Quick oats create a smoother and creamier porridge due to their finely processed texture, which allows them to absorb liquid rapidly and cook in just a few minutes. Traditional oats, or rolled oats, produce a thicker and chewier porridge, offering a heartier texture that retains more bite after cooking. Choosing between quick oats and traditional oats depends on the desired consistency and cooking time preference for your porridge.
Table of Comparison
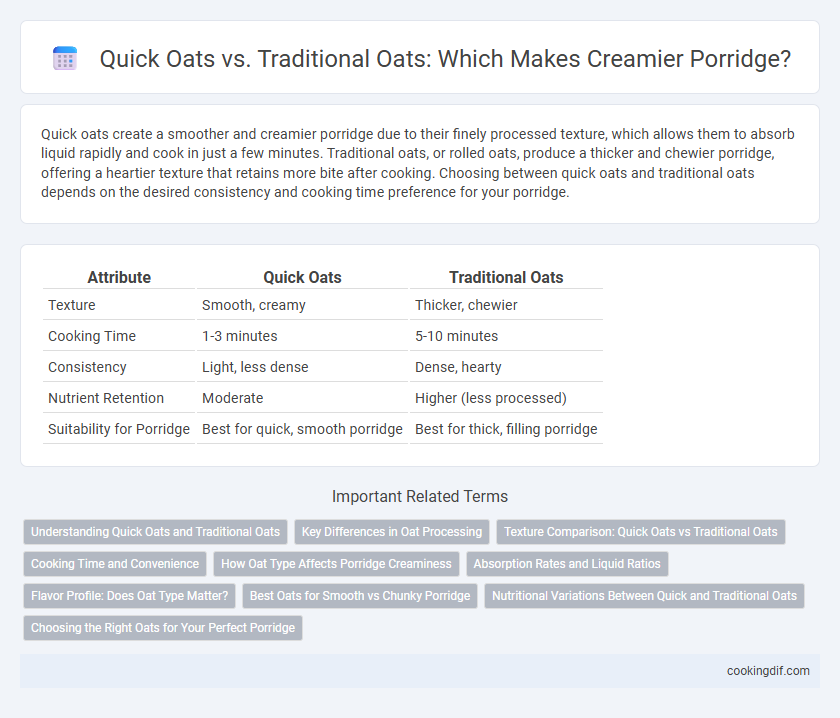
| Attribute | Quick Oats | Traditional Oats |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Smooth, creamy | Thicker, chewier |
| Cooking Time | 1-3 minutes | 5-10 minutes |
| Consistency | Light, less dense | Dense, hearty |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate | Higher (less processed) |
| Suitability for Porridge | Best for quick, smooth porridge | Best for thick, filling porridge |
Understanding Quick Oats and Traditional Oats
Quick oats are rolled thinner and steamed longer than traditional oats, resulting in faster cooking times and a softer, creamier porridge texture. Traditional oats, or old-fashioned oats, retain a chewier consistency with a heartier texture due to their larger, thicker flakes. Choosing between quick and traditional oats impacts porridge consistency by balancing smoothness and bite, catering to different texture preferences.
Key Differences in Oat Processing
Quick oats are steamed and rolled thinner than traditional oats, allowing them to cook faster and produce a smoother, creamier porridge consistency. Traditional oats, also known as old-fashioned oats, retain a thicker texture due to minimal processing, resulting in a heartier porridge with more bite. The key difference lies in the thickness and steaming time, which directly affects porridge texture and cooking duration.
Texture Comparison: Quick Oats vs Traditional Oats
Quick oats have a finer texture and cook rapidly, creating a smoother, creamier porridge ideal for those seeking a silky consistency. Traditional oats retain larger flakes, resulting in a chewier, heartier porridge with more pronounced oat flavor and a slightly coarse texture. Choosing between the two depends on whether a velvety or rustic porridge texture is preferred.
Cooking Time and Convenience
Quick oats cook in about 1 to 2 minutes, offering a softer, smoother porridge consistency ideal for fast preparation. Traditional oats require 5 to 10 minutes of cooking, producing a thicker, chewier texture preferred for heartier porridge. Selecting quick oats provides convenience and speed, while traditional oats deliver a more substantial mouthfeel.
How Oat Type Affects Porridge Creaminess
Quick oats, processed into smaller, thinner flakes, absorb liquid faster, resulting in a smoother and creamier porridge compared to traditional oats. Traditional oats maintain more texture and chewiness due to their larger, less processed flakes, offering a heartier consistency. The choice between quick and traditional oats significantly influences porridge creaminess, with quick oats favored for a softer texture and traditional oats preferred for a more substantial mouthfeel.
Absorption Rates and Liquid Ratios
Quick oats absorb liquid faster due to their smaller particle size, resulting in a smoother, creamier porridge with a liquid ratio of roughly 1:1.5 oats to water or milk. Traditional oats require a longer cooking time and a higher liquid ratio, about 1:2, to achieve a thicker, chewier texture with more defined oat grains. Understanding these absorption rates and liquid ratios helps customize porridge consistency from creamy to hearty.
Flavor Profile: Does Oat Type Matter?
Quick oats and traditional oats offer distinct flavor profiles that impact porridge taste and texture. Traditional oats, less processed than quick oats, provide a nuttier and heartier flavor with a chewier consistency, enhancing the overall porridge experience. Quick oats deliver a milder taste with a smoother texture, ideal for those preferring creamier porridge but sacrificing some depth of oat flavor.
Best Oats for Smooth vs Chunky Porridge
Quick oats produce a smooth, creamy porridge consistency due to their finely processed texture, allowing for faster cooking and easier digestion. Traditional oats retain their whole, flattened shape, creating a chunky, chewy porridge with more bite and a heartier mouthfeel. Choosing quick oats suits those preferring a silky, uniform texture, while traditional oats are ideal for a robust, textured porridge experience.
Nutritional Variations Between Quick and Traditional Oats
Quick oats and traditional oats differ in texture and cooking time, impacting porridge consistency with quick oats producing a smoother and creamier texture due to their finer cut. Nutritionally, traditional oats retain more fiber and have a slightly lower glycemic index, contributing to more sustained energy release and better blood sugar control. Both types provide essential nutrients such as beta-glucan, protein, and iron, but traditional oats generally offer higher antioxidant levels and more heart-healthy compounds.
Choosing the Right Oats for Your Perfect Porridge
Quick oats absorb liquid faster and create a smoother, creamier porridge consistency ideal for a silky texture, while traditional oats retain a chewier bite and result in a thicker, heartier porridge. Choosing the right oats depends on your texture preference: quick oats offer convenience and softness, whereas traditional oats provide more substance and a rustic feel. For an optimal porridge experience, experiment with the ratio of oats to liquid and cooking time to balance taste and consistency.
Quick oats vs traditional oats for porridge consistency Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com