Pasta dough with egg offers a richer texture and a smoother, more elastic consistency, making it ideal for fresh pasta varieties like tagliatelle or fettuccine. Dough without egg tends to be firmer and slightly denser, often preferred for traditional dried pasta such as penne or spaghetti. Choosing between egg and eggless dough depends on the desired texture and cooking method of the pasta.
Table of Comparison
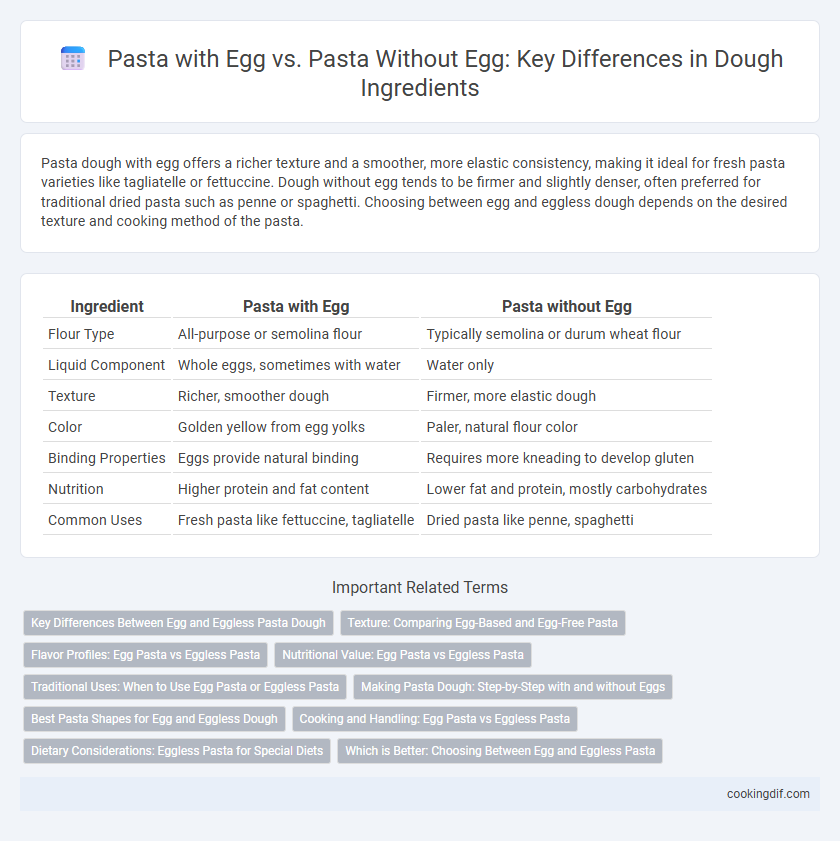
| Ingredient | Pasta with Egg | Pasta without Egg |
|---|---|---|
| Flour Type | All-purpose or semolina flour | Typically semolina or durum wheat flour |
| Liquid Component | Whole eggs, sometimes with water | Water only |
| Texture | Richer, smoother dough | Firmer, more elastic dough |
| Color | Golden yellow from egg yolks | Paler, natural flour color |
| Binding Properties | Eggs provide natural binding | Requires more kneading to develop gluten |
| Nutrition | Higher protein and fat content | Lower fat and protein, mostly carbohydrates |
| Common Uses | Fresh pasta like fettuccine, tagliatelle | Dried pasta like penne, spaghetti |
Key Differences Between Egg and Eggless Pasta Dough
Egg pasta dough contains eggs, which contribute to a richer flavor, a yellow hue, and a more elastic texture, making it ideal for shapes that require sturdiness like fettuccine or ravioli. Eggless pasta dough relies solely on flour, water, and sometimes olive oil, resulting in a lighter color and a chewier texture often preferred in traditional varieties such as orecchiette or cavatelli. The presence of eggs increases protein content and binding properties, while eggless dough offers a vegan-friendly alternative with a simpler ingredient profile.
Texture: Comparing Egg-Based and Egg-Free Pasta
Egg-based pasta dough offers a richer, silkier texture with greater elasticity, resulting from the protein and fat content in eggs that enhance dough structure and chewiness. Egg-free pasta tends to have a firmer, denser texture with a slightly rougher surface, which improves sauce adhesion but lacks the smoothness and tenderness characteristic of egg pasta. The choice between egg and no-egg pasta dough directly influences the mouthfeel and overall culinary experience, making texture a key factor in pasta preparation and pairing.
Flavor Profiles: Egg Pasta vs Eggless Pasta
Egg pasta offers a richer, creamier flavor and a tender, silky texture due to the egg yolks, which contribute natural fats and proteins enhancing its savory depth. Eggless pasta features a cleaner, more neutral taste that highlights the wheat's natural nuttiness, making it versatile for bold sauces and lighter preparations. The choice between egg and eggless dough directly influences the final dish's flavor intensity and mouthfeel, with egg pasta providing a more luxurious, indulgent profile compared to the straightforward, slightly firm bite of eggless pasta.
Nutritional Value: Egg Pasta vs Eggless Pasta
Egg pasta typically contains higher protein and vitamin A levels due to the inclusion of whole eggs, contributing to a richer nutrient profile compared to eggless pasta. Eggless pasta, made primarily from flour and water, is generally lower in fat and cholesterol, making it a suitable option for those with dietary restrictions or seeking a lighter alternative. Both types provide essential carbohydrates for energy, but egg pasta offers additional micronutrients such as riboflavin and biotin, enhancing its overall nutritional value.
Traditional Uses: When to Use Egg Pasta or Eggless Pasta
Egg pasta offers a richer texture and is traditionally preferred in Italian regions like Emilia-Romagna for dishes such as tagliatelle and tortellini, where a tender yet firm dough enhances the sauce absorption. Eggless pasta, commonly found in southern Italy and other Mediterranean cuisines, provides a lighter, more elastic dough ideal for robust sauces and long cooking times, as seen in spaghetti and penne dishes. Choosing between egg and eggless pasta depends on regional culinary traditions and the desired dish texture, with egg pasta suited for delicate, flavorful meals and eggless pasta favored for hearty, sauce-heavy recipes.
Making Pasta Dough: Step-by-Step with and without Eggs
Making pasta dough with eggs creates a richer, more elastic texture due to the protein and fat content in the eggs, which enhances the dough's pliability and flavor. In contrast, pasta dough without eggs, typically made from just flour and water, results in a lighter, more delicate pasta ideal for shapes like orecchiette or trofie. Both methods require careful kneading and resting to achieve the ideal dough consistency for rolling and shaping.
Best Pasta Shapes for Egg and Eggless Dough
Egg pasta dough is richer and more elastic, ideal for shapes like tagliatelle, pappardelle, and fresh filled pastas such as ravioli and tortellini that require a pliable texture. Eggless pasta dough, often made from semolina and water, is firmer and perfect for shapes like orecchiette, cavatelli, and trofie that benefit from a denser bite. Selecting the best pasta shape depends on the dough's moisture and elasticity, with egg dough favoring delicate, broad ribbons and eggless dough suiting sturdier, textured forms.
Cooking and Handling: Egg Pasta vs Eggless Pasta
Egg pasta dough tends to be richer and firmer, making it easier to roll out thinly and hold shape during cooking, while eggless pasta often requires more careful handling to prevent sticking or tearing due to its higher hydration. Cooking times for egg pasta are generally shorter because of its denser texture, whereas eggless pasta demands vigilant monitoring to avoid overcooking and becoming mushy. Proper kneading and resting are crucial for both types, but egg pasta benefits from slightly more elastic dough, enhancing its pliability and resilience during preparation.
Dietary Considerations: Eggless Pasta for Special Diets
Eggless pasta dough is ideal for individuals with egg allergies, vegans, or those following cholesterol-restricted diets, as it eliminates cholesterol and animal-derived proteins. Typically made from semolina flour and water, eggless pasta offers a lower fat content and reduced allergenic potential compared to traditional egg-based recipes. This substitution maintains texture and versatility while catering to special dietary needs such as lactose intolerance and religious restrictions.
Which is Better: Choosing Between Egg and Eggless Pasta
Egg pasta offers a richer flavor and a firmer texture due to the protein and fat content from eggs, making it ideal for hearty dishes like tagliatelle or fettuccine. Eggless pasta, typically made with just flour and water, provides a lighter, more neutral base suitable for delicate sauces and vegan diets. The choice depends on dietary preferences, desired texture, and the specific recipe requirements.
pasta with egg vs pasta without egg for dough ingredients Infographic
 cookingdif.com
cookingdif.com