Millet porridge offers higher nutritional value compared to rice porridge, providing more fiber, protein, and essential minerals such as magnesium and phosphorus. Its unique grain composition supports better digestion and sustained energy release, making it ideal for a balanced diet. Rice porridge, while gentler on the stomach, lacks the same density of nutrients, making millet a superior choice for those seeking grain porridge with enhanced health benefits.
Table of Comparison
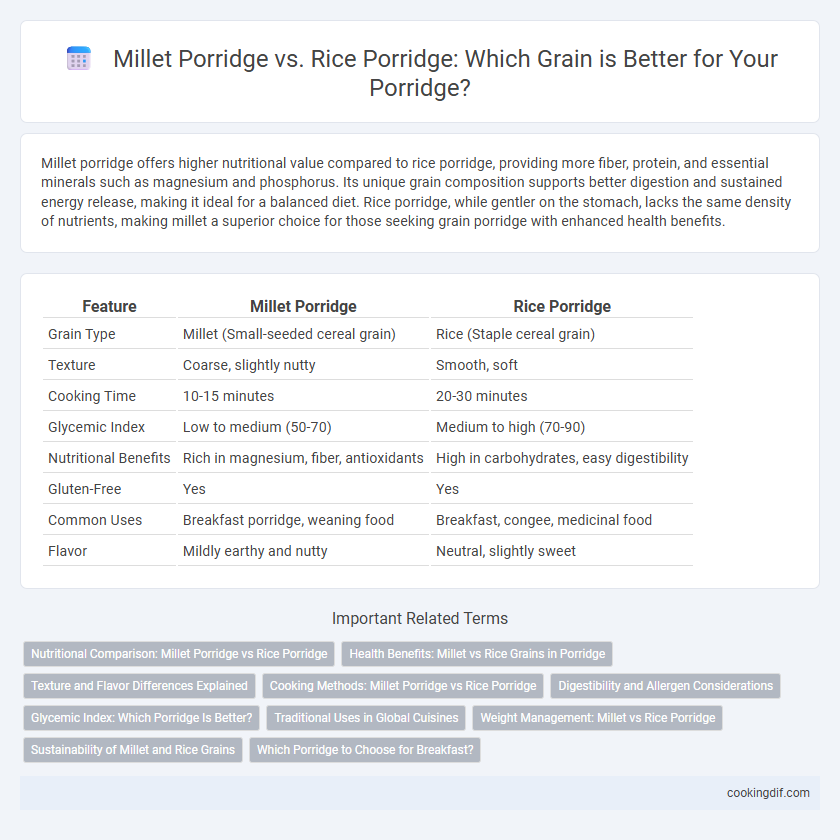
| Feature | Millet Porridge | Rice Porridge |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Type | Millet (Small-seeded cereal grain) | Rice (Staple cereal grain) |
| Texture | Coarse, slightly nutty | Smooth, soft |
| Cooking Time | 10-15 minutes | 20-30 minutes |
| Glycemic Index | Low to medium (50-70) | Medium to high (70-90) |
| Nutritional Benefits | Rich in magnesium, fiber, antioxidants | High in carbohydrates, easy digestibility |
| Gluten-Free | Yes | Yes |
| Common Uses | Breakfast porridge, weaning food | Breakfast, congee, medicinal food |
| Flavor | Mildly earthy and nutty | Neutral, slightly sweet |
Nutritional Comparison: Millet Porridge vs Rice Porridge
Millet porridge contains higher levels of magnesium, fiber, and protein compared to rice porridge, making it a more nutrient-dense option for sustained energy and digestive health. Rice porridge, especially when made from white rice, tends to have a higher glycemic index and fewer essential vitamins like B-complex, resulting in quicker blood sugar spikes and lower overall nutritional value. The presence of antioxidants and minerals such as phosphorus and potassium in millet further supports cardiovascular and bone health, distinguishing it from the more starch-centric profile of rice porridge.
Health Benefits: Millet vs Rice Grains in Porridge
Millet porridge offers higher fiber content and essential minerals like magnesium and phosphorus compared to rice porridge, promoting better digestion and bone health. Rice porridge, particularly when made from white rice, is easier to digest and lower in allergens, making it suitable for sensitive stomachs. Millet's low glycemic index also supports stable blood sugar levels, beneficial for managing diabetes, whereas rice porridge provides quick energy due to its higher glycemic index.
Texture and Flavor Differences Explained
Millet porridge has a coarser, grainier texture compared to the smooth, creamy consistency of rice porridge. The flavor of millet porridge is nuttier and earthier, offering a slightly sweet and robust taste, while rice porridge presents a mild, neutral flavor that easily absorbs added ingredients. These differences make millet porridge ideal for those seeking a more textured and flavorful grain experience, whereas rice porridge suits those preferring a softer, subtler base.
Cooking Methods: Millet Porridge vs Rice Porridge
Millet porridge typically requires simmering millet grains in water or milk for 20-30 minutes until soft, often with occasional stirring to prevent clumping. Rice porridge, commonly prepared as congee, involves boiling rice in a larger volume of water for 1-2 hours, allowing the grains to break down and create a creamy texture. While millet porridge cooks faster and maintains a slightly grainier consistency, rice porridge achieves a smoother, more gelatinous texture through prolonged cooking.
Digestibility and Allergen Considerations
Millet porridge offers superior digestibility compared to rice porridge due to its higher fiber content and lower glycemic index, which aids in smoother digestion and sustained energy release. Millet is naturally gluten-free, making it an excellent hypoallergenic choice for individuals with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease, while rice porridge is also gluten-free but can sometimes contain trace allergens depending on processing. Both grains provide essential nutrients, but millet's unique protein profile and antioxidant properties support better gastrointestinal health and reduced allergy risks.
Glycemic Index: Which Porridge Is Better?
Millet porridge has a lower glycemic index (GI) compared to rice porridge, making it a better option for blood sugar management and sustained energy release. While rice porridge typically has a higher GI, causing quicker spikes in blood glucose, millet porridge's complex carbohydrates digest more slowly. This characteristic makes millet porridge preferable for individuals seeking stable blood sugar levels and improved glycemic control.
Traditional Uses in Global Cuisines
Millet porridge holds a significant place in African and South Asian cuisines, prized for its high nutritional content and easy digestibility, often consumed as a breakfast staple or weaning food. Rice porridge, known as congee in East Asia, serves as a versatile comfort food, traditionally used for its soothing properties during illness and as a base for savory or sweet toppings. Both grains offer unique cultural value, with millet porridge frequently associated with rustic, hearty meals and rice porridge symbolizing medicinal and ceremonial importance across various Asian cultures.
Weight Management: Millet vs Rice Porridge
Millet porridge is favored for weight management due to its high fiber content and low glycemic index, which promote satiety and stable blood sugar levels. Rice porridge, while easier to digest, has a higher glycemic index leading to quicker spikes in blood sugar and less prolonged fullness. Choosing millet porridge supports better appetite control and sustained energy release, making it more suitable for weight-conscious diets.
Sustainability of Millet and Rice Grains
Millet porridge offers a more sustainable option compared to rice porridge due to millet's drought-resistant nature and lower water consumption during cultivation. Millet grains require significantly less land and chemical inputs, enhancing soil health and reducing environmental impact. Rice cultivation often demands intensive water resources and contributes to methane emissions, making millet a more eco-friendly grain choice for porridge production.
Which Porridge to Choose for Breakfast?
Millet porridge offers higher fiber and essential minerals such as magnesium and phosphorus compared to rice porridge, making it a nutrient-dense choice for breakfast. Rice porridge is easier to digest and provides quick energy due to its higher carbohydrate content and lower fiber levels. Choosing millet porridge supports sustained fullness and better blood sugar control, while rice porridge suits those needing light, easily digestible breakfasts.
Millet porridge vs rice porridge for grains Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com