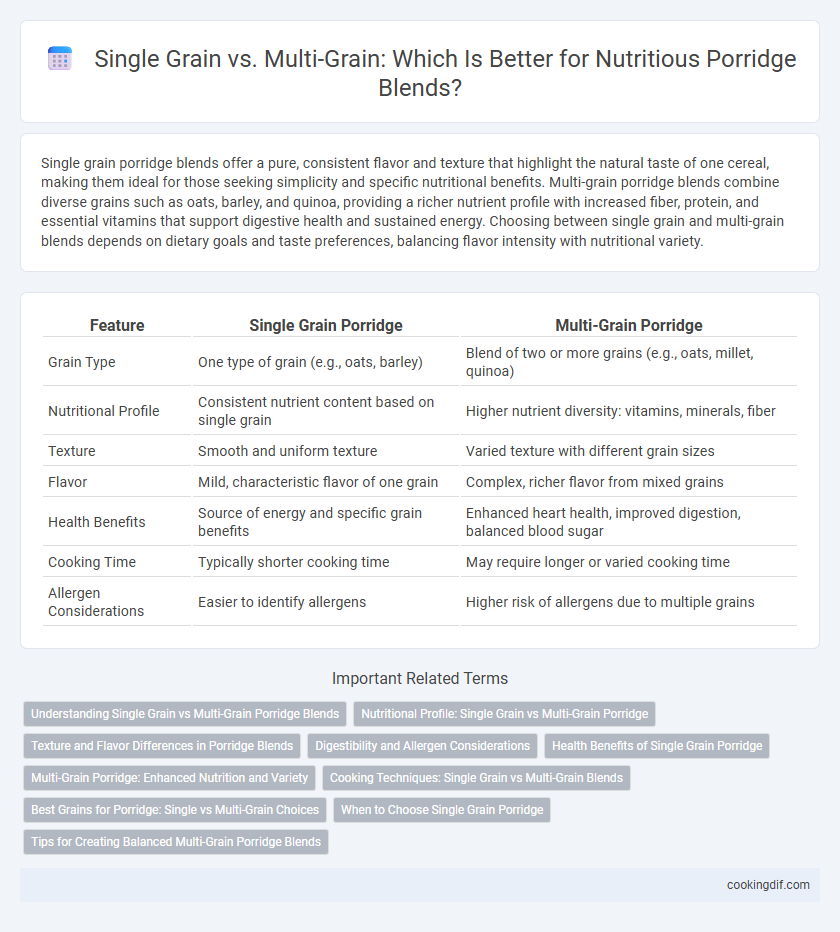
| Feature | Single Grain Porridge | Multi-Grain Porridge |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Type | One type of grain (e.g., oats, barley) | Blend of two or more grains (e.g., oats, millet, quinoa) |
| Nutritional Profile | Consistent nutrient content based on single grain | Higher nutrient diversity: vitamins, minerals, fiber |
| Texture | Smooth and uniform texture | Varied texture with different grain sizes |
| Flavor | Mild, characteristic flavor of one grain | Complex, richer flavor from mixed grains |
| Health Benefits | Source of energy and specific grain benefits | Enhanced heart health, improved digestion, balanced blood sugar |
| Cooking Time | Typically shorter cooking time | May require longer or varied cooking time |
| Allergen Considerations | Easier to identify allergens | Higher risk of allergens due to multiple grains |
Understanding Single Grain vs Multi-Grain Porridge Blends
Single grain porridge blends, typically made from oats, millet, or quinoa, offer a concentrated source of specific nutrients and a consistent texture, ideal for targeted dietary needs. Multi-grain porridge blends combine several grains such as barley, rye, and wheat, enhancing nutrient diversity by providing a broader spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and fibers that support digestive health and sustained energy release. Choosing between single grain and multi-grain blends depends on desired nutritional benefits, flavor complexity, and dietary restrictions.
Nutritional Profile: Single Grain vs Multi-Grain Porridge
Single grain porridges, such as oatmeal or quinoa, offer a consistent nutritional profile rich in specific nutrients like beta-glucan fiber or complete protein. Multi-grain porridge blends combine various grains, enhancing the nutritional diversity with a broader spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. The inclusion of multiple grains often increases dietary fiber, essential amino acids, and micronutrients, promoting improved digestive health and balanced nutrition compared to single grain options.
Texture and Flavor Differences in Porridge Blends
Single grain porridge blends often provide a smoother and more consistent texture, allowing the natural flavor of the specific grain, such as oats or quinoa, to shine through distinctly. Multi-grain blends enhance complexity by combining different grains like millet, barley, and rye, resulting in a varied texture that can be both creamy and slightly chewy with a richer, layered flavor profile. The choice between single and multi-grain blends impacts the mouthfeel and taste intensity, tailoring the porridge experience from mild and simple to robust and nuanced.
Digestibility and Allergen Considerations
Single grain porridge blends often offer superior digestibility due to their simpler composition, making them easier on the stomach and suitable for individuals with sensitive digestive systems. Multi-grain blends provide a wider nutritional profile but may introduce allergens such as gluten or nuts, requiring careful selection for those with food sensitivities or allergies. Choosing the right porridge blend depends on balancing digestive tolerance and potential allergenic ingredients to optimize health benefits.
Health Benefits of Single Grain Porridge
Single grain porridge blends offer concentrated nutritional benefits, featuring higher bioavailability of essential vitamins and minerals such as iron, magnesium, and B vitamins compared to multi-grain options. These blends promote easier digestion and reduced allergenic risks due to the absence of multiple grain proteins, supporting gut health and nutrient absorption. Consuming single grain porridge enhances energy levels and provides sustained release of complex carbohydrates, ideal for blood sugar regulation and metabolic health.
Multi-Grain Porridge: Enhanced Nutrition and Variety
Multi-grain porridge blends combine various grains like oats, barley, quinoa, and millet, offering a richer array of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants compared to single grain options. This diversity in grain sources enhances dietary fiber, protein content, and essential amino acids, promoting better digestion and sustained energy release. Consumers seeking improved nutritional profiles and flavor complexity benefit most from multi-grain porridge blends.
Cooking Techniques: Single Grain vs Multi-Grain Blends
Single grain porridge blends require precise water ratios and consistent simmering to achieve a smooth texture, as each grain's unique starch content affects cooking time and water absorption. Multi-grain blends demand careful layering of grains based on their cooking durations, often starting with denser grains like barley or oats, and finishing with softer grains, to ensure an even consistency throughout. Utilizing a slow cooker or soaking grains overnight can enhance the melding of flavors and textures in multi-grain porridge, delivering a balanced and nutrient-rich meal.
Best Grains for Porridge: Single vs Multi-Grain Choices
Single grain porridges, such as oat or barley, offer a pure and consistent flavor profile with specific nutritional benefits like high beta-glucan content for heart health. Multi-grain blends combine the nutrients of several grains like quinoa, millet, and brown rice, providing a richer texture and a wider spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Choosing between single and multi-grain blends depends on desired taste complexity and nutritional diversity, with multi-grain options often favored for their balanced macro- and micronutrient profiles.
When to Choose Single Grain Porridge
Single grain porridge blends are ideal when seeking simplicity, digestibility, and a distinct flavor profile, often preferred by those with sensitive digestion or specific dietary restrictions like gluten intolerance. Single grains such as oats, millet, or quinoa provide concentrated nutritional benefits and are easier to monitor for allergenic responses compared to multi-grain blends. Choosing single grain porridge supports controlled nutrient intake and maximizes the absorption of specific vitamins and minerals unique to each grain variety.
Tips for Creating Balanced Multi-Grain Porridge Blends
Combining single grain porridge, such as oatmeal, with multiple grains like quinoa, millet, and barley enhances nutritional diversity and texture complexity. Use a ratio that balances grains with different cooking times, soaking harder grains beforehand to achieve even softness. Incorporate seeds or nuts to boost protein and healthy fats while maintaining a harmonious flavor profile in multi-grain porridge blends.
Single grain vs multi-grain for porridge blends Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com