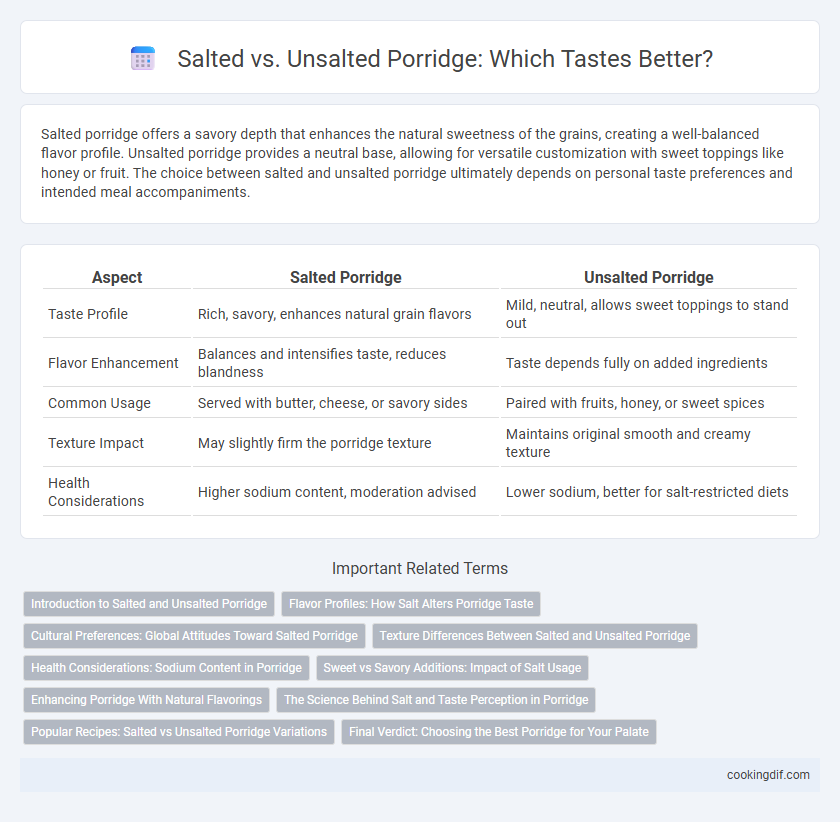
Salted porridge offers a savory depth that enhances the natural sweetness of the grains, creating a well-balanced flavor profile. Unsalted porridge provides a neutral base, allowing for versatile customization with sweet toppings like honey or fruit. The choice between salted and unsalted porridge ultimately depends on personal taste preferences and intended meal accompaniments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Salted Porridge | Unsalted Porridge |
|---|---|---|
| Taste Profile | Rich, savory, enhances natural grain flavors | Mild, neutral, allows sweet toppings to stand out |
| Flavor Enhancement | Balances and intensifies taste, reduces blandness | Taste depends fully on added ingredients |
| Common Usage | Served with butter, cheese, or savory sides | Paired with fruits, honey, or sweet spices |
| Texture Impact | May slightly firm the porridge texture | Maintains original smooth and creamy texture |
| Health Considerations | Higher sodium content, moderation advised | Lower sodium, better for salt-restricted diets |
Introduction to Salted and Unsalted Porridge
Salted porridge enhances flavor by adding a savory depth that balances the natural sweetness of grains, making it popular in traditional recipes. Unsalted porridge offers a neutral taste, allowing for customizable toppings such as fruits, honey, or nuts to create diverse flavor profiles. Choosing between salted and unsalted porridge depends on individual preference and the desired culinary experience.
Flavor Profiles: How Salt Alters Porridge Taste
Salted porridge enhances the natural nuttiness of oats while balancing sweetness, creating a savory depth that highlights umami notes and reduces bitterness. Unsalted porridge offers a more neutral, mild flavor, allowing the subtle taste of oats and added ingredients like fruits or honey to dominate. The presence of salt intensifies aroma and flavor complexity, making each spoonful more robust and satisfying.
Cultural Preferences: Global Attitudes Toward Salted Porridge
Salted porridge enjoys widespread popularity in Scandinavian and African cultures, where it is often seasoned with savory ingredients to enhance flavor and nutritional value. In contrast, many Asian and Western cultures prefer unsalted or subtly sweetened porridge, emphasizing natural grains and mild taste profiles. Global attitudes toward salted porridge reflect deep-rooted culinary traditions and regional ingredient availability, influencing daily dietary practices and flavor expectations.
Texture Differences Between Salted and Unsalted Porridge
Salted porridge develops a creamier and smoother texture as the salt interacts with starch molecules, enhancing gelatinization during cooking. Unsalted porridge tends to have a thicker, slightly grainier consistency due to less starch breakdown. These texture differences influence overall mouthfeel and flavor absorption in porridge dishes.
Health Considerations: Sodium Content in Porridge
Salted porridge contains added sodium, which can elevate daily salt intake and increase the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular issues. Unsalted porridge offers a lower sodium option, promoting better heart health and reduced water retention. Choosing unsalted porridge allows control over sodium levels, aligning with dietary guidelines recommending less than 2,300 mg of sodium per day.
Sweet vs Savory Additions: Impact of Salt Usage
Salted porridge enhances savory additions like cheese, herbs, and smoked meats by balancing flavors and reducing bitterness, while unsalted porridge serves as a neutral base that highlights the natural sweetness of ingredients such as honey, fruits, or cinnamon. The presence of salt modifies the porridge's flavor profile, making it more suitable for savory dishes and masking subtle sweetness. Choosing salted or unsalted porridge depends on whether the intended taste is sweet or savory, influencing the overall culinary experience.
Enhancing Porridge With Natural Flavorings
Salted porridge brings out a savory depth that enhances the natural sweetness of oats, creating a balanced flavor profile favored in many traditional recipes. Unsalted porridge serves as a neutral base, perfect for adding natural flavorings such as fresh fruit, honey, cinnamon, or nuts, which elevate the taste without overwhelming the subtle oat flavor. Using natural ingredients like vanilla extract, maple syrup, or toasted seeds can transform plain porridge into a rich, flavorful dish tailored to personal preferences.
The Science Behind Salt and Taste Perception in Porridge
Salt enhances the flavor of porridge by stimulating the taste buds and increasing the perception of sweetness and umami, making the dish more palatable. Sodium ions in salt interact with taste receptors, amplifying flavor compounds naturally present in oats and altering the mouthfeel. Unsalted porridge tends to have a blander taste because it lacks this chemical interaction that intensifies flavor signals in the brain.
Popular Recipes: Salted vs Unsalted Porridge Variations
Salted porridge recipes, such as savory oatmeal with cheese and herbs, offer a rich, umami flavor that balances creamy texture, making them popular for hearty breakfasts. Unsalted porridge variations focus on natural sweetness, often enhanced with fruits, honey, or cinnamon, appealing to those who prefer a milder, dessert-like taste. Both salted and unsalted versions feature in popular recipes worldwide, highlighting versatile uses from traditional Scottish porridge to modern, nutrient-dense bowls.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Best Porridge for Your Palate
Salted porridge enhances flavor complexity by balancing the natural sweetness of oats, creating a savory taste preferred by those who enjoy a hearty breakfast. Unsalted porridge offers a neutral base, allowing customization with sweet or savory toppings, ideal for individuals seeking versatility in taste. The best choice depends on personal preference, dietary needs, and whether you prioritize a robust or mild flavor profile in your morning meal.
Salted vs unsalted porridge for taste Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com