Polenta and cornmeal are both ground corn products but differ in texture and flavor, making them suitable for distinct savory porridge experiences. Polenta is coarser and often results in a creamier, more robust porridge with a slightly nutty taste, while cornmeal has a finer grind that creates a smoother, lighter consistency. Choosing between polenta and cornmeal depends on whether you prefer a hearty, rustic porridge or a delicate, soft base for savory toppings.
Table of Comparison
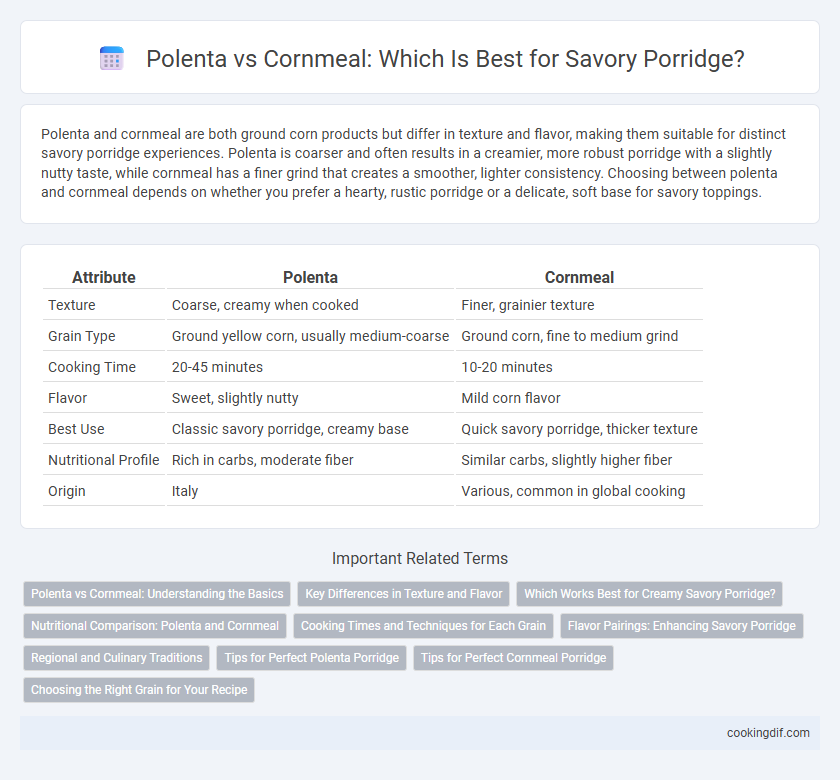
| Attribute | Polenta | Cornmeal |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Coarse, creamy when cooked | Finer, grainier texture |
| Grain Type | Ground yellow corn, usually medium-coarse | Ground corn, fine to medium grind |
| Cooking Time | 20-45 minutes | 10-20 minutes |
| Flavor | Sweet, slightly nutty | Mild corn flavor |
| Best Use | Classic savory porridge, creamy base | Quick savory porridge, thicker texture |
| Nutritional Profile | Rich in carbs, moderate fiber | Similar carbs, slightly higher fiber |
| Origin | Italy | Various, common in global cooking |
Polenta vs Cornmeal: Understanding the Basics
Polenta and cornmeal differ primarily in texture and grind size, with polenta typically made from coarsely ground yellow corn and cornmeal encompassing both fine and medium grinds from various corn types. Polenta's coarse grind provides a creamier, heartier texture ideal for savory porridge, while fine cornmeal produces a smoother, more delicate consistency. Understanding these distinctions helps tailor savory porridge recipes to desired texture and flavor outcomes.
Key Differences in Texture and Flavor
Polenta offers a coarser, creamier texture with a slightly nutty flavor, making it ideal for savory porridge where a rich, hearty mouthfeel is desired. Cornmeal, being finer and more granular, creates a smoother porridge with a milder corn taste, better suited for delicate, subtly flavored dishes. The choice between polenta and cornmeal fundamentally shapes the porridge's texture profile and intensity of corn flavor, influencing the overall culinary experience.
Which Works Best for Creamy Savory Porridge?
Polenta, made from coarse-ground cornmeal, yields a creamier and smoother texture ideal for savory porridge, while regular cornmeal tends to create a grainier consistency. The coarse grind of polenta absorbs liquids more effectively, resulting in a richer mouthfeel that enhances the comfort-food appeal. For a creamy savory porridge, polenta is preferred due to its superior ability to achieve a velvety and cohesive dish.
Nutritional Comparison: Polenta and Cornmeal
Polenta and cornmeal differ in nutritional profiles, with polenta often being more processed and having a finer texture, which affects its glycemic index and digestibility. Polenta generally contains slightly fewer calories and carbohydrates per serving compared to coarser cornmeal, but cornmeal offers more dietary fiber, promoting better digestion and satiety. Both provide essential nutrients such as iron, magnesium, and B vitamins, but cornmeal's higher fiber content makes it a better choice for savory porridge aiming for sustained energy release and enhanced gut health.
Cooking Times and Techniques for Each Grain
Polenta requires longer cooking times, typically 30 to 45 minutes, to achieve a creamy, smooth texture as the coarse grains absorb ample liquid during slow simmering. Cornmeal cooks much faster, often within 5 to 10 minutes, and needs constant stirring to prevent lumps and ensure even cooking, making it ideal for quicker savory porridges. Techniques for polenta include gradual water addition and low-heat simmering, while cornmeal benefits from rapid boiling and vigorous stirring to reach the desired porridge consistency.
Flavor Pairings: Enhancing Savory Porridge
Polenta's coarse texture and slightly nutty flavor complement robust herbs like rosemary and thyme for savory porridge, creating a rich, earthy base that pairs well with sauteed mushrooms and sharp cheeses. Cornmeal, being finer and milder, allows delicate ingredients like scallions, garlic, and soft cheeses to shine without overpowering the dish's subtle variations. Both grains intensify savory porridge when combined with savory broths, cured meats, or roasted vegetables, enhancing depth and balancing the palate.
Regional and Culinary Traditions
Polenta, a staple in Northern Italian cuisine, utilizes coarser ground cornmeal, lending a hearty texture ideal for savory porridge dishes paired with robust sauces or cheeses. In contrast, finer ground cornmeal common in Southern American cooking produces a smoother porridge, often seasoned with spices and herbs for a versatile savory base. These regional preferences highlight culinary traditions where grain texture and preparation methods define the porridge's flavor profile and cultural significance.
Tips for Perfect Polenta Porridge
For perfect polenta porridge, use coarse-ground cornmeal to achieve a creamy texture with a slight bite, avoiding finely ground cornmeal that can become gummy. Constant stirring over low heat prevents lumps and ensures even cooking, while gradually adding liquid helps control consistency. Finishing with butter and Parmesan cheese enhances the savory flavor and smoothness of the porridge.
Tips for Perfect Cornmeal Porridge
For perfect cornmeal porridge, choose finely ground cornmeal for a smoother texture and cook it slowly over low heat to avoid lumps. Stir continuously to ensure even cooking and to prevent sticking, adding water or broth gradually for desired consistency. Season with salt, butter, or cheese to enhance the savory flavor, and consider incorporating herbs like thyme or rosemary for an aromatic boost.
Choosing the Right Grain for Your Recipe
Selecting the right grain for savory porridge hinges on understanding the distinct textures and flavors of polenta versus cornmeal. Polenta, coarser and often pre-cooked, yields a creamy, hearty porridge ideal for slow cooking and absorbing rich broths. Cornmeal, in finer grinds, cooks faster with a smoother consistency, making it better suited for lighter, delicate savory porridge dishes.
polenta vs cornmeal for savory porridge Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com